Properties of Regulatory B Cells Suppressing B Cells
1Organ Transplantation Center, Sichuan Provincial People's Hospital, University of Electronic Sciences and Technology of China, Chengdu, China, 2Center for Transplantation Sciences, MGH, Boston, MA
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 516
Keywords: B cells
Session Information
Session Name: B-cell / Antibody /Autoimmunity
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Our previous study showed that TLR-Bregs, regulatory B cells generated in vitro through TLR activation, suppressed naïve B cell proliferation triggered by a mitogen (LPS-B cells). The mechanism underlying Breg suppression is presently unknown. The present study on batch and single-cell RNAseq analyses of suppressed LPS-B cells and suppressive TLR Bregs provide important insights on pathways associated with suppression.
*Methods: TLR-Bregs were generated from enriched C57BL/6 splenic CD19+B cells cultured in the presence of CpG ODN1668 for 3 days (CpG-B cells), followed by the addition of LPS (10ug/ml), PMA (50ng/ml), and ionomycin (1ug/ml) for the last 5 hours. Suppression was measured in 3 day-cocultures of TLR-Bregs and naïve B cells stimulated with LPS (LPS-B cells). B cell proliferation/ differentiation was assessed by flow cytometry. RNAseq analysis was performed on naive B, CpG-B cells, and TLR-Bregs. RNA-Seq data of the LPS-B cells (LPS-B24h and LPS-B72h) and TLR-Bregs were analyzed using R programming (version 3.6.3). Gene Ontology (GO) was used to perform enrichment analysis on differentially expressed genes (DEGs).
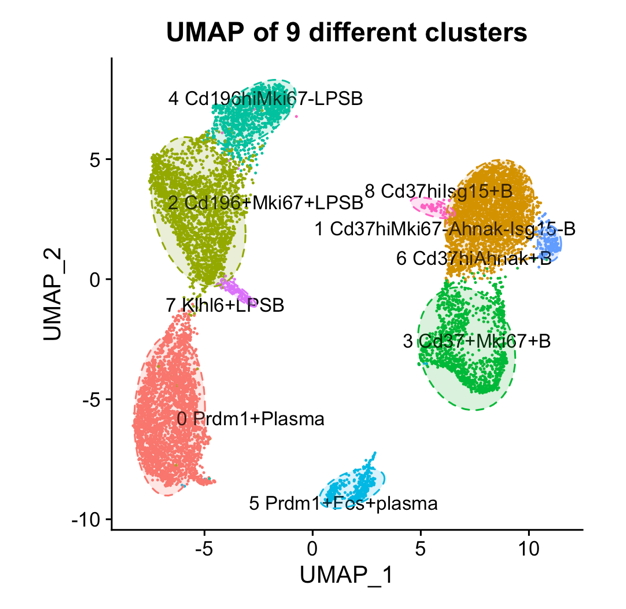
*Results: Co-DEGs among those LPS-B cells identified 23 and 6 genes with up or down-regulation of expression among LPS-B72h, LPS-B24h, and naive B cells. Among those 29 genes, 17 were also differentially expressed in TLR-Bregs in comparison with CpG-B and naive B cells. Go pathway analysis for these 17 co-genes found that Il10, Prdm1, and Il2ra (CD25) were positively enriched in B cell proliferation. Among those three genes, Il10 and Il2ra both increased in LPS-B cells and TLR-Bregs while Prdm1 increased in LPS-B cells and decreased in TLR-Bregs. Flow cytometry revealed that TLR-Bregs, but not CpG-B cells, inhibited Prdm1 expression. The scRNA-seq analysis suggested clusters 0, 2, 5, and 7 were proliferated B cells after LPS stimulation (Figure 1). Clusters 0 and 5 also highly-expressed Prdm1 and Sdc1, which were identified as plasma cells. These combined results indicated that TLR-Bregs suppressed clusters 0, 2, 5, and 7 and eventually suppressed proliferation and differentiation of LPS-B cells.
*Conclusions: TLR-Bregs can suppress the proliferation and differentiation of naïve B cells induced by LPS. The suppression of Prdm1 may indicate that the mechanism for which TLR-Bregs suppress other B cells lies in the Prdm1-relevant pathway.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fu Q, Lee K, Deng K, Huai G, Rickert C, Yang H, LeGuern C, Deng S, Markmann JF. Properties of Regulatory B Cells Suppressing B Cells [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/properties-of-regulatory-b-cells-suppressing-b-cells/. Accessed February 27, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress