Surveillance Renal Allograft Biopsies Prognosticate Graft Function.
MUSC, Charleston, SC.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 101
Keywords: Glomerular filtration rate (GFR), Kidney transplantation, Nephropathy, Protocol biopsy
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Delayed Graft Function and Protocol Biopsy
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, June 12, 2016
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:18pm-5:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:18pm-5:30pm
Location: Room 302
Background: Surveillance biopsy of the renal allograft provides a window into the health of the allograft and could allow prognostication of function by affording better understanding of structure-function relationships in the kidney. We examined the relationship between Banff lesion scores obtained during protocol biopsies and subsequent graft function.
Methods: This was a retrospective analysis of first protocol biopsy data obtained from solitary renal transplants performed between 2005 and 2013, with last follow up October 2015. Protocol biopsies were performed 3 to 6 months post transplant. We calculated “chronic Banff score” as the sum of chronic glomerular (cg), interstitial (ci), tubular (ct), and fibrointimal thickening (cv) lesion scores. Estimated GFR was calculated by the 4 variable MDRD equation. We compared serum creatinine at multiple time points to chronic Banff scores by repeated measures of ANOVA. Covariates examined included age, gender, race, recipient hypertension, recipient diabetes and KDRI.
Results: Of 1320 patients with 1720 biopsies, 279 were the patient's first protocol biopsy. There was creatinine data available for up to 2 years after transplant for 160 biopsies. The mean time to first protocol biopsy was 125.39 days. The mean eGFR at time of first protocol biopsy was 53.5 ml/min/1.73 m2, with Banff lesion scores ≤ 2 and > 2 at 54.39 and 51.8 ml/min/1.73m2, respectively. The mean serum creatinine at time of first protocol biopsy for those with chronic Banff ≤2 was 1.393 vs 1.562 (P=0.020). Between the 6 month and 24 month time points, patients who had a chronic Banff lesion score > 2 saw a creatinine rise of 10.52% vs. a 4.33% rise for those with a score ≤2.
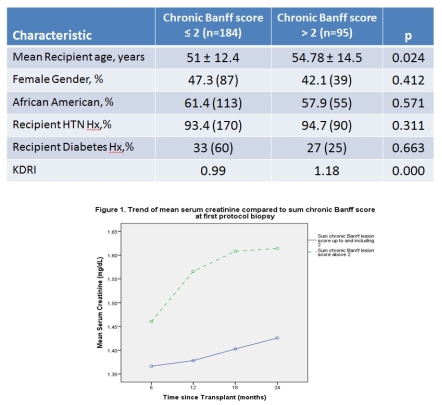
Conclusion: Higher cumulative chronic Banff score at first protocol biopsy predicts higher serum creatinine at subsequent time points. The slope of creatinine rise is more rapid in those with higher chronic lesion scores. Patients with higher chronic scores may need consideration for treatments that minimize nephrotoxic insults and maximize renoprotection. Further study is needed to examine relationships between biopsy scores and graft survival.
CITATION INFORMATION: Thompson J, Taber D, Baliga P, Chavin K, Srinivas T. Surveillance Renal Allograft Biopsies Prognosticate Graft Function. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Thompson J, Taber D, Baliga P, Chavin K, Srinivas T. Surveillance Renal Allograft Biopsies Prognosticate Graft Function. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/surveillance-renal-allograft-biopsies-prognosticate-graft-function/. Accessed February 20, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
