The Implications of Donor Proteinuria in Deceased Donor Kidney Transplantation
Dalhousie University, Halifax, NS, Canada
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B159
Keywords: Donors, marginal, Graft failure, Kidney, Proteinuria
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney Donor Selection / Management Issues
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: The implications of pre-terminal donor urinalysis findings on post-transplant kidney graft survival has not been previously explored. An abnormal donor urinalysis may reflect donor pathology, or be of little consequence, therefore the purpose of this study was to determine if pre-terminal (< 72 hours from organ retrieval) donor urinalysis findings are associated with an increased risk of the composite outcome of death or graft loss.
*Methods: We analyzed a retrospective cohort of adult patients (≥18 years old) who underwent a kidney transplant at a tertiary care transplant center in Halifax, Nova Scotia, between Jan 1, 2000 and June 30, 2016. Donor proteinuria and all other donor urine variables (the presence of hematuria, leukocyte esterase, nitrites, ketones, glucose, and urine PH) were assessed for their association with the outcome of death or kidney graft failure using multivariable Cox Proportional Hazard’s regression models.
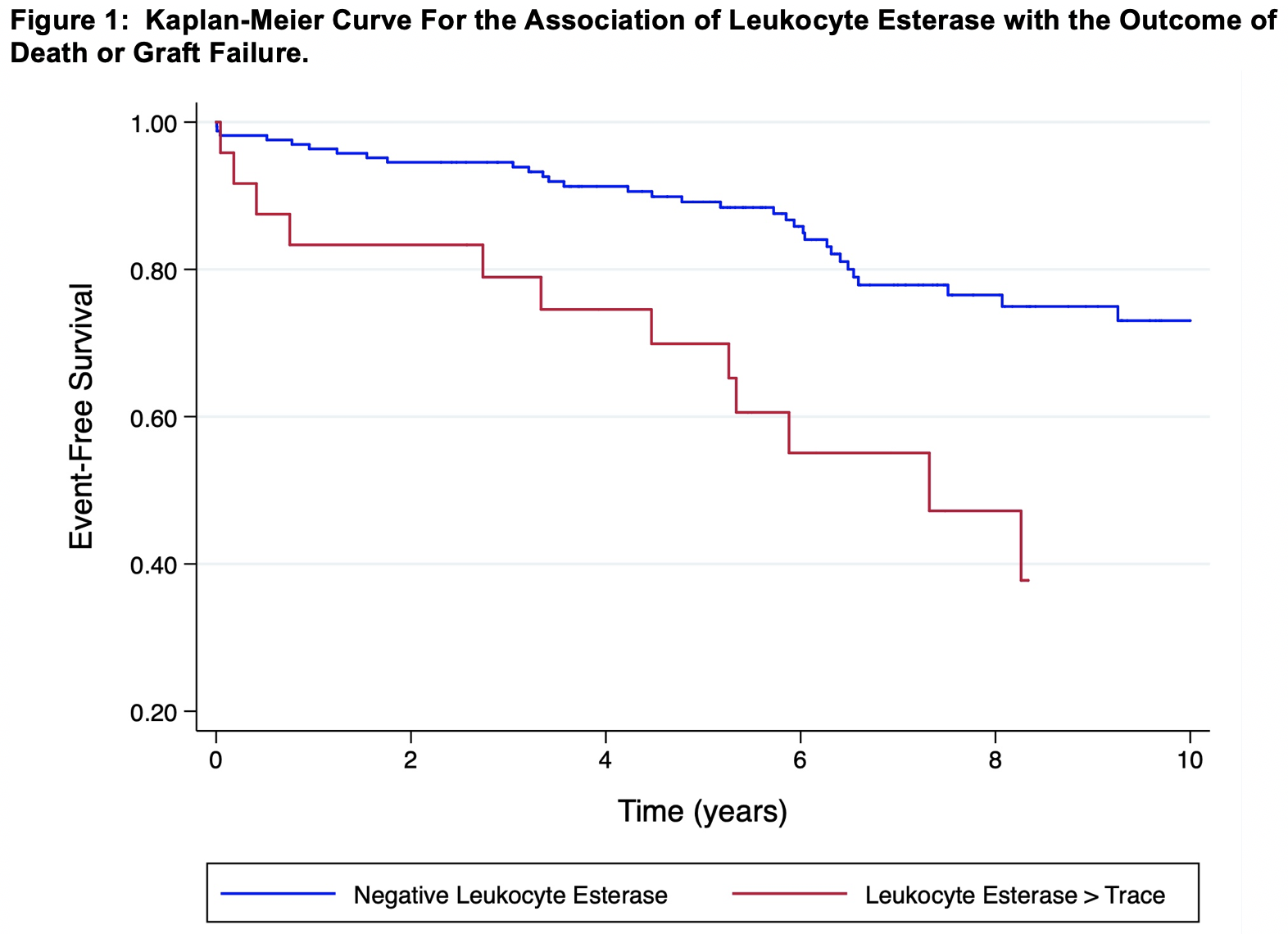
*Results: 199 patients underwent kidney transplant and 52 (26.1%) developed graft loss or death (26 graft failures, 26 deaths). Median length of follow-up was 6.23 years (Q1, Q3 4.48, 8.38). In multivariable analysis, only cumulative panel reactive antibody (HR 1.01 per percent, 95% CI 1.00-1.02), the presence of leukocyte esterase (HR 4.19, 95% CI 1.91-9.22) and > 10 epithelial cells/hpf (HR 3.33, 95% CI 1.10-10.09) were associated with the composite outcome of death or graft loss. A Kaplan Meier curve showing the association of leukocyte esterase with the outcome of interest is shown in Figure 1.
*Conclusions: Pre-terminal donor urinalysis findings (the presence of leukocyte esterase and epithelial cells) are associated with an increased risk of death or graft loss. This finding warrants further exploration in a larger population.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Vinson A, Keough-Ryan T, West K, Tennankore K. The Implications of Donor Proteinuria in Deceased Donor Kidney Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/the-implications-of-donor-proteinuria-in-deceased-donor-kidney-transplantation/. Accessed February 28, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress