Surveillance with Allosure for Allograft Rejection and Infection in Lung Transplant
1Pulmonary, Critical Care & Sleep Medicine, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, 2Medical Affairs, CareDx, South San Francisco, CA, 3Division of Transplant Surgery, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 340
Keywords: Lung infection, Lung transplantation, Monitoring, Rejection
Topic: Clinical Science » Lung » 64 - Lung: All Topics
Session Information
Session Name: Early and Late Outcomes in Lung Transplantation
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Monday, June 6, 2022
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:40pm-6:50pm
Presentation Time: 6:40pm-6:50pm
Location: Hynes Room 210
*Purpose: Measurement of plasma donor-derived cell-free DNA (dd-cfDNA; AlloSure, CareDx) has been shown to be a useful non-invasive diagnostic test for injury and infection after lung transplant (LT). dd-cfDNA consists mainly of 100-200 base pair double stranded DNA fragments resulting from apoptosis, necrosis, or release of nuclear DNA into the systemic circulation. These fragments have a short half-life (30-90 min) due to rapid hepatic and renal clearance. Thus, dd-cfDNA offers real-time monitoring of graft tissue damage. Unfortunately, reported levels of dd-cfDNA vary across the literature, and literature is lacking regarding the kinetics of dd-cfDNA in the early phase following LT.
*Methods: This is a single-center, prospective cohort study of LT recipients. All LT recipients were approached to participate in the study. Those consented to participate received AlloSure testing twice a week for month 1, once a week for month 2, once every 2 weeks for months 1-5, and once a month for months 6-12. We utilized a non-linear regression curve-fitting model and Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparison for analysis.
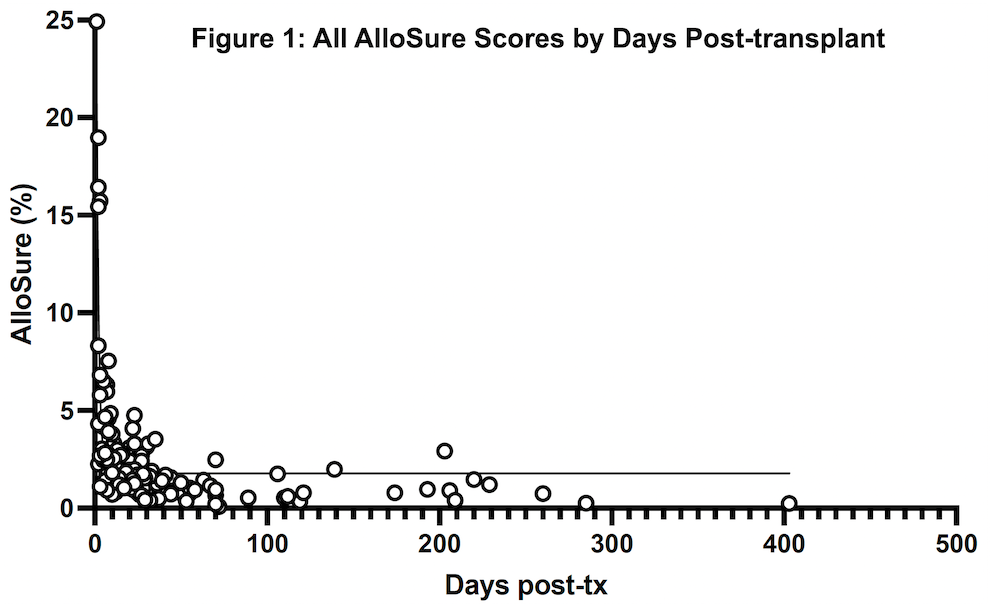
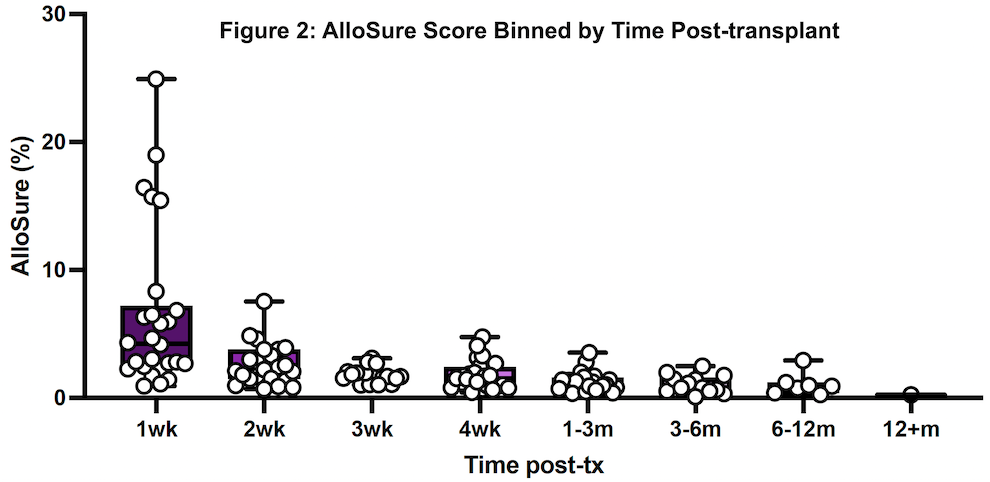
*Results: Twenty patients representing 156 AlloSure samples were included, and AlloSure scores were plotted against time post-LT (Figure 1). In LT patients, AlloSure follows an exponential decay with Goodness of fit being r2 = 0.6447. When binned into discrete timepoints at week 1, 2, 3, 4, and month 1-3, 3-6, 6-12, 12 and beyond, there is a strong effect of post-transplant time on dd-cfDNA value (p = 3.1 e-9) (Figure 2). AlloSure values at week 1 are significantly higher than later timepoints beginning at week 4 with significance at week 2 versus later also emerging.
*Conclusions: This study is the first to demonstrate the early kinetics of AlloSure after LT. There is a statistically significant correlation of decline in AlloSure values over time post-LT in the absence of graft dysfunction, rejection, or clinical events. Understanding the kinetics of AlloSure in the lung transplant patient population allows for determination of appropriate testing frequency.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Botros MM, Sulejmani N, Reader BF, Keller BC. Surveillance with Allosure for Allograft Rejection and Infection in Lung Transplant [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/surveillance-with-allosure-for-allograft-rejection-and-infection-in-lung-transplant/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress