Risk Analysis of Patients with Proven Coronary Artery Disease Undergoing Liver Transplant.
Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, TX
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B210
Keywords: Arteriosclerosis, Liver transplantation, Outcome, Risk factors
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Liver Retransplantation and Other Complications
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, April 30, 2017
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall D1
Objectives
Coronary artery disease is increasing common in liver transplant (LT) candidates due to the aging population. We sought to longitudinally evaluate of outcomes of LT recipients with known CAD.
Methods
Retrospective single center analysis was performed for LTs performed from 2008-14 with regards to cardiac disease, recipient demographics, and outcomes.
Results:
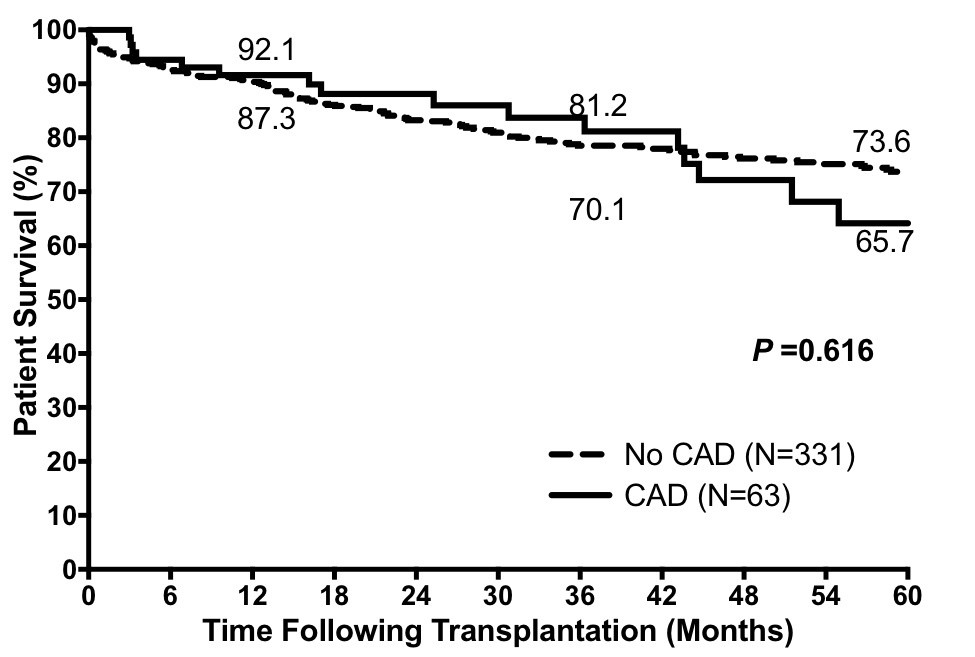
Of 394 LTs performed, 63 (16%) had a preTx diagnosis of CAD (single vessel >50% or multi-vessel disease, history of myocardial infarction (MI), stenting, or coronary artery bypass (CABG). Pts with CAD were significantly older (p<0.001) and had greater incidence of obesity (BMI>30, p=0.05) diabetes (p=0.006), hypertension (p<0.001), and renal insufficiency (CRI, p=0.05, Table). There was no significant difference in 1-, 3- and 5-yr survival of LT recipients with CAD (91.6, 88.1, & 64.1%, respectively) versus those without CAD (90.3%, 83.3%, & 73.7%, Figure; p=0.62). Pts with CAD were at greater risk of reperfusion syndrome (p=0.02) but not postTx MI (p=0.07), cardiomyopathy (p=0.84), or cardiac-related death (p=0.43).
| No CAD (n=331) | CAD (n=63) | p-value | |
| Age (yrs) | 67 (22-77) | 62 (45-75) | <0.01 |
| Male | 203 (61%) | 47 (75%) | <0.01 |
| BMI>30 | 114 (34%) | 30 (48%) | 0.05 |
| Lab MELD>35 | 128 (39%) | 23 (37%) | 0.75 |
| Diabetes | 99 (30%) | 30 (48%) | <0.01 |
| HTN | 139 (42%) | 50 (79%) | <0.01 |
| CHF | 9 (9%) | 13 (22%) | <0.01 |
| CRI (GFR<30) | 59 (18%) | 18 (29%) | 0.05 |
| CABG | 0 (0%) | 5 (9%) | <0.01 |
| PCI | 0 (0%) | 12 (21%) | <0.01 |
| Reperfusion Syndrome | 3 (0.9%) | 2 (3.2%) | 0.02 |
| Post Tx Cardiomyopathy | 1 (0.3%) | 0 (0%) | 0.84 |
| PostTx MI | 1 (0.3%) | 2 (3.2%) | 0.07 |
Pts with CAD demonstrate equivalent survival to those without known CAD; however, they are at increased risk for peri-operative cardiac complications. With proper preTx stratification and intervention, pre-existing CAD should not preclude LT.
CITATION INFORMATION: Balogh J, Lunsford K, Nguyen D, Gravis E, Cercio O, Mobley C, Saharia A, Gordon Burroughs S, Gaber A, Ghobrial R. Risk Analysis of Patients with Proven Coronary Artery Disease Undergoing Liver Transplant. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Balogh J, Lunsford K, Nguyen D, Gravis E, Cercio O, Mobley C, Saharia A, Burroughs SGordon, Gaber A, Ghobrial R. Risk Analysis of Patients with Proven Coronary Artery Disease Undergoing Liver Transplant. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/risk-analysis-of-patients-with-proven-coronary-artery-disease-undergoing-liver-transplant/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress