Sirolimus Regimens After Kidney Transplantation: Role of Pre-Transplant Risk Factors in Modifying the Risk of Mortality in Adult Recipients
A. Santos1, H. Ibrahim1, M. A. Leghrouz1, X. Wen2
1University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, 2University of Rhode Island, Kinston, RI
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 758
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Risk factors, Sirolimus (SLR), Survival
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » 35 - Kidney: Cardiovascular and Metabolic Complications
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney: Cardiovascular and Metabolic Complications
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Saturday, June 4, 2022
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: We aimed to investigate the role of risk factors in modifying the association of sirolimus with mortality in kidney transplant (KT) recipients (KTRs).
*Methods: Using 2000-2016 Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients data, Cox multivariable regressions were used to analyze the 5-year mortality associated with SRL + tacrolimus (SRL-TAC), SRL+ cyclosporine (SRL-CSA), or SRL+ mycophenolate (SRL-MPA) compared with standard tacrolimus + mycophenolate (TAC-MPA) regimen in the pooled cohort and in cohorts characterized by presence or absence of risk factors at transplantation.
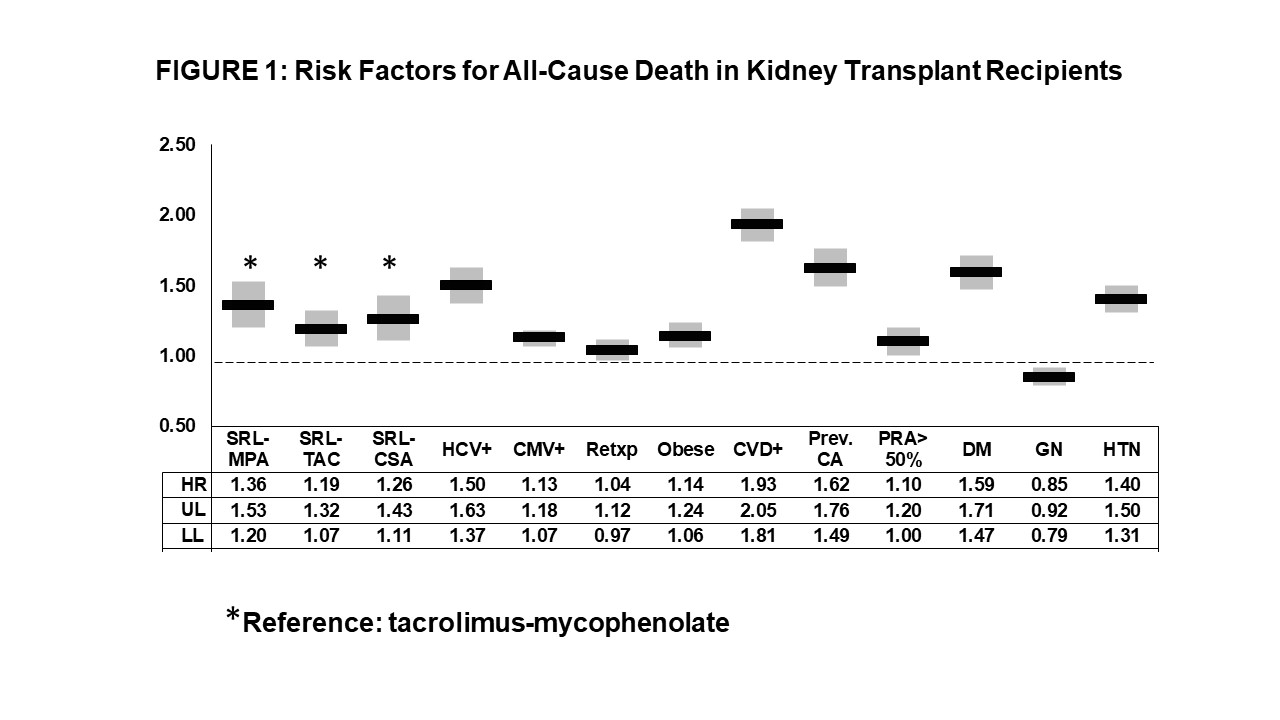
*Results: SRL regimens were associated with higher mortality risk than standard-regimen (SRL-TAC, HR=1.19, 95% CI=1.07-1.32; SRL-CSA, HR=1.26, 95% CI=1.11-1.43); SRL-MPA, HR=1.36, 95% CI=1.20-1.53). Other risk factors for increased mortality in KTRs were positive (+) Hepatitis C (HCV) or Cytomegalovirus (CMV) serology, obesity, previous cancer, cardiovascular disease, PRA>50%, and diabetes mellitus or hypertension as primary kidney diagnosis (Fig. 1)
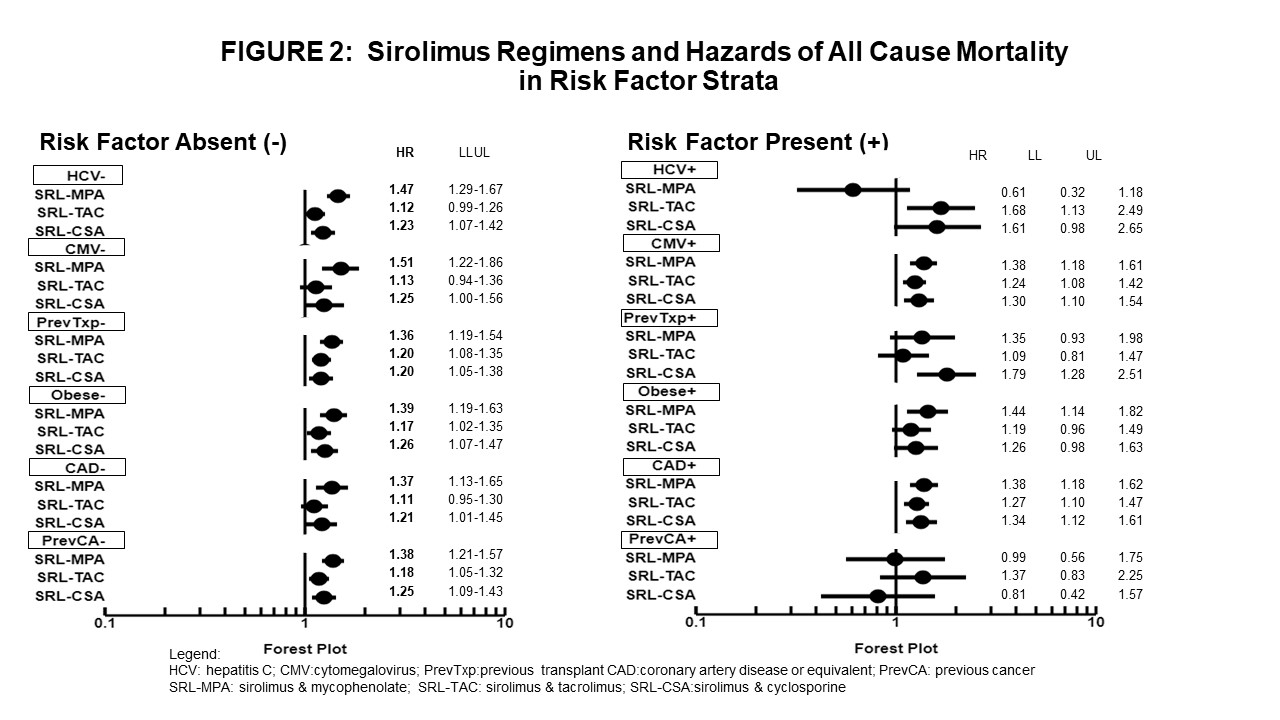
In stratified analyses based on risk factors at the time of KT (Fig. 2), results showed that compared with KTRs on standard TAC-MPA:
1. the risk of mortality was higher in KTRs on any SRL regimen regardless of present or absent CMV+ serology, obesity, or coronary artery disease; but the risk of mortality trended lower in KTR on SRL-MPA with HCV+ serology;
2. the risk of mortality was higher in KTRs with first transplant on any SRL regimen and similar in KTRs with previous transplant on SRL-TAC and SRL-MPA; and
3. the risk of mortality in KTRs without previous cancer was higher with any SRL regimen and not different in KTR with previous cancer on SRL-CSA and SRL-MPA.
*Conclusions: The higher mortality risk with SRL-MPA, SRL-TAC or SRL-CSA versus TAC-MPA appeared to be attenuated in KTRs with HCV+ serology, previous transplant, and history of cancer; respectively.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Santos A, Ibrahim H, Leghrouz MA, Wen X. Sirolimus Regimens After Kidney Transplantation: Role of Pre-Transplant Risk Factors in Modifying the Risk of Mortality in Adult Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/sirolimus-regimens-after-kidney-transplantation-role-of-pre-transplant-risk-factors-in-modifying-the-risk-of-mortality-in-adult-recipients/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress