Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome (MetS) and Insulin Resistance in Living Kidney Donors
I. Agboli, L. Moore, D. Nguyen, E. Graviss, H. Ibrahim, A. Gaber, A. Sadhu.
Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, TX.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D183
Keywords: Donation, Kidney transplantation, Metabolic disease
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Kidney Living Donor: Selection
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, June 5, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Living kidney donors (LD) are routinely evaluated for components of MetS such as diabetes (T2D), hypertension (HTN), and hyperlipidemia (HLD). MetS is associated with T2D, HTN, HLD and higher cardiovascular risk in the general population, however, its prevalence in LD is unknown. Likewise, it is unclear if MetS at donation has long term consequences. Therefore, we aimed to characterize our kidney donor population and identify the demographic and clinical characteristics associated with MetS.
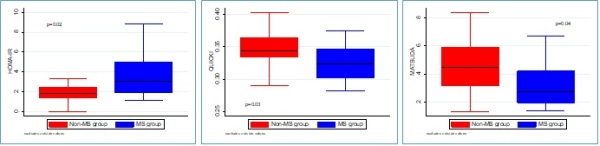
MetS was defined by NCEP ATP III 2005 criteria with substitution of the waist circumference with ethnic specific BMI. In a subpopulation where OGTT was available, beta cell function and insulin resistance were calculated using HOMA IR, HOMA B, area under the ROC curve for glucose and insulin, QUICKI, and Matsuda indices. Between 2009 and 2016, there were a total of 389 living kidney donors of which 17 were excluded due to incomplete data. Of the remaining 372, 52 (14.0%) donors met the criteria for MetS. Those with MetS were found having higher weight, BMI, systolic blood pressure, median fasting glucose, fasting glucose ≥100 mg/dl, TG ≥ 150 mg/dl, median LDL, and a lower median HDL. However, there was no significant difference in median A1C. Of all the LD in our dataset, 78.5% had ≥1 component of MetS. Additionally, 52 LD also had an OGTT to further evaluate beta cell function and insulin resistance. In this subgroup, 15 had MetS. Those with MetS also had a 63% higher HOMA IR and lower QUICKI and Matsuda indices, all of which are consistent with increased insulin resistance and propensity for progression to T2D (Fig 1). This data demonstrates that MetS is common in kidney donors. Future studies should be aimed at following LD with MetS for long term outcomes.
CITATION INFORMATION: Agboli I., Moore L., Nguyen D., Graviss E., Ibrahim H., Gaber A., Sadhu A. Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome (MetS) and Insulin Resistance in Living Kidney Donors Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Agboli I, Moore L, Nguyen D, Graviss E, Ibrahim H, Gaber A, Sadhu A. Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome (MetS) and Insulin Resistance in Living Kidney Donors [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/prevalence-of-metabolic-syndrome-mets-and-insulin-resistance-in-living-kidney-donors/. Accessed March 6, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress