Risk Factors for Hospitalization Among Waitlisted End Stage Renal Disease Patients.
1Emory University Rollins School of Public Health, Atlanta, GA
2Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B198
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Medicare, Risk factors, Waiting lists
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney Transplantation: KDPI, HCV/Matching, Donor Age
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 12, 2016
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Halls C&D
Background: For End Stage Renal Disease Patients (ESRD) waitlisted for a deceased donor kidney, hospitalization is associated with lower likelihood of transplantation and worse outcomes. Hospitalization for these patients may also add to higher Medicare costs. However, risk factors for hospitalization among patients waitlisted for kidney transplantation have not been investigated.
Methods: We used United States Renal Data System Medicare-linked data on waitlisted ESRD patients between 2005 and 2009 with continuous enrollment in Medicare Parts A & B (n=27,594) to examine the association between annual hospitalization rate and a variety of demographic, clinical, and social factors. We used multivariable ordinal logistic regression to estimate odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI).
Results: Nationally, factors associated with significantly increased hospitalization rates among waitlisted individuals included black race, panel reactive antibody>0, female sex, public insurance at ESRD diagnosis, years on dialysis, ESRD caused by diabetes, being underweight, and having a history of tobacco use (Table 1, all p<0.05).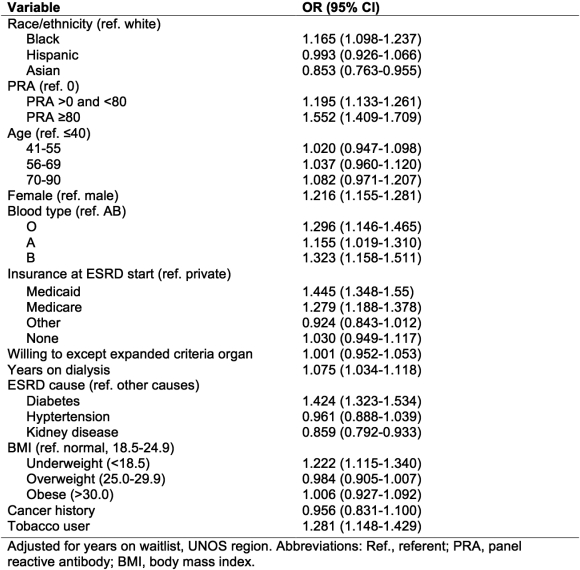 Factors associated with significantly lower hospitalization rates include Asian race and ESRD caused by kidney-specific diseases (Table 1, all p<0.05). There was also regional variation in hospitalization rates, with the lowest rates in the northwest (UNOS region 6) and the highest rates in the mid-atlantic (region 2).
Factors associated with significantly lower hospitalization rates include Asian race and ESRD caused by kidney-specific diseases (Table 1, all p<0.05). There was also regional variation in hospitalization rates, with the lowest rates in the northwest (UNOS region 6) and the highest rates in the mid-atlantic (region 2).
Conclusion: Individual-level variables are significantly associated with hospitalization while waitlisted. However, there are also regional differences in hospitalization, suggesting that system-level factors may also contribute to the risk of hospitalization.
CITATION INFORMATION: Newman K, Adams A, Pastan S, Lynch R, Zhang R, Patzer R. Risk Factors for Hospitalization Among Waitlisted End Stage Renal Disease Patients. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Newman K, Adams A, Pastan S, Lynch R, Zhang R, Patzer R. Risk Factors for Hospitalization Among Waitlisted End Stage Renal Disease Patients. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/risk-factors-for-hospitalization-among-waitlisted-end-stage-renal-disease-patients/. Accessed July 12, 2025.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
