Rituximab: Summarizing the Intracacies of the Black Box Warning and Expenses in Transplantation
Department of Pharmacy, NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital, New York, NY.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D234
Keywords: Hepatitis B
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Regulatory Issues in Transplant Administration
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, May 5, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Post-transplant use of rituximab has become common, yet is associated with significant safety concerns and cost. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation following rituximab therapy poses a significant health risk and the FDA recently (Nov 2013) added a black box warning. There is a critical need to evaluate rituximab use with respect to safety and cost following solid organ transplantation (SOT).
Single-center, retrospective review of adult SOT recipients transplanted between Jan 2011 – Jun 2014 treated with rituximab. Our rituximab dosing strategy for desensitization and treatment of AMR consists of up to two doses of 375mg/m2. The primary endpoint was to determine the incidence of HBV reactivation. Secondary endpoints include patient and graft survival and financial review of rituximab use.
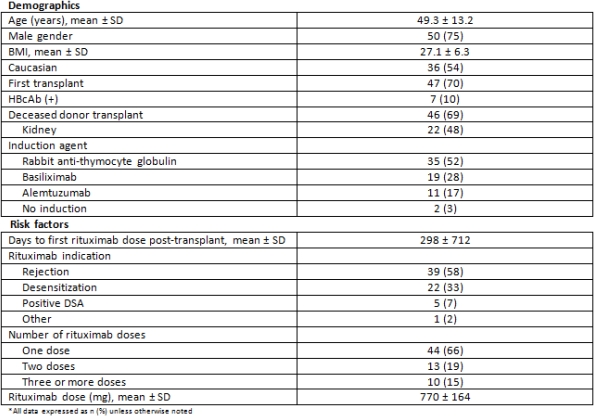
During the period of the study 67 patients were treated with rituximab; renal (64%), cardiac (16%), lung (15%), multi-organ (3%), liver (2%). Patients received an average of 1.7±1.2 of rituximab doses and the mean duration of follow-up for the cohort was 1.5years±1.0. The median time to follow-up HBV serology was 70days (43-234). To date, none of the 7 recipients at risk (HBcAb positive) experienced HBV reactivation. Graft survival was 86.5% and patient survival was 97%. Administration of rituximab in the outpatient side was associated with median revenue of $1,600 ($1300-$2700).
Despite minimal risk of HBV reactivation previous literature has suggested there is a need for standardized hepatitis-B testing following rituximab therapy. HBV serologies should be obtained 6 months after rituximab. Additionally, administration of rituximab in the outpatient setting provides opportunities for revenue generation. Integrating clinical decision making and fiscal stewardship provide cost effectiveness through outpatient therapy administration when appropriate.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jandovitz N, Lee J, Bezman M, Tsapepas D. Rituximab: Summarizing the Intracacies of the Black Box Warning and Expenses in Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/rituximab-summarizing-the-intracacies-of-the-black-box-warning-and-expenses-in-transplantation/. Accessed July 18, 2025.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
