Risk Factors Associated with Severe COVID19 Illness in Kidney Transplant Recipients
E. Abuhelaiqa, M. Alkadi, H. Tohid, R. Elidrisi, R. Abdul Rahiman, M. F. Elshirbeny, T. A. Ghonaimi, A. I. Hamad, A. Nauman, A. A Aziz, O. Fituri, M. Asim, M. A. Othman, H. Al-Malki
Hamad Medical Corporation, Doha, Qata
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 718
Keywords: Infection, Kidney transplantation, N/A, Prognosis
Topic: Clinical Science » Infectious Disease » All Infections (Excluding Kidney & Viral Hepatitis)
Session Information
Session Name: All Infections (Excluding Kidney & Viral Hepatitis)
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: COVID19 is an acute respiratory infection that is caused by the SARS-COV-2 that has been shown to be highly contagious and poses a significant mortality risk. Kidney transplant recipients are shown to be at increased risk of acquiring and developing a severe form of the disease compared to the general population. There is limited evidence to guide the transplant community on methods to reduce disease severity. We aim to evaluate risk factors associated with severe [requiring hospitalization] or critical [requiring ICU care] COVID-19 illness in kidney transplant recipients.
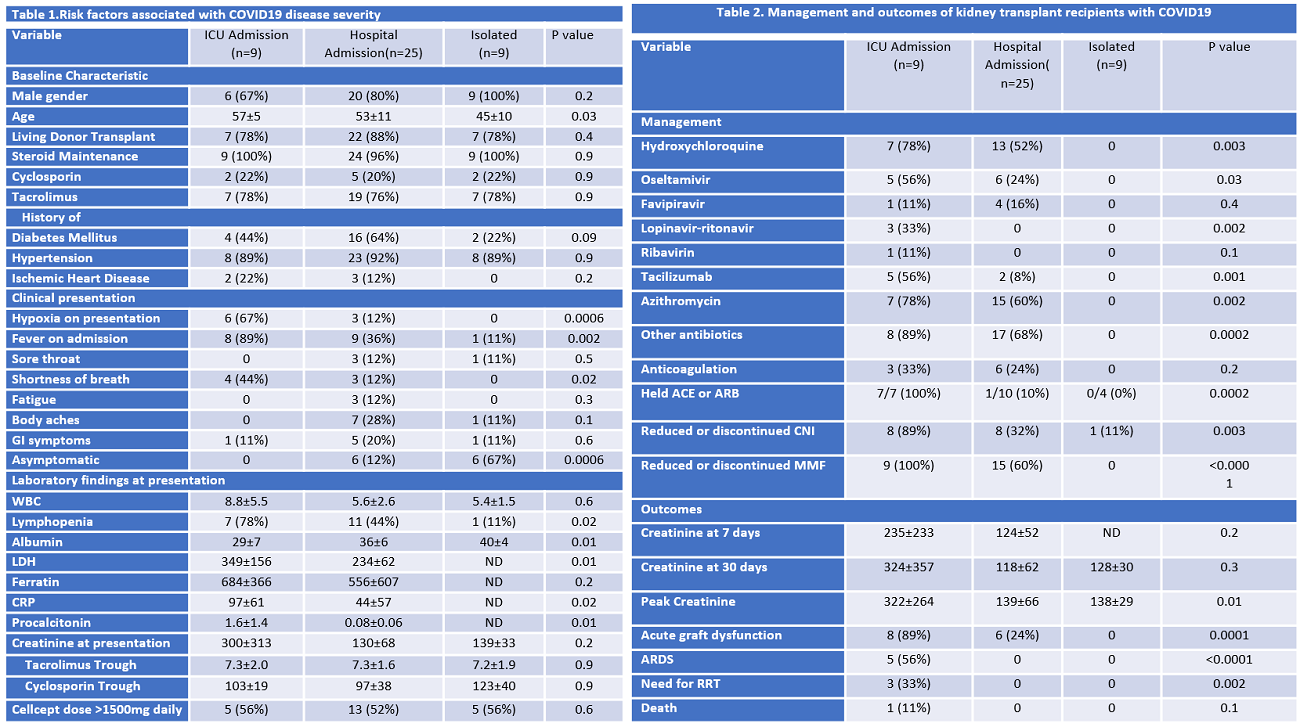
*Methods: We evaluated kidney transplant recipients with COVID19 between February to August 2020. Among 748 recipients followed at our center, 43 recipients (5.7%) were diagnosed with COVID19 infection through nasopharyngeal swab PCR. Of those, 9 patients were treated within an isolation facility, 25 patients admitted to the hospital and 9 patients were admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU). We evaluated demographic, clinical and laboratory factors to evaluate severity of illness by using Kruskal-Wallis for continuous variables and chi square test for categorical.
*Results: Older age was associated with ICU admission (57 vs. 53 vs. 45 P=0.03) while gender, ethnicity and type of transplant were similar between the three groups (Table 1). In addition, CNI level, MMF dose or base line creatinine was not significantly different between the three groups. Presentation with fever, shortness of breath and hypoxia were more frequent in ICU group. Laboratory findings of lymphopenia, low Albumin, high CRP and high procalcitonin at presentation were also more frequent in ICU group. Treatment with hydroxychloroquine, Oseltamivir, Ritonavir, Azithromycin, and reduction of immunosuppression were more frequent in ICU (table 2). We observed 14 patients with graft dysfunction and majority were in ICU group. Furthermore, in the ICU group, 3 recipients required renal replacement therapy and of those there was a single death.
*Conclusions: Severity of COVID19 infection is variable among our transplant population. Prognostication of COVID19 severity in kidney transplant recipient is crucial for early recognition of critical illness and may offer the benefit of early therapy such as antiviral or immunosuppression reduction in this high-risk
group.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Abuhelaiqa E, Alkadi M, Tohid H, Elidrisi R, Rahiman RAbdul, Elshirbeny MF, Ghonaimi TA, Hamad AI, Nauman A, Aziz AA, Fituri O, Asim M, Othman MA, Al-Malki H. Risk Factors Associated with Severe COVID19 Illness in Kidney Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/risk-factors-associated-with-severe-covid19-illness-in-kidney-transplant-recipients/. Accessed February 27, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress