Single Cell RNA Transcriptomics to Further the Precision Transplantation Medicine Approaches in Kidney Allograft Recipients
Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 218
Keywords: Gene expression, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Biomarker Discovery and Immune Modulation
Session Type: Oral Abstract Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:45pm
 Presentation Time: 4:15pm-4:27pm
Presentation Time: 4:15pm-4:27pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Test the hypothesis that single cell RNA transcriptomics will further the precision transplantation medicine approaches and address important conundrums in clinical transplantation.
*Methods: We studied the cellular transcriptome of 3 kidney biopsies—(i) native kidney (HK), (ii) allograft kidney with transplant glomerulopathy, fibrosis, and worsening kidney function but with undetectable circulating donor-specific antibodies (AK1), and (iii) allograft kidney after successful treatment of an episode of antibody-mediated rejection but with persistent circulating donor-specific antibodies (AK2). We digested the biopsy tissues and generated single cell suspensions. We used droplet-based 10X Chromium platform (10X Genomics) to capture single cells in emulsion, followed by cDNA synthesis, sequencing, and data analysis.
*Results: We generated 7677 single cell transcriptomes from the 3 biopsies.
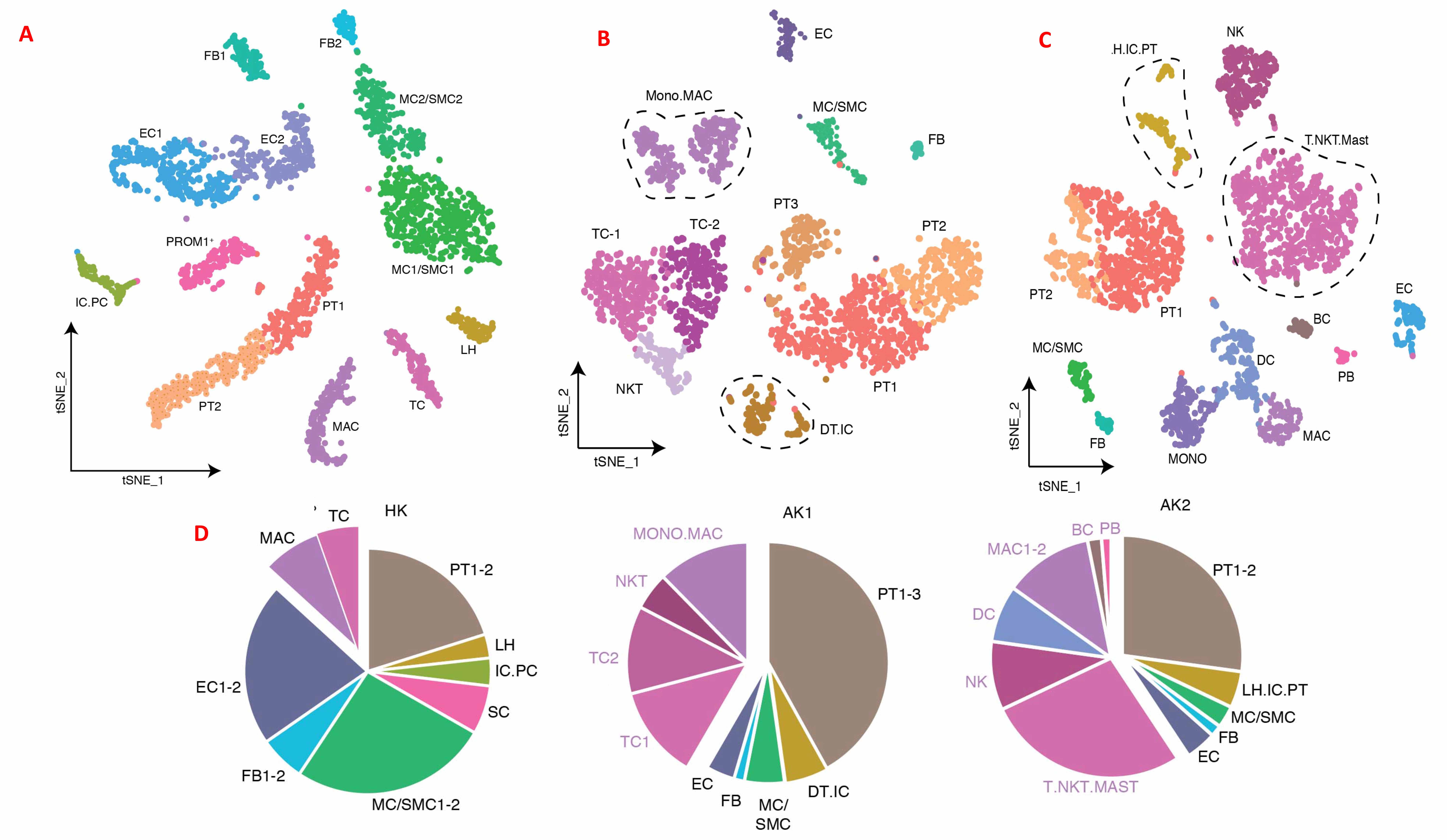
Figure 1: t-SNE-based visualization of individual cells obtained from 3 kidney biopsies; HK (A), AK1 (B), and AK2 (C), and the proportion of kidney parenchymal and immune cells in the biopsies (D).
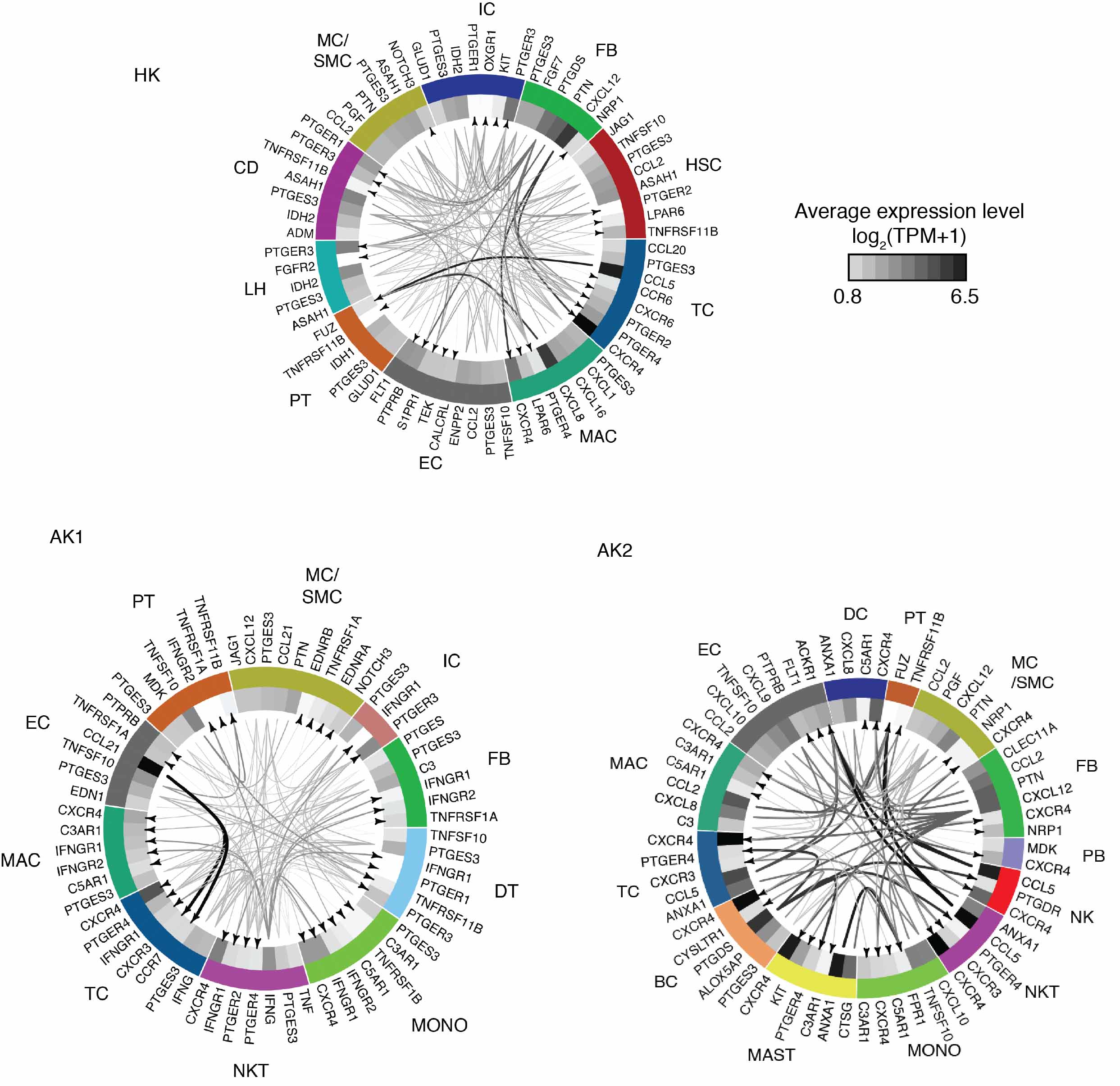
In the healthy native kidney we identified multiple distinct cell clusters including fibroblasts, macrophages and T-cells. In AK1, endothelial cells had the highest abundance of chemokine CCL21, whereas its receptors CXCR3 and CCR7 were expressed on the T cells. In contrast, AK2 had low abundance of CCL21. Endothelial cells in AK2 showed an interferon stimulated-like expression signature, including chemokines CXCL9 and CXCL10, with its cognate receptor CXCR3 highest expressed in T-cells and macrophages, suggesting that endothelial cells in this patient—successfully treated for antibody-mediated rejection several months prior to the index biopsy—continued to produce chemokines that were chemoattractant for T-cells and macrophages. T-cell subtypes included granzyme K-producing CD8+ and central memory CD4+ T-cells (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Putative signaling within the cells of HK, AK1, and AK2.
*Conclusions: These unique findings indicate single cell transcriptomics enables precision transplantation medicine approaches in the care of individual transplant recipients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Suryawanshi H, Yang H, Lubetzky M, Seshan S, Tuschl T, Suthanthiran M, Muthukumar T. Single Cell RNA Transcriptomics to Further the Precision Transplantation Medicine Approaches in Kidney Allograft Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/single-cell-rna-transcriptomics-to-further-the-precision-transplantation-medicine-approaches-in-kidney-allograft-recipients/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress