Role of Urinary Biomarkers in RWE Clinical Paradigm
1Nephrosant, Brisbane, CA, 2NephroSant, Brisbane, CA
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 212
Keywords: Graft survival, Kidney transplantation, Rejection
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » 34 - Kidney: Acute Cellular Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney: Acute Cellular Rejection
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Monday, June 6, 2022
Session Time: 3:30pm-5:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:20pm-4:30pm
Presentation Time: 4:20pm-4:30pm
Location: Hynes Ballroom A
*Purpose: Due to heterogeneity observed in the kidney transplant population, it has been extremely challenging for traditional methods such as histopathology to predict graft outcomes. In this real-world evidence(RWE) study, we applied machine learning (ML) models to a multi-analyte urinary biomarker assay to predict whether a kidney allograft would experience a rejection episode.
*Methods: A cohort of 550 (37.5% biopsy matched) urine samples from patients across 3 renal transplant centers were used to develop a predictive ML model (scaled 0-100) to prognosticate allograft failure. Samples were collected between 1-1539 days post-transplant from allograft recipients with ages ranging from 7-77 years. Of the 206 biopsy matched samples, acute kidney allograft rejection (AR) and no-rejection (NR) phenotypes were confirmed in 136 and 70 respectively. We also evaluated the developed ML model on two additional cohorts of 15 COVID+ transplant recipients and 30 non-transplant healthy population. The ML model incorporates clinico-demographics with 6 urinary biomarkers: Clusterin, total protein, CXCL10, Creatinine, cfDNA and methylated cfDNA. Monte Carlo confidence intervals for the model incorporated biomarker assay and sample variances.
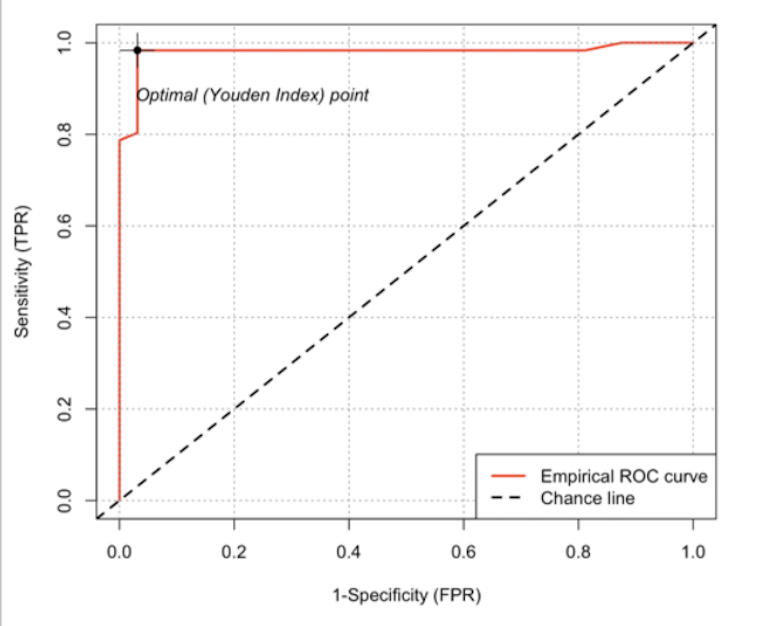
*Results: The novel rejection score was able to discriminate AR from NR efficiently. Score below 32 classified stable allograft, score range of 32 – 55 identified progression of AR, and Score > 55 identified AR with high sensitivity: 92%, and specificity: 89%; AUC: 96% and accuracy: 91%(figure). The associated NPV and PPV of 87% and 93% respectively. In the COVID cohort with 86% clinician assessed rejection, the median score was 51(IQR:30-87). In the non-transplants the median score was 19(IQR:13-26). It was established that presence of COVID was not a confounder in the model.
*Conclusions: The accuracy of the novel rejection score emphasizes the promise of applying ML algorithms as an aid to decision-making in evaluating graft outcomes with high sensitivity and specificity. Moreover, this RWE retrospective analysis demonstrates the efficacy of the urine multi-analyte approach to accurately predict acute rejection in kidney transplant recipients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yazar W, Sarwal R, Titzler N, Sarwal M, Ghosh S. Role of Urinary Biomarkers in RWE Clinical Paradigm [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/role-of-urinary-biomarkers-in-rwe-clinical-paradigm/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress