Prevention of the Progression in Chronic Calcineurin Inhibitors Nephrotoxicity via Steroids Anti-Inflammatory Effects
1Hokkaido Univercity, Sapporo, Japan, 2Sapporo City General Hospital, Sapporo, Japan, 3Jichi Medical University, Shimotsuke, Japan
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1687
Keywords: FK506, Inflammation, Kidney, Nephrotoxicity
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » 38 - Kidney Immunosuppression: Novel Regimens and Drug Minimization
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney Immunosuppression: Novel Regimens and Drug Minimization
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Tuesday, June 7, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
Session Information
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Location: Hynes Hall C
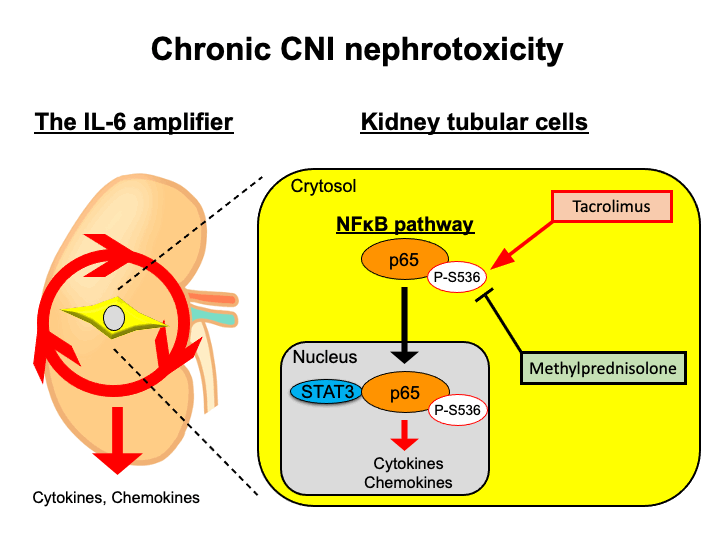
*Purpose: Calcineurin inhibitors (CNI) lead to an excellent short-term kidney allograft outcome. However, chronic nephrotoxicity is a major concern, which affects a long-term allograft survival. We have previously reported that a hyper NFκB activating machinery in non-immune cells, called the IL-6 amplifier. The IL-6 amplifier is induced by a coactivation of NFκB and STAT3, and this activation induces various inflammatory factors and can develop chronic inflammation diseases. We here investigated whether tacrolimus (TAC) can activate IL-6 amplifier and steroid can suppress it to understand the pathogenesis of chronic CNI nephrotoxicity.
*Methods: A total of 186 transplant recipients received a TAC as induction and maintenance immunosuppression. They were divided into steroid early withdrawal group (SEW: steroid was withdrawn at 3 days after transplantation) and steroid continuous group (Control: daily 2 or 4 mg of methylprednisolone [MP]). We compared histological findings at 1, 3, and 5 years protocol biopsies between 2 groups. Next, biopsy samples were analyzed by immunohistochemistry and investigated by RNA sequencing. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction, confocal microscopy, and western blotting were performed to investigate the activation of IL-6 amplifier in TAC and the action of MP.
*Results: Alternative arteriolar hyalinosis score (aah) increased over time in both groups. Moreover, we found that aah score at 5 years protocol biopsies was significantly higher in SEW compared to Control group. Furthermore, biopsy samples obtained from SEW at 5 years showed higher coactivation of IL-6 amplifier activation (ie. the activation of NFκB p65 and STAT3) in kidney tubular cells but not in glomerulus. Consistently, RNA sequence experiments showed that IL-6 and NFκB related genes were increased more among SEW group. In vitro experiments showed that TAC enhanced the IL-6 amplifier activation and those increasement was suppressed by MP. Mechanistically, TAC enhanced a nuclear localization of NFkB p65, while MP suppressed it. Consistently, phosphorylation of NFkB p65 at serin 536 was increased by TAC, while it was suppressed by MP.
*Conclusions: Our analysis suggested that chronic CNI nephrotoxicity was one of inflammation status in kidney allografts. Moreover, steroids suppress this inflammation and prevent the progression of chronic CNI nephrotoxicity.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Iwahara N, Hotta K, Tanaka Y, Takahashi I, Hasebe R, Okada H, Tsuji T, Takada Y, Higuchi H, Sasaki H, Tanabe T, Iwami D, Shinohara N, Murakami M. Prevention of the Progression in Chronic Calcineurin Inhibitors Nephrotoxicity via Steroids Anti-Inflammatory Effects [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/prevention-of-the-progression-in-chronic-calcineurin-inhibitors-nephrotoxicity-via-steroids-anti-inflammatory-effects/. Accessed February 28, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress