The Efficacy of Spheroidal Hepatocyte in Hepatocyte Transplantation
Department of Gastroenterological Surgery Ⅰ Hokkaido University Graduate School, Sapporo, Japan
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 431
Keywords: Graft function
Session Information
Session Name: Islet/Cell Transplantation
Session Type: Oral Abstract Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:45pm
 Presentation Time: 4:27pm-4:39pm
Presentation Time: 4:27pm-4:39pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Hepatocyte transplantation (HCTx) has been expected as a next generation cell therapy alternative to liver transplantation. Following HCTx, the liver function improves in many cases but is temporary. As a problem to be overcome, single hepatocyte (SH) is injured during isolation process from the liver, damaged by the innate immune response after HCTx, and a long-term engraftment cannot be achieved. Spheroidal hepatocyte (SP) can be developed by 3-dimensional self-aggregation of SH. SP has a cellular environment close to the liver tissue, is structurally stronger, and maintains liver functions. We investigated the efficacy of SP in hepatocyte transplantation.
*Methods: The SHs were isolated from the C57BL/6 mouse liver by 3 steps collagenase perfusion technique, and SPs were induced by hanging drop method. The viability and the liver functions of SPs were evaluated in vitro and compared with SHs cultured on collagen coat dish. SPs or SHs were transplanted into the liver of apolipoprotein E (Apo E) KO (-/-) mice via the portal vein, and graft function was evaluated. The transplanted grafts were investigated immunohistochemistry by using the recipient animal livers.
