Safety and Activity of Anti-C1s Humanized Monoclonal Antibody TNT009 in Late Antibody-Mediated Kidney Allograft Rejection – Results of a First-in-Human Phase 1 Trial.
1Department of Medicine III, Medical University Vienna, Vienna, Austria
2Department of Clinical Pharmacology, Medical University Vienna, Vienna, Austria
3Department of Surgery, Medical University Vienna, Vienna, Austria
4Department of Clinical Pathology, Medical University Vienna, Vienna, Austria
5True North Therapeutics Inc., San Frnacisco
6Alberta Transplant Applied Genomics Centre, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Canada
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 292
Keywords: HLA antibodies, Humanized antibodies, Kidney transplantation, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Treatment of Antibody Mediated Rejection in Kidney Transplant Recipients
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, May 1, 2017
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:06pm-3:18pm
Presentation Time: 3:06pm-3:18pm
Location: E354a
Study purpose:The classical pathway (CP) of complement may significantly contribute to antibody-mediated rejection (ABMR). Blockade of CP key component C1 may be a promising strategy to counteract rejection. In this first-in-human phase 1 trial (NCT02502903), we evaluated the safety and activity of TNT009, a humanized monoclonal antibody against C1s, in late ABMR. Methods: We enrolled 10 kidney transplant recipients with late ABMR [median time to index biopsy (Bx): 4.3 yrs]. Major inclusion criteria were (i) an involvement of CP activation (capillary C4d and/or C1q/C3d-fixing DSA), (ii) a g+ptc score ≥2, and (iii) a molecular ABMR score ≥0.2. Patients received TNT009 (IV) at an initial test dose of 10 followed by 60 mg/kg at 4 weekly doses. After the last infusion, a follow-up (FU) Bx was performed. Results:TNT009 was well tolerated without SAEs. As shown in Fig.1A, median C4d scores decreased from 2 to 0 in FU-Bx (p=0.016), whereby 5 of 8 C4d+ cases turned completely negative. A limited course of treatment, however, did not affect g+ptc or molecular ABMR scores. 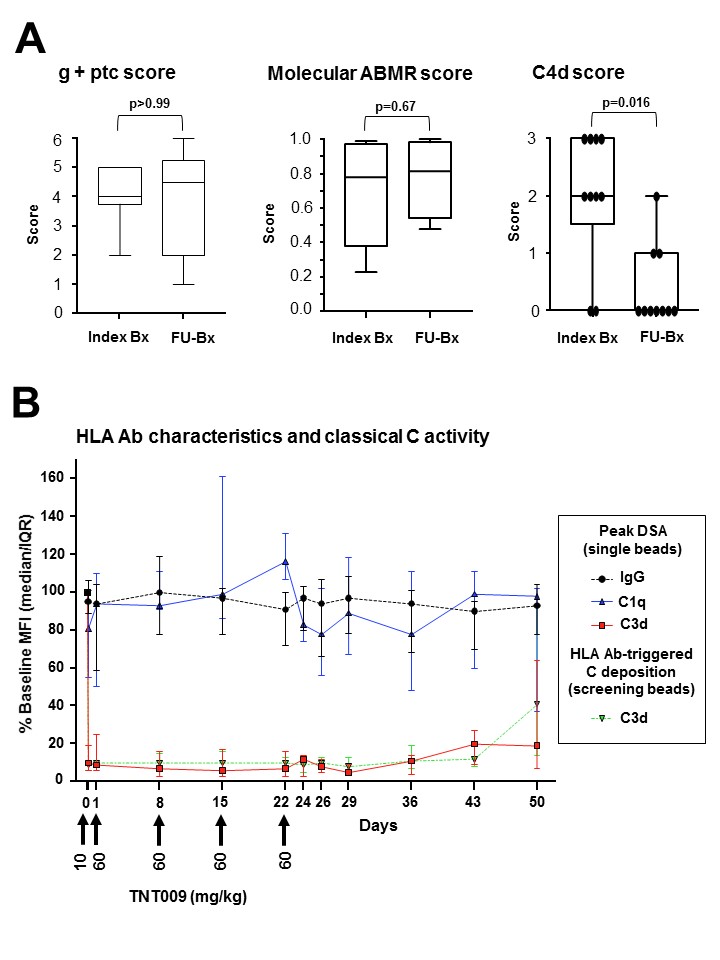 While Ab-triggered solid phase C3d fixation was profoundly inhibited (patient sera as CP source), there was no change in IgG MFI and fixation of recombinant C1q (Fig.1B). Renal parameters did not change during the study period. Conclusion:We demonstrate that TNT009 is safe and well-tolerated in transplant recipients. This trial shows that TNT009 can effectively prevent intragraft CP activation, and provides a valuable basis for future studies designed to investigate the effect of prolonged C1s blockade in the treatment of ABMR.
While Ab-triggered solid phase C3d fixation was profoundly inhibited (patient sera as CP source), there was no change in IgG MFI and fixation of recombinant C1q (Fig.1B). Renal parameters did not change during the study period. Conclusion:We demonstrate that TNT009 is safe and well-tolerated in transplant recipients. This trial shows that TNT009 can effectively prevent intragraft CP activation, and provides a valuable basis for future studies designed to investigate the effect of prolonged C1s blockade in the treatment of ABMR.
CITATION INFORMATION: Eskandary F, Jilma B, Muehlbacher J, Wahrmann M, Regele H, Kozakowski N, Panicker S, Reeve J, Halloran P, Gilbert J, Bohmig G. Safety and Activity of Anti-C1s Humanized Monoclonal Antibody TNT009 in Late Antibody-Mediated Kidney Allograft Rejection – Results of a First-in-Human Phase 1 Trial. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Eskandary F, Jilma B, Muehlbacher J, Wahrmann M, Regele H, Kozakowski N, Panicker S, Reeve J, Halloran P, Gilbert J, Bohmig G. Safety and Activity of Anti-C1s Humanized Monoclonal Antibody TNT009 in Late Antibody-Mediated Kidney Allograft Rejection – Results of a First-in-Human Phase 1 Trial. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/safety-and-activity-of-anti-c1s-humanized-monoclonal-antibody-tnt009-in-late-antibody-mediated-kidney-allograft-rejection-results-of-a-first-in-human-phase-1-trial/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
