The Providers Can't Let Go! An Analysis of an RN Driven Tacrolimus Dose Adjustment Protocol
MUSC, Charleston.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A392
Keywords: Calcineurin, Kidney, Kidney transplantation, Pharmacokinetics
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Quality Assurance Process Improvement
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 2, 2018
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Introduction: Tacrolimus (FK) dose adjustment is frequently performed by non-MD staff. Standard protocols to evaluate the ability of non-providers to maintain pts within a goal FK trough range are lacking in the literature. We developed a RN driven FK dose adjustment protocol and implemented it in 7/2016. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of an RN driven protocol for FK adjustment at a large academic health center.
Methods: A retrospective review of KTX pts transplanted from 8/2016 to 5/2017 was completed. Adult KTX patients were excluded from the protocol based on Table 1. The first 10 encounters after entering the protocol were evaluated including: who provided the intervention & whether it was appropriate. Appropriateness was defined as: FK dosage adjust protocol for low, mod, or high intensity 12 hr trough levels.
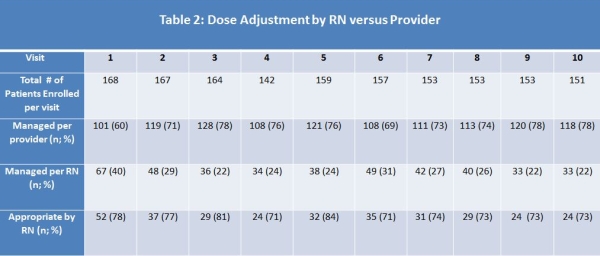
Results: 218 pts were evaluated, with 173 enrolled and 45 not enrolled. A total of 168 patients had adjustments based on protocol. Pts in the protocol were mainly male (59%); AA (59%); had a median PRA 52 (0-100). The DGF rate was 15% b/c of this 91% actually qualified for the protocol based on criteria. Of the pts who had a dose adjustments: 42% received RATG induction vs 58% received IL2RA. Table 2 details the 10 visits past enrollment & indicates that the majority of adjustments were made by providers vs RNs. However when RNs did make dose adjustments they were able to do so appropriately >70% of the time.
Conclusion: The implementation of a CDTM protocol for FK dosing managed by RNs, is intended to increase provider efficacy in the workplace. Although RNs did achieve a reasonable appropriateness, rate providers made the vast majority of the dosage adjustments. Additional provider education is needed to increase the utilization of a RN driven protocol.
CITATION INFORMATION: Elmaasarani Z., Mardis C., Gylten L., Fleming J., Meadows H., Patel N., Perez C., Taber D., Rao V., Rohan V., Baliga P., Dubay D., Pilch N. The Providers Can't Let Go! An Analysis of an RN Driven Tacrolimus Dose Adjustment Protocol Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Elmaasarani Z, Mardis C, Gylten L, Fleming J, Meadows H, Patel N, Perez C, Taber D, Rao V, Rohan V, Baliga P, Dubay D, Pilch N. The Providers Can't Let Go! An Analysis of an RN Driven Tacrolimus Dose Adjustment Protocol [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/the-providers-cant-let-go-an-analysis-of-an-rn-driven-tacrolimus-dose-adjustment-protocol/. Accessed March 6, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
