The Impact of KDPI on Post Transplant Kidney Function: Intercept versus Slope. A Single Center Study
1University of Pittsburgh Medical Centre, Pittsburgh, PA, 2Surgery, University of Pittsburgh Medical Centre, Pittsburgh, PA, 3Medicine, University of Pittsburgh Medical Centre, Pittsburgh, PA
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A212
Keywords: Area-under-curve (AUC), Glomerular filtration rate (GFR), Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Kidney Deceased Donor Allocation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 1, 2019
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: We evaluated the impact of Kidney Donor Profile Index (KDPI) on post-transplant renal function and graft survival.
*Methods: Between January-2013 and December- 2017, a total of 605 adult recipients received kidney alone DD transplantation at our center. They were divided into 4 groups according to KDPI values: Group A-KDPI<25 (n=141), Group B-KDPI 25-50 (n=183), Group C,-KDPI 51-75 (n=185), and Group D-KDPI>75 (n= 96). Recipient and donor characteristics and transplant variables were compared among groups. GFR was evaluated at various time points and the burden of renal disease was calculated using the Area Under the Curve (AUC: serum creatinine mg*month/dL) for each group. In the presence of graft loss, GFR was set at 10 ml per minute.
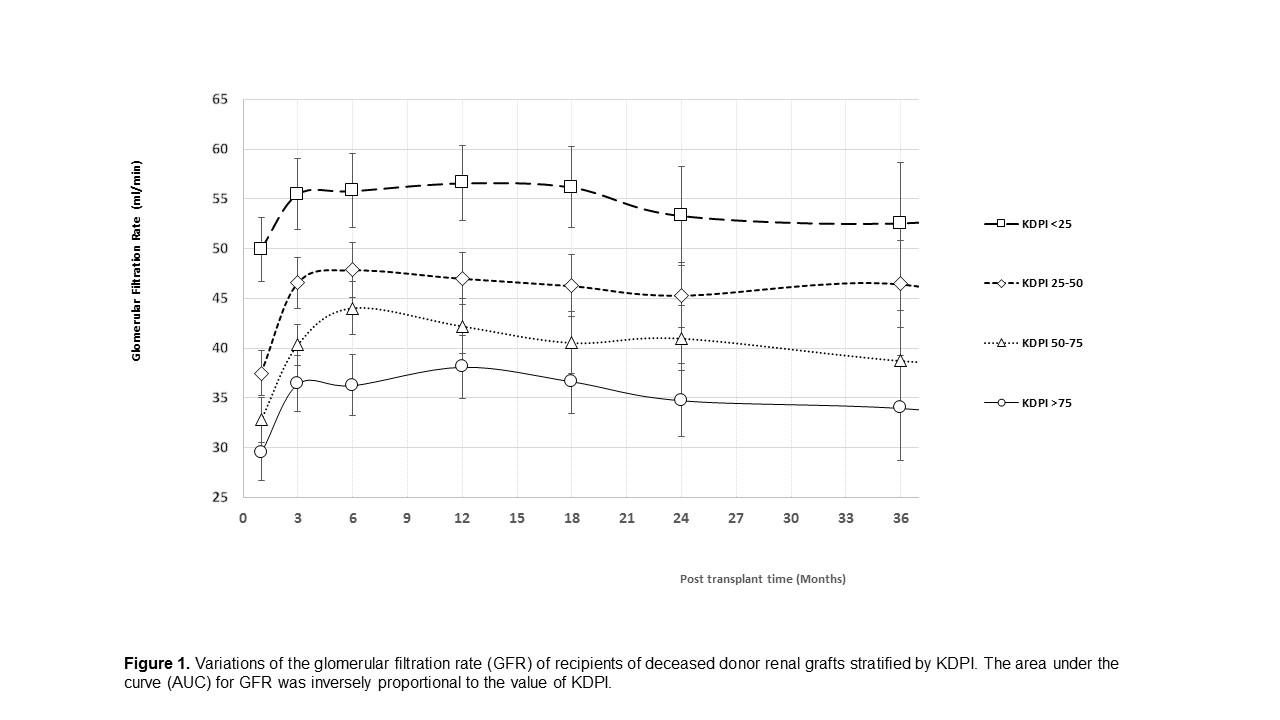
*Results: Donor/recipient demographics and transplant variables were similar among groups for most of the variables. However, recipients of DD transplants with KDPI>75 were older and more frequently had ESRD due to hypertension or diabetes and a higher proportion received kidneys from older and/or female donors. The incidence of DGF in Group A,B,C and D were 14%, 27%, 27% and 30 (P=0.01). With a median follow up of 44 months (range 10-78 months), the rates of graft failure was similar among groups (P=0.13) but the patient loss was higher among recipients of grafts with KDPI>75 (P=0.03). The mean GFR at various time points is shown in Figure 1. Higher KDPI was associated with worse GFR from the very early post-transplant period, however the slope of renal function decline was similar among groups. The cumulative function of the graft (AUC) showed a negative correlation with the increased values of KDPI. The mean value of AUC for group D was 978 (95% CI 827-1128), significantly lower when compared to 1,610 (95% CI 1425-1790), 1,372 (95% CI 1237-1508), 1,232 (95% CI 1109-1354) for group A, B, C respectively (P<0.001).
*Conclusions: Patients receiving DD kidney transplants with KDPI >75 had higher rates of DGF. The mean values of GFR were lower among those with elevated KDPI. The renal function of high KDPI grafts started with lower values compared to their counterparts (intercept), and remained inferior over the study period (slope) without any differences among groups.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Molinari M, Jorgensen D, Mehta R, Sood P, Ganoza A, Puttarajappa C, Lopez R, Wijkstrom M, Tevar A, Hariharan S. The Impact of KDPI on Post Transplant Kidney Function: Intercept versus Slope. A Single Center Study [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/the-impact-of-kdpi-on-post-transplant-kidney-function-intercept-versus-slope-a-single-center-study/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress