Pushing the Limits: A Large Multicentric Case-Control Study Evaluating the Impact of Kidney Transplants from Expanded Criteria Donors after Controlled Circulatory Death the Limits: A Large Multicentric Case-Control Study Evaluating the Impact of Kidney Transplants from Expanded Criteria Donors after Controlled Circulatory Death
1Kidney Transplantation Unit, Vall d'Hebron University Hospital, Barcelona, Spain, 2Kidney Transplantation Unit, Bellvitge University Hospital- IDIBELL, L'Hospitalet de Llobregat. Barcelona, Spain, 3Kidney Transplantation Unit, Puigvert University Hospital, Barcelona, Spain, 4Kidney Transplantation Unit, Clinic University Hospital, Barcelona, Spain
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B151
Keywords: Cadaveric organs, Donors, marginal, Donors, non-heart-beating, Graft failure
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney Donor Selection / Management Issues
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: Controlled donation after circulatory death (cDCD) has allowed to significantly increase the deceased donors pool. However, while excellent previous reports have been shown using cDCD younger than 65-years old, there is no robust data supporting the same outcomes among extended-criteria (ECD) cDCD. The aim of this study was to evaluate in a cohort of kidney transplant (KTx) patients from 4 centres in Barcelona (Spain), KTx outcomes of cDCD and brain death donors (DBD) stratified according to ECD characteristics.
*Methods: In this retrospective analysis we included all consecutive KTx patients from deceased donor since the initiation of the cDCD program in each Hospital, until march 2017 (n=992). Donor types were classified in 4 categories: DBD of standard or extended criteria (DBD-SCD; DBD-ECD) and cDCD of standard or extended criteria (DCD-SCD; DCD-ECD). Mean follow-up: 39±21 months. Main outcomes were allograft and patient survival as well as 1 year kidney graft function.
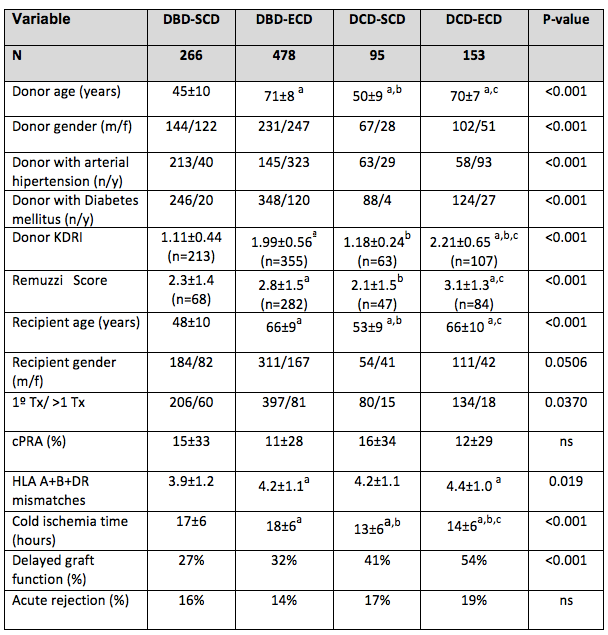
*Results: Out of the 992 kidney transplants performed during the study period, 248(25%) were cDCD transplants. In Figure 1, donors and recipients’ characteristics are described. Mean 1 and 3-years graft survival were: 93% and 91% for DBD-SCD; 88% and 82% for DBD-ECD; 90% and 86% for DCD-SCD and 74% and 67% for DCD-ECD (Log Rank p<0.001). Primary non-function or graft thrombosis were causes of graft loss in 2.6%, 3.7%, 3.1% and 7.8%, respectively (p<0.001), and patient’s death in 1.5%, 7.5%, 4.2% and 15% (p<0.001). eGFR (MDRD-4) at 1 year was 59±21 ml/m/1.73m2 in DBD-SCD; 43±16 ml/m/1.73m2 in DBD-ECD, 55±22 ml/m/1.73m2 in DCD-SCD and 40±13 ml/m/1.73m2 in DCD-ECD (p<0.001). Graft and patient survival after the 1st year was comparable across groups (data not shown).
*Conclusions: In this large cohort of KTx patients DCD-ECD patients showed worse patient and graft outcome as compared to all other groups. This data has to be taken with caution and should be balanced with patient death probability while remaining on dialysis therapy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Toapanta N, Alvarez R, Lluís G, Facundo C, Diekmann F, Revuelta I, Meneghini M, Moreso F, Bestard O. Pushing the Limits: A Large Multicentric Case-Control Study Evaluating the Impact of Kidney Transplants from Expanded Criteria Donors after Controlled Circulatory Death the Limits: A Large Multicentric Case-Control Study Evaluating the Impact of Kidney Transplants from Expanded Criteria Donors after Controlled Circulatory Death [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/pushing-the-limits-a-large-multicentric-case-control-study-evaluating-the-impact-of-kidney-transplants-from-expanded-criteria-donors-after-controlled-circulatory-death-the-limits-a-large-multicentri/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress