The Impact of Hepatitis C Treatment on GFR and Immunosuppression in Renal Transplant Recipients.
J. Husson, R. Adekunle, B. Ravichandran, P. Mathur, S. Jonchhe, K. Stafford.
University of Maryland Medical Center, Baltimore, MD
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A294
Keywords: Glomerular filtration rate (GFR), Hepatitis C, Induction therapy, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Viral Conundrums
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, April 29, 2017
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall D1
Background: Renal transplant recipients (RTRs) with HCV are at an increased risk of graft rejection, making treatment of HCV in this population of the utmost importance. Treatment options have progressed from interferon-based regimens to the better tolerated and more efficacious directly-acting antiviral agents (DAAs). However, their safety and efficacy in RTRs has not been established.
Methods: We performed a retrospective cohort study of varying DAA regimens in RTRs who were treated between 12/2014 and 07/2016. Maintenance immunosuppression included tacrolimus, mycophenolate, and prednisone taper per institutional protocol. The primary outcome was sustained virological response (SVR) at 12 weeks after completion of treatment. Secondary outcomes were increase in tacrolimus levels and association between induction therapy and GFR. Linear mixed models to account for the repeated GFR measurements were used to estimate mean GFR over time by induction therapy.
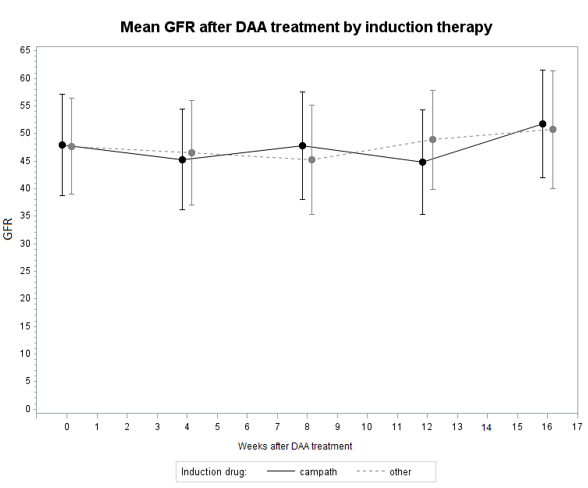
Results: A total of 21 patients completed treatment for HCV with a 100% SVR12 rate among 16 patients in whom SVR data was available. Baseline demographics are in Table 1. GFR remained stable throughout the duration of treatment. There was no statistically significant difference in GFR over the course of treatment by induction therapy (Figure 1). During therapy, 8 patients had an increase in tacrolimus levels greater than 2 ng/mL. Of these, 6 were on Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir, one was on Daclatasvir/Sofosbuvir and one was on Elbasvir/Grazoprevir. 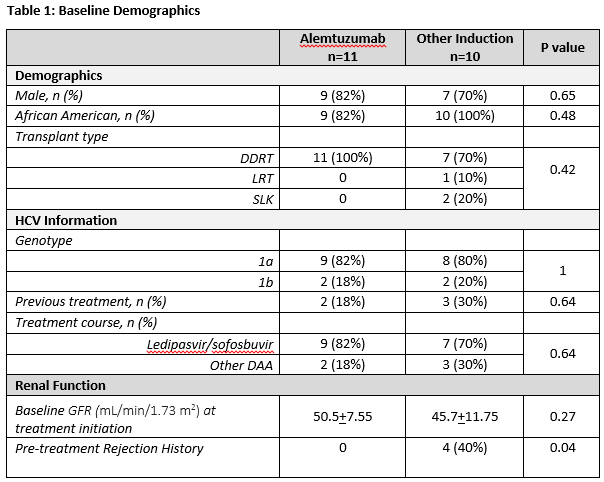
 Conclusions: Treatment of Hepatitis C in renal transplant recipients is safe and efficacious. While there was a noted impact on tacrolimus levels, there was no impact on overall renal function during treatment.
Conclusions: Treatment of Hepatitis C in renal transplant recipients is safe and efficacious. While there was a noted impact on tacrolimus levels, there was no impact on overall renal function during treatment.
CITATION INFORMATION: Husson J, Adekunle R, Ravichandran B, Mathur P, Jonchhe S, Stafford K. The Impact of Hepatitis C Treatment on GFR and Immunosuppression in Renal Transplant Recipients. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Husson J, Adekunle R, Ravichandran B, Mathur P, Jonchhe S, Stafford K. The Impact of Hepatitis C Treatment on GFR and Immunosuppression in Renal Transplant Recipients. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/the-impact-of-hepatitis-c-treatment-on-gfr-and-immunosuppression-in-renal-transplant-recipients/. Accessed March 11, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