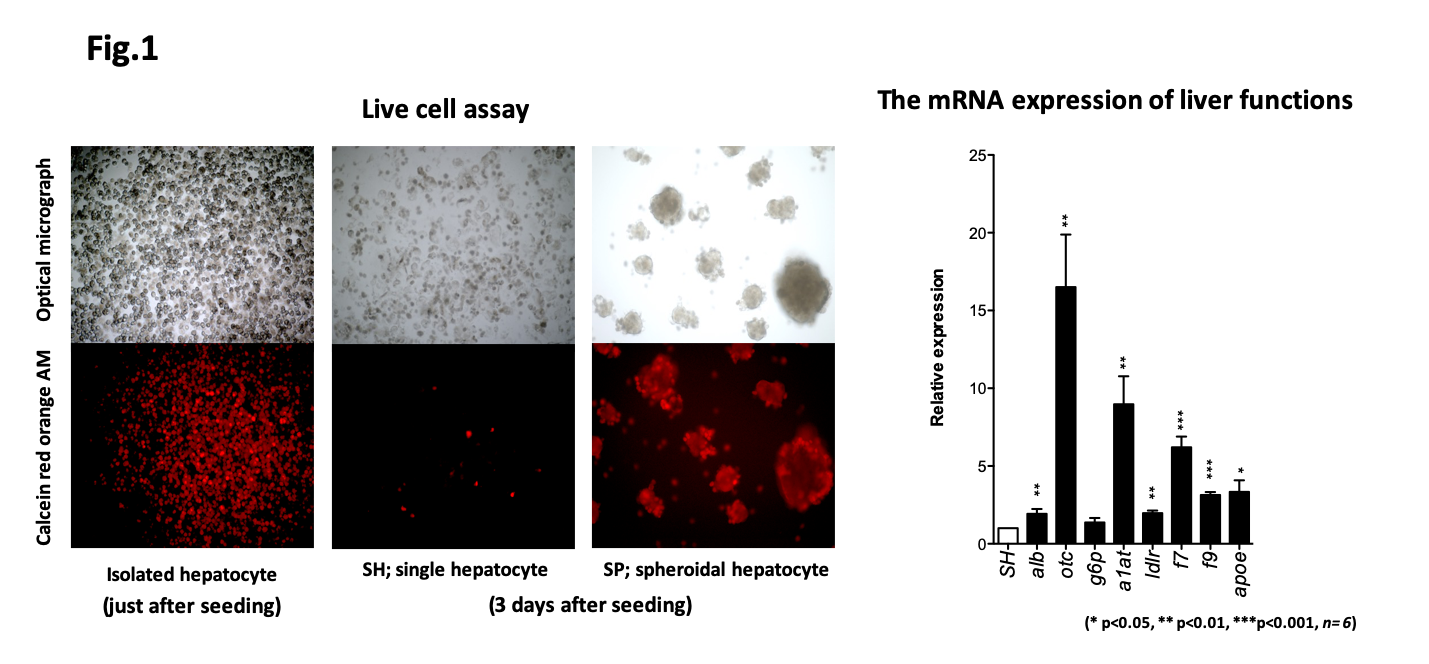
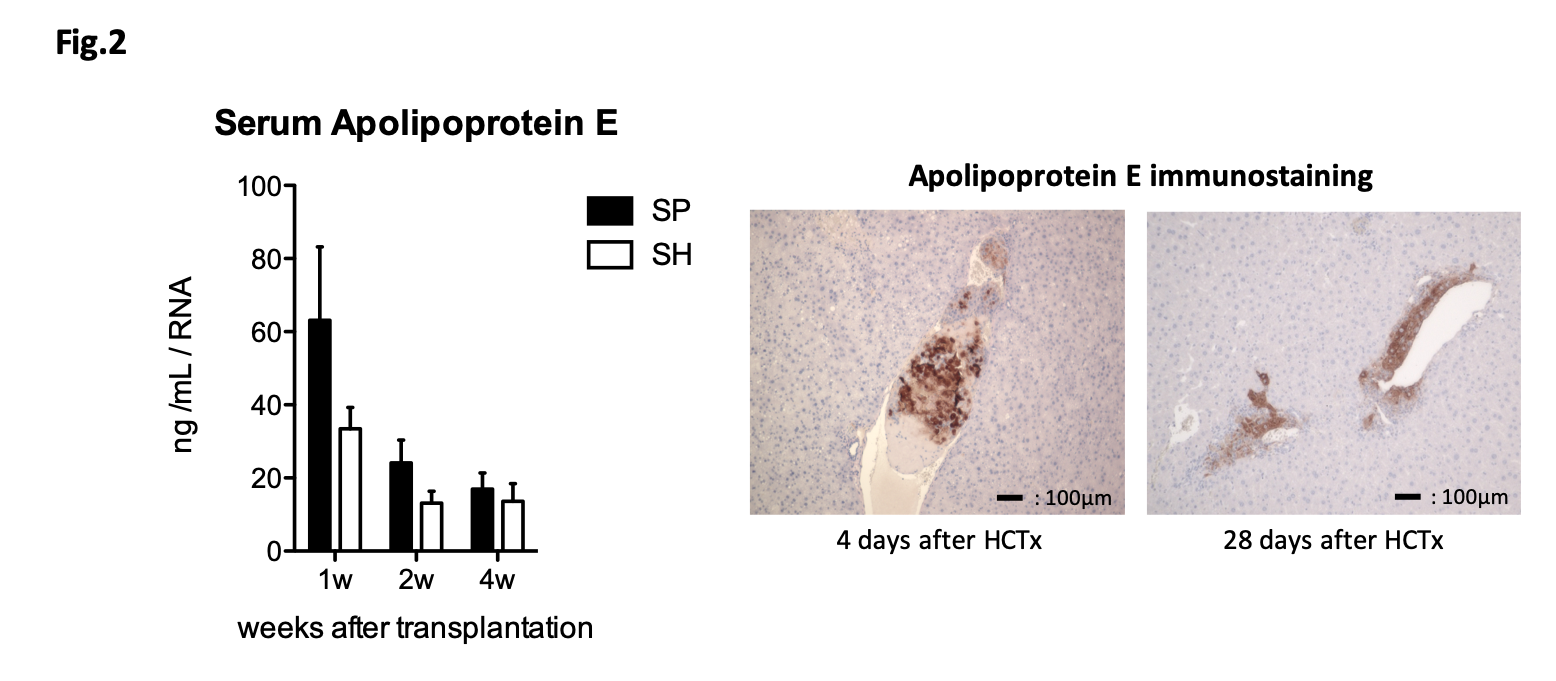
*Results: The SH viability declined rapidly whereas SP maintained well its viability during the culture period. The relative mRNA expression of liver functions (albumin, ornithine transcarbamylase, glucose-6-phosphate, alpha 1 anti-trypsin, coagulation factor 7, coagulation factor 9, low-density lipoprotein receptor and apolipoprotein e) of SP were higher than those of SH, and albumin concentration in the SP culture medium (9.5 ± 2.5 μg/dL) was significantly higher than SH (3.5 ± 1.8 μg/dL, p = 0.006) (Fig.1). Following the mouse SP HCTx, Apo E positive cells were observed pathologically in the poral vein at early after HCTx (4 days after HCTx), and in the liver parenchymal thereafter (28 days after HCTx). Apo E was consistently detected in the serum of Apo E KO recipient animals at least until 4 weeks after transplantation (Fig.2).
*Conclusions: The spheroidal hepatocyte functioned well and maintained its functions even after transplantation. The spheroidal hepatocyte can be applied to hepatocyte transplantation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Shibuya K, Watanabe M, Kanazawa R, Ganchiku Y, Goto R, Taketomi A. The Efficacy of Spheroidal Hepatocyte in Hepatocyte Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/the-efficacy-of-spheroidal-hepatocyte-in-hepatocyte-transplantation/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress