Prospective Investigation of the Reliability and Validity of the Live Donor Assessment Tool (LDAT).
D. LaPointe Rudow, A. Shenoy, J. Hunt, Z. Filipovic-Jewell, B. Haydel, B. Iacoviello.
Recanati Miller Transplantation Institute, Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, NY.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C160
Keywords: Kidney, Liver, Living-related liver donors, Psychosocial
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Kidney Donor Evaluation and Donor Nephrectomy
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 13, 2016
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Halls C&D
Purpose: The LDAT was the first psychosocial assessment instrument developed to standardize the live donor (LD) psychosocial evaluation (PsychE). Previously, it was found to be reliable and valid in yielding results similar to our current psychosocial evaluation in retrospective chart review. We conducted the current study to prospectively replicate LDAT inter-rater reliability and validity.
Methods: The LDAT tool assesses motivation, knowledge of and expectations for LD, support, closeness to the recipient, feelings about donation, stability in life and psychiatric and addiction history. All LDs completing an evaluation in 2015 underwent the traditional semi structured PsychE and were administered the LDAT. We assessed inter-rater reliability between the social worker and psychiatrist by calculating Pearson's correlation coefficient for LDAT scores assigned by each rater. Validity was assessed by comparing LDAT scores to PsychE outcomes (e.g., overall psychosocial risk level assessment).
Results: 174 LDs completed the evaluation (38 Liver, 136 Kidney). Mean age was 40.8 years (range 19 – 68). 78 LDs were male, 96 female. The LDAT exhibited strong and significant inter-rater reliability in 90 donors with 2 LDAT's: r = .627, p< .0001. ANOVA analysis indicated significant differences in mean LDAT scores between the psychosocial risk groups (declined [n=10; LDAT=52.3], high risk [n=3; LDAT=56.2], medium risk [n=84; LDAT=63.74], and low risk [n=77; LDAT=69.77]; F(3,170) = 41.21, p< .0001). Follow-up analyses indicated significant differences in LDAT score between all groups except the declined and high risk groups. 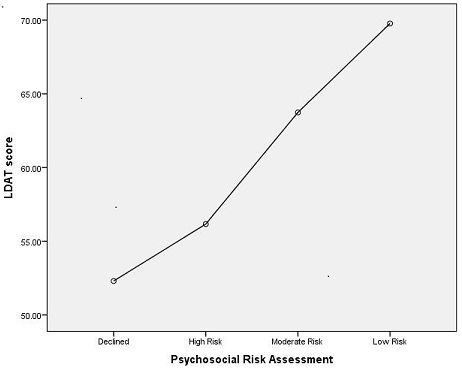
Conclusion: The LDAT shows strong promise as a quantitative index of LD psychosocial risk. It is a useful tool to standardize determination of psychosocial suitability for LD between different providers at the same transplant center. In this study, LDAT scores were significantly associated with the LD evaluation outcome. Investigation of LDAT associations with post-donation outcomes, and replication of LDAT inter-rater reliability and validity across sites, is warranted.
CITATION INFORMATION: LaPointe Rudow D, Shenoy A, Hunt J, Filipovic-Jewell Z, Haydel B, Iacoviello B. Prospective Investigation of the Reliability and Validity of the Live Donor Assessment Tool (LDAT). Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rudow DLaPointe, Shenoy A, Hunt J, Filipovic-Jewell Z, Haydel B, Iacoviello B. Prospective Investigation of the Reliability and Validity of the Live Donor Assessment Tool (LDAT). [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/prospective-investigation-of-the-reliability-and-validity-of-the-live-donor-assessment-tool-ldat/. Accessed February 27, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
