The Negative Impact of Hepatitis C Infection (HCV+) On Orthotopic Liver Transplantation (OLT) for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
1Transplant Center, Methodist Hospital, Houston, TX
2Pathology and Genomic Medicine, Methodist Hospital, Houston, TX
3Internal Medicine Department, Cairo University Medical school, Cairo, Egypt.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D173
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma, Liver transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, May 5, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Background: HCC is commonly associated with viral infections such as HCV & HBV.
Aim: To determine whether Hepatitis viral status has impact on survival after OLT for HCC.
Methods: We reviewed OLTs for HCC reported to UNOS between 2002 & 2013 after excluding all patients transplanted out of Milan criteria .We classified HCC patients into 4 groups according to Hepatitis viral status and compared survival outcomes between groups.
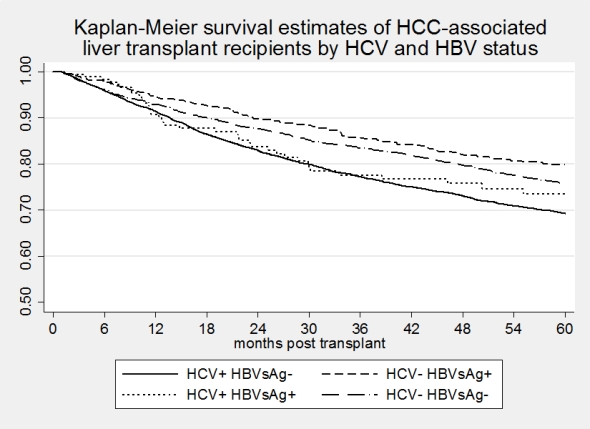
Results: 11,928 patients were transplanted for HCC, of which 11,555 were within Milan. 6869 patients (65%) were HCV+, 788 patients (7%) were HBV+, 184 patients were both HCV+ & HBV+, and 2771 patients (26%) were not infected. HCV patients were significantly older than HBV patients (mean age 57 vs 56.1, p<0.001) & younger than patients with no Hepatitis infection (mean age 59.5, p<0.001). Most of the HBV patients were Asians (60%), while most of the patients in the other 3 groups were Caucasians (69.8%). DM was more common in no Hepatitis (37%) compared to HCV+ (23%;p<0.001), HBV+ (23%;p<0.001) & patients with both infections (26%; p=0.003). HBV patients had a lower BMI than HCV patients (mean BMI 25.8 vs 28.3, p<0.001). HBV patients had higher AFP than HCV patients (P<0.001) who had higher AFP than patients with no Hepatitis infection (P<0.001). HCV patients had a higher MELD at listing than HBV patients (P<0.001). No differences were observed in tumor burden ( number of tumors, total & largest tumor diameter) within the groups. The 5 year post OLT survival was lowest (57%) in HCV patients & in patients with both HBV & HCV infections (59%; p=0.633, vs HCV+ alone). In contradistinction HBV patients had higher 5 year survival rates 74% (p<0.001 vs HCV+). Intermediate results (64% 5 yr. survival) were seen in patients with no hepatitis infection (p<0.001, vs HCV+)
Conclusion: HCV viral infections negatively impact survival of patients undergoing OLT for HCC. HBV infected patients with HCC have excellent survival rates after OLT.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Daoud A, Teeter L, Graviss E, Burroughs S, Gaber A. The Negative Impact of Hepatitis C Infection (HCV+) On Orthotopic Liver Transplantation (OLT) for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/the-negative-impact-of-hepatitis-c-infection-hcv-on-orthotopic-liver-transplantation-olt-for-hepatocellular-carcinoma-hcc/. Accessed March 14, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
