Refill-Based Immunosuppression Non-Adherence Is Associated with Increased Death Censored Graft Loss.
Medicine, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A224
Keywords: Graft survival, Immunosuppression, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Long Term Outcomes in Kidney Transplantation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 11, 2016
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Halls C&D
Introduction
Medication non-adherence is a major contributor of graft loss in kidney transplant(KTX) recipients. We aim to evaluate the association of immunosuppression non-adherence to graft loss, via dispensing record auditing of a centralized pharmacy model in a single transplant centre.
Methods
For all KTX recipients followed at our transplant centre, available records for dispencing of calcineurin-inhibitor were obtained. The difference between days of medications supplied and the refill intervals were calculated as percentage medications missed. Medication non-adherence were categorized into tertiles based on percentage medications missed. Time-to-event analysis for death-censored graft loss was performed by Kaplan-Meier curve and log rank test. Cox proportional hazard modeling was performed to examine the magnitude graft loss risk for each percent increase in medications missed.
Results
Dispensing records were available for 1586 KTX recipients transplanted between 1977-2014. Median follow up time period was 3178 days. The mean percentage medications missed was -4.9%(SD 25.8%). 40.1% had more than zero percent missed days. By assuming those with negative percentage missed days to be zero percent, the tertiles of non-adherence were zero percent, zero to 3 percent and great than 3 percent missed days. Kaplan Meier curves demonstrates that the third tertile of non-adherence had significant decreased median death censored graft survival of 9326 days vs 10101 days (p<0.001)(Fig 1A). Comparing with perfect adherence, KTX recipients with any missed days had decreased death censored graft survival(Fig 1B). Hazard ratio for is 1.005 for each percentage increase in medications missed. 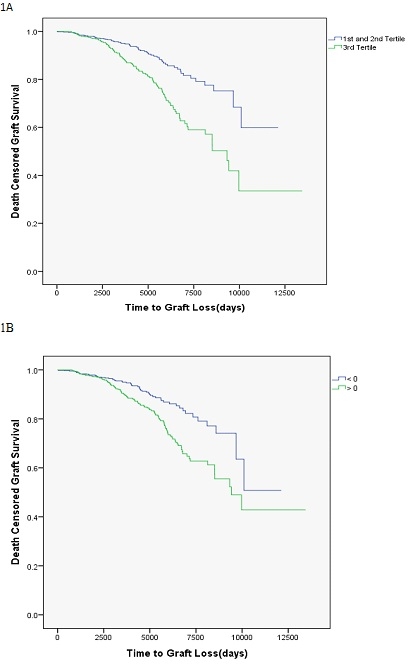
Conclusions
Centralized dispensing pharmacy model allows medication non-adherence which is associated increased risk of graft loss over time. This allows early identification of non-adherence, which may facilitate target resource intensive patient specific strategies to improve adherence and graft outcomes.
CITATION INFORMATION: Wen K, Gourishankar S, Shojai S, Wong A, Bae M, Grynoch D, Halloran P. Refill-Based Immunosuppression Non-Adherence Is Associated with Increased Death Censored Graft Loss. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wen K, Gourishankar S, Shojai S, Wong A, Bae M, Grynoch D, Halloran P. Refill-Based Immunosuppression Non-Adherence Is Associated with Increased Death Censored Graft Loss. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/refill-based-immunosuppression-non-adherence-is-associated-with-increased-death-censored-graft-loss/. Accessed February 25, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
