Sub-Optimal Renal Recovery and Progressive Chronic Kidney Disease after Living Kidney Donation
1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 2Department of Urology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 3Department of Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea, Republic of
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 449
Keywords: Donation, Kidney, Nephropathy, Renal dysfunction
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney Living Donor: Long Term Outcomes
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Tuesday, June 4, 2019
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:18pm-3:30pm
Presentation Time: 3:18pm-3:30pm
Location: Room 304
*Purpose: Post-operative renal recovery after nephrectomy is a substantial problem to be addressed in living kidney donors. Herein, we explored factors associated with renal recovery and progression to advanced chronic kidney disease (CKD) in living donors.
*Methods: A total of 1,588 kidney donors who underwent donor nephrectomy from 1982 to 2016 were retrospectively reviewed. We extracted donors who had estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) at 1 month after kidney donation with follow-up period over one year. Percent change of eGFR from initial to one month after donation was calculated. The sub-optimal renal recovery was defined as recovery of eGFR less than 70%. The development of advanced CKD, latest eGFR < 60 ml/min/m2 were the clinical end-point. We used continuous value for laboratory variables except uric acid which was divided by sex specific criteria of hyperuricemia; male ≥ 7.0 mg/dL, female ≥ 6.0 mg/dL. Cox-regression and logistic regression analysis were used to determine the risk factor related with sub-optimal renal recovery and progressive CKD.
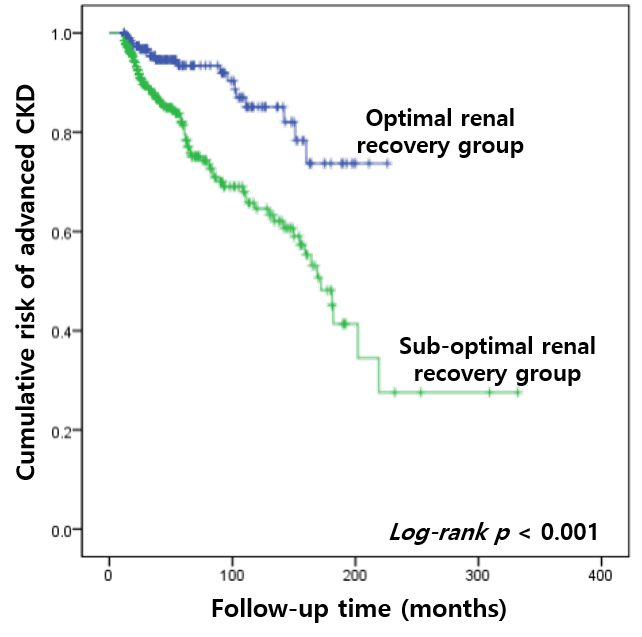
*Results: In total, 606 donors were included in the study. The mean follow-up period was 82.3 ± 65.1 months. Of which, 402 showed sub-optimal renal recovery at 1 month, and 107 developed advanced CKD. The initial eGFR (adjusted HR 0.950, 95% CI 0.933 – 0.968, p < 0.001) and sub-optimal renal recovery at 1 month (adjusted HR 3.228, 95% CI 1.869 - 5.574, p < 0.001) were the significant risk factors for development of advanced CKD in multivariate Cox-regression analysis. In addition, donors having older age (adjusted OR 1.053, 95% CI 1.033 - 1.073, p < 0.001), male sex (adjusted OR 1.839, 95% CI 1.043 - 3.243, p = 0.035), lower serum protein (adjusted OR 0.559, 95% CI 0.352 - 0.888, p = 0.014), hyperuricemia (adjusted OR 2.599, 95% CI 1.239 - 5.451, p = 0.012), and initial eGFR (adjusted OR 1.047, 95% CI 1.031 - 1.062, p < 0.001) tended to develop sub-optimal renal recovery after donation.
*Conclusions: Earnest evaluation and management to reduce risk factors for sub-optimal renal recovery after donation could be helpful in improving long-term renal outcomes in living kidney donors.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kim Y, Jeong C, Kim H, Ha J, Ahn C, Kim Y, Lee H. Sub-Optimal Renal Recovery and Progressive Chronic Kidney Disease after Living Kidney Donation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/sub-optimal-renal-recovery-and-progressive-chronic-kidney-disease-after-living-kidney-donation/. Accessed March 7, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress