The Clinical Significance of Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW) in Kidney Transplant Recipients.
S. Park,1 J. Ha,1 Y. Kim,1 H. Lee,1 Y. Kim,1 C. Lim,1 I. Jung,1 D.-J. Han,2 S.-K. Park,2 Y. Kim,2 J. Lee.1
1Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
2Asan Medican Center, Seoul, Korea
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D154
Keywords: Graft survival, Kidney transplantation, Mortality
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Kidney: Cardiovascular and Metabolic
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, May 2, 2017
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall D1
Background Increased red cell distribution width (RDW) has been known to be associated with worse prognosis in various populations. Although the levels of RDW are easily available in complete blood cell counts, the clinical significance of RDW in kidney transplant recipients was scarcely described.
Methods We reviewed 2,960 kidney transplant recipients in two university hospitals in Korea. The laboratory values were collected in 3 months after kidney transplantation, and those without available red blood cell indices or follow-up duration less than 3 months were excluded. The patients with the RDW values higher than the upper quartile level (>14.9 %) was included in the study group and the others in the control group. The clinical outcomes were patient mortality and death-censored graft failure. The association of increased RDW levels and the patient prognosis was assessed by multivariate Cox proportional hazard model.
Results A number of 690 patients were included in the study group. Age [by year, OR 1.022 (1.012-1.032), P<0.001], male sex [OR 2.238 (1.680-2.982), P<0.001], previous history of smoking [OR 1.359 (1.049-1.760), P=0.020], and acute rejection within 3 months [OR 1.559 (1.078-2.257), P=0.018] were risk factors for the presence of high RDW (>14.9 %). Those with presence of renal dysfunction [OR 0.646 (0.499-0.837), P=0.001], higher hemoglobin levels (by g/dL, OR 0.676 (0.635-0.721), P<0.001) had relatively normal range of RDW levels. Interestingly, high RDW levels were significantly related to both patient mortality [HR 2.154 (1.385-3.350), P=0.001] and graft failure [1.564, (1.152-2.122), P=0.004], even after adjusted for multiple clinical characteristics including hemoglobin levels.
Conclusion The post-transplant RDW levels are significantly associated with patient prognosis, independently from hemoglobin levels. Clinicians should pay attention to this laboratory values, which are frequently reported in routine blood cell counts, and consider further examination for the cause of the high RDW levels.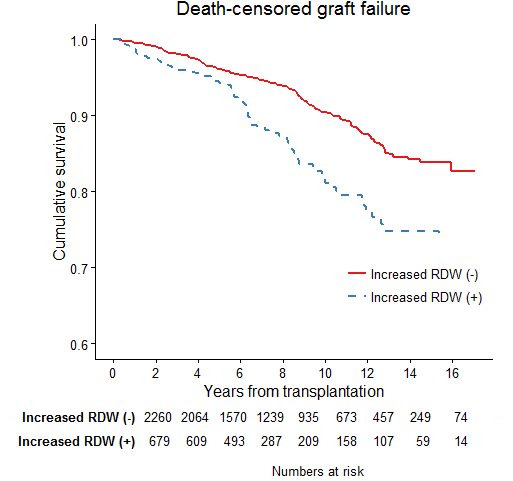
CITATION INFORMATION: Park S, Ha J, Kim Y, Lee H, Kim Y, Lim C, Jung I, Han D.-J, Park S.-K, Kim Y, Lee J. The Clinical Significance of Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW) in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Park S, Ha J, Kim Y, Lee H, Kim Y, Lim C, Jung I, Han D-J, Park S-K, Kim Y, Lee J. The Clinical Significance of Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW) in Kidney Transplant Recipients. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/the-clinical-significance-of-red-cell-distribution-width-rdw-in-kidney-transplant-recipients/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
