The Association of Life Expectancy by Resident Zip Code and Kidney Transplant Outcomes – What Is True Baseline Risk?
Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 176
Keywords: Graft survival, Kidney transplantation, Multivariate analysis, Risk factors
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Novel Predictors of Outcome, Big Data and Technology
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, June 13, 2016
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-3:42pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-3:42pm
Location: Room 302
Many factors beyond traditional clinical risk factors and demographics are associated with outcomes in the general population. These include behavioral, economic, genetic and environmental risks that are difficult to codify but associated with access to care, mental/physical health and protocol adherence. There is also significant heterogeneity in health conditions and outcomes across the US. We used a novel database published by Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation which includes estimates of life expectancy(LE) by US residence location. We merged data by zipcode with national SRTR and tested that LE(stratified by race and ethnicity) was associated with kidney transplant recipient outcomes independent of recipient/donor risk factors.
We included adult solitary kidney transplant recipients between 2004-2009 with follow up through 2014. There was significant variability in LE by recipient zip code ranging from 65yrs for males(similar to North Korea Iraq,Mongolia,Ghana) to 82 yrs(similar to Japan with longest LE). Overall graft and patient survival were significantly associated with residential LE consistent after risk adjustment. 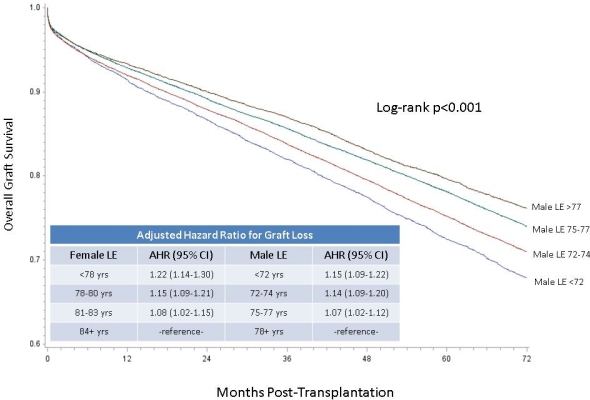 Gender/ethnic specific LE estimates had stronger association with outcomes within respective groups. Estimated effects of LE were virtually unchanged with additional adjustment for zip code median income and percent of poverty suggesting LE is a proxy for conditions beyond socioeconomic status. There was significant variation in LE by individual transplant center (female LE median=81 years, 10th percentile=78, 90th percentile =83) suggesting heterogeneity in baseline risk between centers.
Gender/ethnic specific LE estimates had stronger association with outcomes within respective groups. Estimated effects of LE were virtually unchanged with additional adjustment for zip code median income and percent of poverty suggesting LE is a proxy for conditions beyond socioeconomic status. There was significant variation in LE by individual transplant center (female LE median=81 years, 10th percentile=78, 90th percentile =83) suggesting heterogeneity in baseline risk between centers.
Findings support the notion that factors outside of the standard transplant registries are strongly associated with patient outcomes. Patients' baseline risk as measured by resident life expectancy may provide insights for risk assessment and potentially be utilized as a readily available tool for risk adjustment and center performance evaluations. Further considerations of the mechanisms of this association and potential interventions for patients from residence with lower life expectancy are warranted.
CITATION INFORMATION: Buccini L, Goldfarb D, Poggio E, Flechner S, Schold J. The Association of Life Expectancy by Resident Zip Code and Kidney Transplant Outcomes – What Is True Baseline Risk? Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Buccini L, Goldfarb D, Poggio E, Flechner S, Schold J. The Association of Life Expectancy by Resident Zip Code and Kidney Transplant Outcomes – What Is True Baseline Risk? [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/the-association-of-life-expectancy-by-resident-zip-code-and-kidney-transplant-outcomes-what-is-true-baseline-risk/. Accessed March 2, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
