Sars-cov-2 Antibody and T Cell Response After Vaccination with or without Intensified Immunosuppression Among Pediatric Renal Transplant Recipients
1Pediatric Nephrology, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, 2Comprehensive Transplant Center, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, 3Pediatric Infectious Disease, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 815
Keywords: COVID-19, Immunogenicity
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » 43 - Kidney: Pediatrics
Session Information
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
Session Information
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Hall C
*Purpose: Recent data has shown poor antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination among adult kidney transplant (tx) recipients, with seroconversion ranging between 22%-58% after two mRNA vaccine doses. Here, we evaluated the antibody and T cell response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination and evaluate the effects of intensified immunosuppression on such response in pediatric (ped) kidney tx recipients.
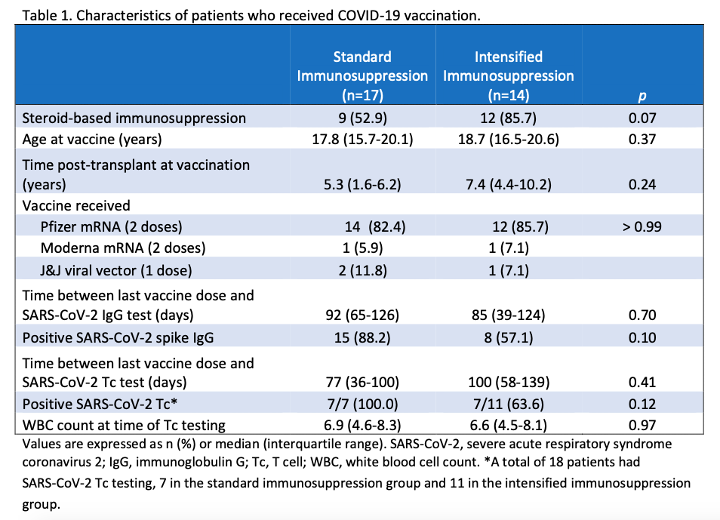
*Methods: Between April and November 2021, 31 ped renal tx patients (pts)aged 13-22 years old had SARS-CoV-2 spike IgG assessment after receiving 2 doses of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA or 1 dose of viral vector vaccine. Pts were evaluated by their level of immunosuppression: A) standard immunosuppression (tacrolimus, mycophenolate mofetil +/- steroids) or B) intensified immunosuppression (standard immunosuppression + solumedrol pulse, IVIG, rituximab, and/or tocilizumab within 11 months prior to and up to 5 months after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination). A subgroup of 18 pts had SARS-CoV-2 Tc assessment post-vaccination.
*Results: 23 of 31 (74.2%) pts seroconverted at a median assessment time of 83 days (IQR 43-124) post-vaccination. There was no difference in the use of steroid-based or steroid-free immunosuppression between the two groups or the type of vaccine received (Table 1). 15 of 17 (88.2%) of those who received standard immunosuppression seroconverted post-vaccination compared to 8 of 14 (57.1%) in those who received intensified immunosuppression (Table 1; p = 0.10). In a subgroup of pts who had SARS-CoV-2 spike-specific Tc testing, 7 of 7 (100%) in the standard immunosuppression group had positive Tc compared to 7 of 11 (63.6%) in the intensified immunosuppression group (Table 1, p = 0.12). There was no leukopenia or difference in the WBC count in either group at the time of Tc testing (Table 1; p = 0.97). No pts developed symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection.
*Conclusions: Ped renal tx recipients appear to have higher rates of seroconversion after the standard 2-dose mRNA or 1-dose viral vector SARS-CoV-2 vaccination compared to adult renal tx recipients. The intensified immunosuppression group appears to have a trend towards lower SARS-CoV-2 spike IgG and Tc conversion, however, results are limited by the small sample size. Larger studies are needed to better understand the humoral and cellular response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in this group.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pizzo H, Shin B, Soni PR, Nadipuram S, Garrison J, Zhang R, Jordan SC, Puliyanda D. Sars-cov-2 Antibody and T Cell Response After Vaccination with or without Intensified Immunosuppression Among Pediatric Renal Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/sars-cov-2-antibody-and-t-cell-response-after-vaccination-with-or-without-intensified-immunosuppression-among-pediatric-renal-transplant-recipients/. Accessed March 6, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress