Renal Transplantation in Patients Older Than 60 Years with High Comorbidity. Is There a Survival Benefit? A Multicenter Study in Argentina
1Nephrology, Hospital Universitario Austral, Derqui, Argentina, 2Nephrology, CEMIC, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 3INCUCAI, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 4Fundacion Favaloro, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 5Hospital Britanico de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 6Clinica Velez Sarsfield, Cordoba, Argentina, 7Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 8Crai Sur, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 9Hospital Privado Universitario de Cordoba, Cordoba, Argentina, 10Hospital Privado Universitario de Cordoba, Buenos Aires, Argentina
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A222
Keywords: Age factors, Kidney transplantation, Survival, Waiting lists
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Kidney Deceased Donor Allocation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 1, 2019
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: The impact of renal transplantation (RT) in the elderly with comorbid conditions is a matter of concern. Our aim was to assess the impact of RT on the survival of patients older than 60 years compared with those remaining on the waiting List (WL) according to their comorbidities. Then we evaluated the impact of comorbidities on graft and patient survival after RT.
*Methods: Muticentric observational retrospective cohort study including all patients older than 60 years admitted on the renal WL from 01/01/2006 to 31/12/2016. Patients were followed on the WL and after RT until their death or last follow up on 30/04/2018. The Charlson comorbidity index (CCI) score was calculated for each patient at inclusion on the WL. KDRI (Kidney donor risk index) was used to assess donor characteristics
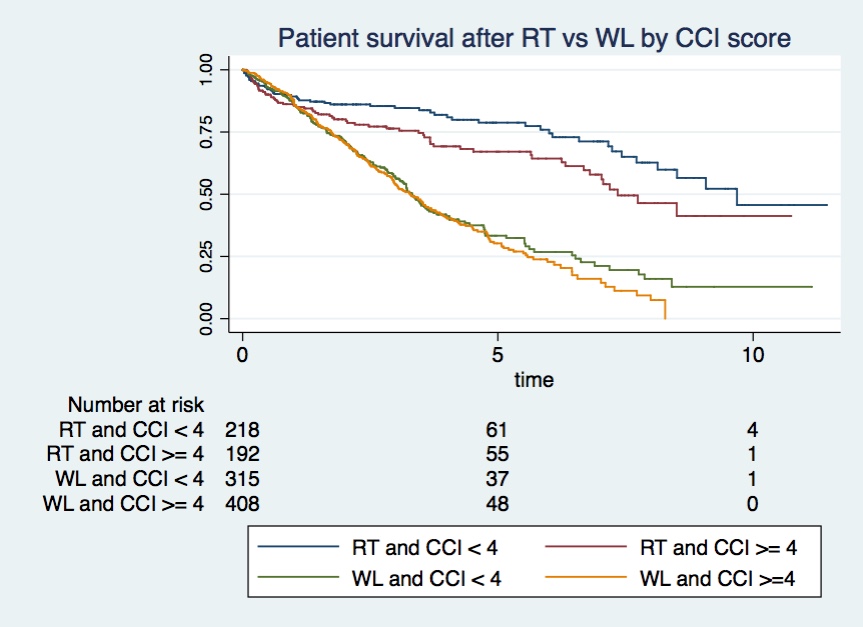
*Results: 1132 patients were included on the WL, 410 (36%) received a RT during a mean follow up period of 3 ± 2.25 years. Mean CCI was 4,23± 2,11. CCI was higher in patients on the WL vs those who received a RT (4,42±2,20 vs 3,89±1,89 p<0,0001). Patients survival was higher after RT compared to patients on the WL, 88%, 80%, 73% vs 87%, 55% y 31% at 1, 3 and 5 years respectively (log-rank 0,0001). After adjusting for CCI, RT had protective effect on patient’s survival (HR 0,35 IC 0,28-0,43 p<0,001). After RT survival at 5 years was 37% higher for patients with CCI ≥4, and 46% higher in those with CCI <4, compared with patients on the WL. CCI did not affect graft survival. Patient’s survival 5 years after RT was 79% in those with CCI <4 and 67% in those with CCI ≥4 (log-rank 0, 02). Patient survival after RT was independently associated with HLA mismatch (HR 1.13 IC 1,02-1.29 p<0,045) and CCI ≥4 (HR 1.48 IC 1,03-2.14 p<0,036).
*Conclusions: Our study showed that RT improved survival in patients older than 60 years even those with high comorbidities. To a lesser extent survival after transplantation was also affected by comorbidities.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fragale GD, Laham GA, Bisignano L, Antik A, Raffaele PM, Fortunato M, Trimarchi H, Pomeranz V, Maldonado R, Matamala N, Imperiali NC, Giordani MC, Taylor MF, Ciappa JM, Naser S, Pujol GSoler. Renal Transplantation in Patients Older Than 60 Years with High Comorbidity. Is There a Survival Benefit? A Multicenter Study in Argentina [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/renal-transplantation-in-patients-older-than-60-years-with-high-comorbidity-is-there-a-survival-benefit-a-multicenter-study-in-argentina/. Accessed March 5, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress