The Impact of De Novo Post-Transplant Diabetes on Hepatic Steatosis and Liver Transplant Outcomes.
1Department of Pharmacy, UNC Health Care, Chapel Hill, NC
2Department of Medicine, UNC Health Care, Chapel Hill, NC
3UNC Center for Transplant Care, UNC Health Care, Chapel Hill, NC
4Department of Surgery, UNC Health Care, Chapel Hill, NC
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D194
Keywords: Hyperglycemia, Liver transplantation, Outcome, Post-transplant diabetes
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Liver - Kidney Issues in Liver Transplantation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, May 2, 2017
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall D1
Introduction: As the prevalence of diabetes (DM) increases in the general population, it is also increasing in the transplant (Tx) population. Post-transplant diabetes (PTDM) has historically led to inferior outcomes after Tx. With the rising population of Tx for fatty liver disease, the impact of DM, de novo PTDM, and, hepatic steatosis on post-liver Tx outcomes has not been clearly defined.
Purpose: To determine the incidence and prevalence of PTDM, post-Tx hepatic steatosis and the impact on liver Tx outcomes.
Methods: This was a single center retrospective cohort study from 2003 to 2016 of adult patients undergoing liver Tx. Pediatric, acute liver failure and retransplants were excluded. DM was defined as ≥ 2 random glucose levels ≥ 200 mg/dl at 1 year. Glucose levels in the first 30 days post-Tx were excluded. The outcomes were recurrent or de novo DM, steatosis at 1, 3, 5 years, and patient survival. Time-to-event analyses were performed with Kaplan-Meier survival curves.
Results: 433 patients met inclusion criteria. 13% of Tx were performed for NAFLD, and 23% of patients had DM at the time of Tx. 81% of patients with DM at the time of Tx continued to have uncontrolled DM at 1 year. Among patients without DM at Tx, 44% developed de novo PTDM by 5 years; 77% of these occurred in the first 12 months (Figure 1). PTDM was associated with de novo hepatic steatosis at 1,3 and 5 years (6% vs 4%, 17% vs 9%, and 27% vs 17%, p=0.05). There was a numerical trend toward inferior survival of patients with DM at 5 years (78% vs 72%) in unadjusted analysis.
Conclusion: De novo PTDM is common and the majority occurs within the first year. PTDM is associated with post-Tx hepatic steatosis and a trend toward inferior patient survival. The early onset of PTDM provides a potential window for intervention that may reduce the risk of steatosis and decreased survival.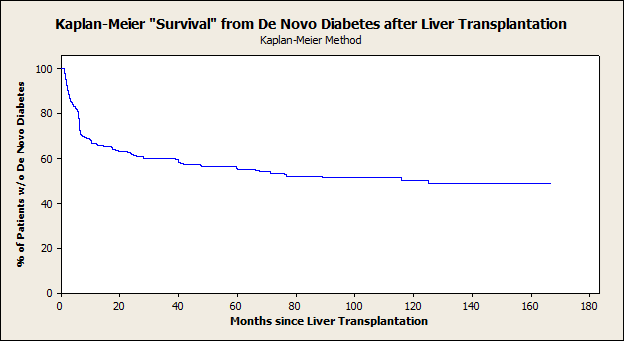
CITATION INFORMATION: Reuter C, Lee R.-A, Watkins R, Lieber S, Szempruch K, Gerber D, DeCherney G, Barritt IV A. The Impact of De Novo Post-Transplant Diabetes on Hepatic Steatosis and Liver Transplant Outcomes. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Reuter C, Lee R-A, Watkins R, Lieber S, Szempruch K, Gerber D, DeCherney G, IV ABarritt. The Impact of De Novo Post-Transplant Diabetes on Hepatic Steatosis and Liver Transplant Outcomes. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/the-impact-of-de-novo-post-transplant-diabetes-on-hepatic-steatosis-and-liver-transplant-outcomes/. Accessed February 22, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
