Single-Dose Anti-Thymocyte Globulin is Non-Inferior to Divided-Dose for Induction Therapy in Kidney and Pancreas Transplantation
1Sentara Norfolk General Hospital, Norfolk, VA, 2Children's Hospital of the King's Daughters, Norfolk, VA
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 9
Keywords: Induction therapy, Kidney/pancreas transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney Immunosuppression: Induction Therapy
Session Type: Oral Abstract Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:45pm
 Presentation Time: 4:03pm-4:15pm
Presentation Time: 4:03pm-4:15pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Emerging studies suggest that single-dose rabbit antithymocyte globulin (rATG) is not inferior to the divided-dose, however this dosing strategy has never been evaluated in a cohort of primarily African American patients or pancreas transplant patients. The aim of the study was to compare the efficacy and safety of single-dose (SD) rATG to divided-dose (DD) rATG for induction in both renal and pancreatic transplant patients.
*Methods: This retrospective crossover study evaluated patients prior to and after the initiation of a SD rATG protocol. All patients who received rATG were included in the study and were maintained with standard immunosuppression of tacrolimus, mycophenolate, and steroids. The dose of rATG was the same between groups, with the SD rATG receiving 6mg/kg in 24 hours while the DD rATG received 1.5mg/kg daily for four days. The primary end-point was rejection at 1 year.
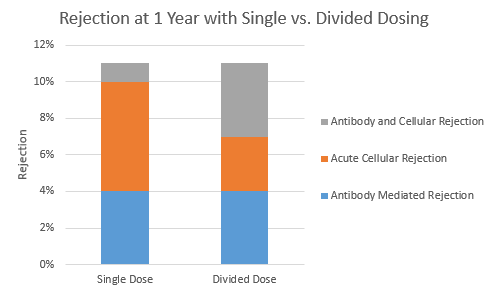
*Results: In the 199 patients included (99 DD/100 SD, 74% African American, 7% pancreas transplant, 94% kidney transplant), there was no difference in rejection at 1 year (11% vs. 11%, p = 0.98). There was also no difference in delayed graft function, serum creatinine or survival at 1 year (p = 0.192, p = 0.501, and p = 0.621). For the pancreas transplant patients (n=13), there was no difference in fasting glucose, amylase or lipase at 1 year. Patients in the SD group were more likely to receive the entire prescribed dose of rATG (5.92mg/kg vs. 5.55mg/kg, p = 0.009). Initially, the SD group had more leukopenia and thrombocytopenia, however thrombocytopenia resolved by post-operative day 4 and leukopenia resolved by 3 months. Patients were more likely to leave the hospital by post-operative day 3 in the SD group (12% vs. 2%, p= 0.006). There was no difference in readmission at 30 days (36% vs. 31%, p = 0.484) or at 1 year (75% vs. 67%, p = 0.196). At one year, more patients in the SD group developed CMV-emia than the DD group (44% vs. 29%, p = 0.031), however there were no differences in other infections.
*Conclusions: Use of single dose rabbit anti thymocyte globin 6 mg/kg over 24 hours is an acceptable alternative to the standard divided-dose for induction therapy in kidney and pancreas transplant in a predominantly African American population. This regimen has the potential to decrease hospital length of stay without increasing hospital 30-day readmission.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ingemi AI, Bangash OF, McCoy S, Hulse L, Colonna J, Sadr H, Sutton S, Coleman M, Wilson T, McCune TR. Single-Dose Anti-Thymocyte Globulin is Non-Inferior to Divided-Dose for Induction Therapy in Kidney and Pancreas Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/single-dose-anti-thymocyte-globulin-is-non-inferior-to-divided-dose-for-induction-therapy-in-kidney-and-pancreas-transplantation/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress