The Efficacy and Safety of Plaquenil in Kidney Transplants Patients with Lupus.
1Washington University, Saint Louis
2Freman Hospital, New Castle, United Kingdom
3Saint Louis University, Saint Louis
4Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Weston
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D107
Keywords: Graft survival, Immunosuppression, Kidney transplantation, Outcome
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Kidney Immunosuppression: Novel Regimens and Drug Minimization
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, May 2, 2017
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall D1
Background: Hydroxychloroquine, also known as Plaquenil ( PLQ) is an antimalarial drug with immunomodulatory action. Recent studies have demonstrated a protective effect of PLQ in the management of native renal lupus nephritis. The use of PLQ in kidney transplant recipients has not been examined.
Methods: A retrospective analysis of 76 kidney transplant patients with history of lupus were transplanted at a large single center between 1998 and 2014. Patients were categorized into three groups according to their PLQ use: Group 1 did not receive; Group 2 received on discharge, Group 3 received after discharge. Associations between pattern of PLQ use and post-transplant graft failure and patient death over 6 years were examined by Kaplan-Meier analysis and Cox regression.
Results: 67% were discharged with standard immunosuppression and never received PLQ (group 1), 18% received PLQ as an alternative or adjunctive to standard immunosuppression at the time of discharge (group 2), and 15% required PLQ at a later time due to lupus nephritis or arthritis (group 3). Graft and Patient Survival at 6 years were similar.
| HR for Graft Survival | HR for Patient Survival | |
| Group 1, N=51 (67%) ( Did not receive PLQ) | Reference | Reference |
| Group 2, N=14 (18%) ( PLQ on discharge) | 0.95, CI 0.27-3.34 | 1.23, CI 0.25-5.9 |
| Group 3, N=11 (15%) ( PLQ after Discharge) | 1.14, CI 0.37-3.49 | 1.02, CI 0.21-4.9 |
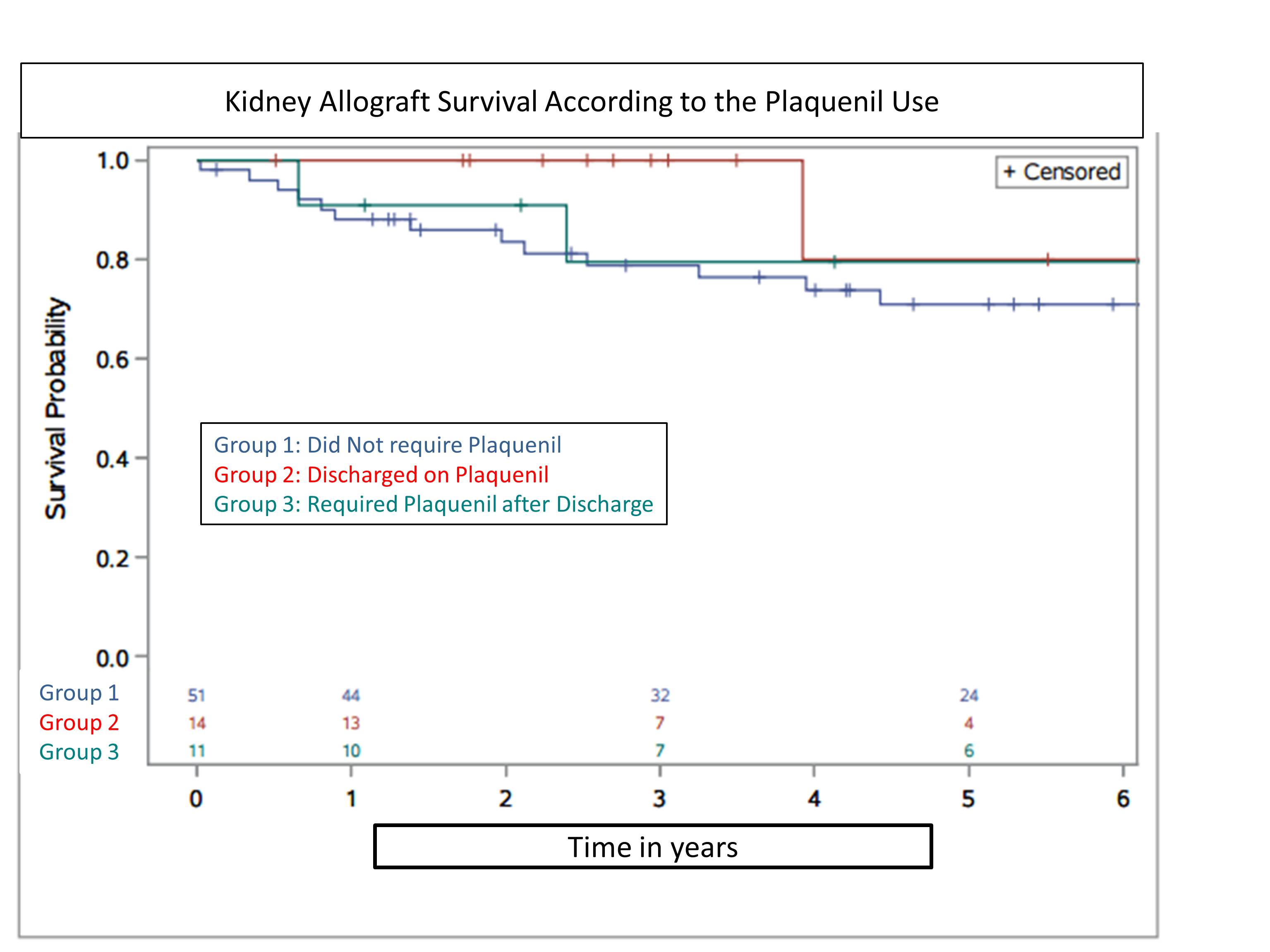 Acute graft rejection during the study period was similar among the three groups (group 1=21.5%, group 2= 28.5% and group3=36.3%, p=0.55). Only 4 out of 25 patients (group 1 and 2) discontinued PLQ, mainly for anemia and leukopenia.
Acute graft rejection during the study period was similar among the three groups (group 1=21.5%, group 2= 28.5% and group3=36.3%, p=0.55). Only 4 out of 25 patients (group 1 and 2) discontinued PLQ, mainly for anemia and leukopenia.
Conclusions: Around 20% of kidney transplant recipients with native kidney lupus nephritis require PLQ after transplant discharge for recurrent lupus symptoms or arthritis. In general, the use of PLQ is safe. Larger studies are needed to determine whether PLQ use protects survival of kidney graft.
CITATION INFORMATION: Rhazouani S, Anwar S, Brennan D, Lentine K, Venkatachalam K, Malone A, Alhamad T. The Efficacy and Safety of Plaquenil in Kidney Transplants Patients with Lupus. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rhazouani S, Anwar S, Brennan D, Lentine K, Venkatachalam K, Malone A, Alhamad T. The Efficacy and Safety of Plaquenil in Kidney Transplants Patients with Lupus. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/the-efficacy-and-safety-of-plaquenil-in-kidney-transplants-patients-with-lupus/. Accessed February 27, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
