The Combined Effects of Simultaneous Portal Vein Thrombosis and Renal Dysfunction in Liver Transplant Recipients
1University of Pittsburgh Medical Centre, Pittsburgh, PA, 2Medicine, University of Pittsburgh Medical Centre, Pittsburgh, PA
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1085
Keywords: Liver transplantation, Portal veins, Renal function, Survival
Topic: Clinical Science » Liver » Liver: Kidney Issues in Liver Transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Liver: Kidney Issues in Liver Transplantation
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Simultaneous portal vein thrombosis (PVT) and renal dysfunction (RD) have unknown effects after liver transplant (LT). We analyzed the outcomes of patients with simultaneous PVT/RD after LT for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and for alcoholic liver disease (ALD), the two most common indications for LT in the US.
*Methods: Data from the UNOS Star files were used to identify adult recipients (>18 years) of deceased donors LT with NASH or ALD. Patients with ABO incompatibility, non-hepatocellular carcinoma malignancies, partial grafts, and multi-visceral transplants were excluded. RD was defined as serum creatinine >1.5 mg/dL or the need for dialysis. Student’s t-test, chi-square, ANOVA, Kaplan-Meier, log-rank test, Cox regression, logistic and Poisson regression were used for statistical analyses.
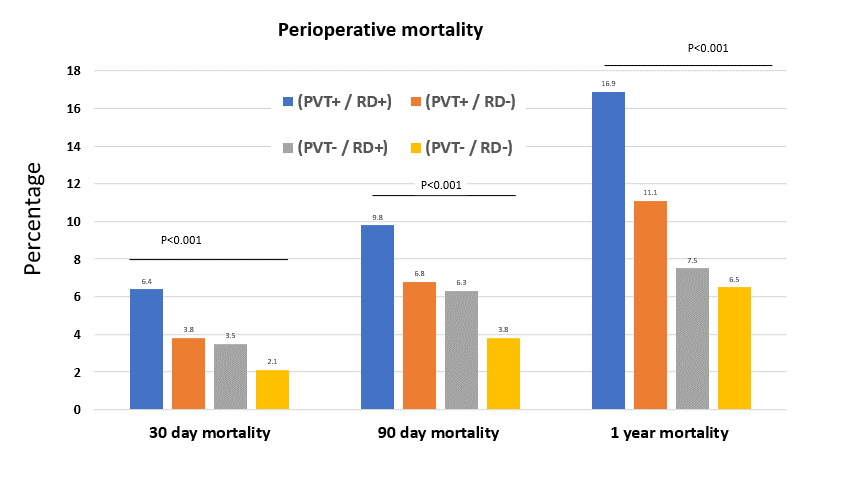
*Results: Between 2006 and 2016, the percentage of patients undergoing LT with PVT, RD, and simultaneous PVT/RD went from 7.2% to 11.3% (P<0.001), from 33.8% to 39.2% (P<0.001) and from 2.4% to 4.5% (P<0.001) respectively. Recipients with simultaneous PVT/RD had a 30-days, 90-days and at 1-year mortality of 6.4%, 9.8% and 16.9% in comparison to 2.1%, 3.8% and 6.5% in patients without PVT or RD (P<0.001). The 5-year survival of recipients without PVT or RD was 82.1% (95% CI 80.9-83.3). For patients with RD alone, the 5-year survival was 75.5% (95% CI 74.3-77.5), for patients with PVT alone was 74.8% (95%CI 71.9-77.9) and for patients with simultaneous PVT/RD was 71.1% (95% 70.1-73.9) (All pairwise comparisons: P<0.05). Cox regression analysis showed that PVT, RD and simultaneous PVT/RD were independent risk factors after adjusting for recipient age, sex, ethnicity, diabetes, BMI, MELD, history of previous abdominal surgeries, ascites, TIPSS, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, donor age, and year of transplantation. The adjusted hazard ratio for RD was 1.45 (95% CI 1.30-1.61; P<0.0001), for PVT was 1.29 (95% CI 1.05-1.58; P=0.012), and for simultaneous PVT/RD was 2.11 (95% CI 1.73-2.56; P<0.0001).
*Conclusions: The number of patients undergoing LT for ALD or NASH with PVT, RD, and simultaneous PVT/RD has increased over time. PVT, RD and simultaneous PVT/RD are associated with increased perioperative mortality and inferior long-term survival. The effects of simultaneous PVT/RD are more pronounced in patients with NASH than in LT recipients with ALD
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Molinari M, Carillo CF, Dongling D, Jorgensen D, Dharmayan S, Kaltenmeier C, Liu H, Behari J, Rachakonda V, Ganesh S, Hughes C, Tevar A, Harakeh HAl, Emmanuel B, Humar A, Bataller R. The Combined Effects of Simultaneous Portal Vein Thrombosis and Renal Dysfunction in Liver Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/the-combined-effects-of-simultaneous-portal-vein-thrombosis-and-renal-dysfunction-in-liver-transplant-recipients/. Accessed February 18, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress