Sequential Monitoring and Stability of Ex Vivo-Expanded Autologous and Non-Autologous Regulatory T Cells Following Infusion in Non-Human Primates
1University of Pittsburgh, pittsburgh, PA
2University of Wisconsin, Madison.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 137
Keywords: CD3, CD4, Immunosuppression, Tolerance
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Regulatory T Cells
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, May 3, 2015
Session Time: 4:00pm-5:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:00pm-5:12pm
Presentation Time: 5:00pm-5:12pm
Location: Room 122-AB
Ex vivo-expanded cynomolgus monkey CD4+CD25+CD127- regulatory T cells (Treg) maintained Foxp3 demethylation status at the Treg-Specific Demethylation Region (TSDR), and potently suppressed T cell proliferation through 3 rounds of expansion. When CFSE- or VPD450-labeled autologous (auto) and non-autologous (non-auto) expanded Treg were infused into monkeys, the number of labeled auto-Treg in peripheral blood declined rapidly during the first week, but persisted at low levels in both normal and anti-thymocyte globulin plus rapamycin-treated (immunosuppressed; IS) animals for at least 3 weeks. By contrast, MHC-mismatched non-auto-Treg could not be detected in normal monkey blood or in blood of two out of the three IS monkeys by day 6 post-infusion. They were also more difficult to detect than auto-Treg in peripheral lymphoid tissue. Both auto- and non-auto-Treg maintained Ki67 expression early after infusion. Sequential monitoring revealed that adoptively-transferred auto-Treg maintained similarly high levels of Foxp3 and CD25 and low CD127 compared with endogenous Treg, although Foxp3 staining diminished over time in these non-transplanted recipients. Thus, infused ex vivo-expanded auto-Treg persist longer than MHC-mismatched non-auto-Treg in blood of non-human primates and can be detected in secondary lymphoid tissue. Host lymphodepletion and rapamycin administration did not consistently prolong the persistence of non-auto-Treg in these sites. 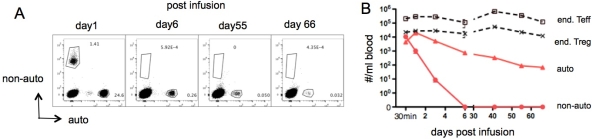
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zhang H, Guo H, Lu L, Zahorchak A, Wiswman R, Raimondi G, Cooper D, Ezzelarab M, Thomson A. Sequential Monitoring and Stability of Ex Vivo-Expanded Autologous and Non-Autologous Regulatory T Cells Following Infusion in Non-Human Primates [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/sequential-monitoring-and-stability-of-ex-vivo-expanded-autologous-and-non-autologous-regulatory-t-cells-following-infusion-in-non-human-primates/. Accessed March 7, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
