Pretransplant microRNAs in Liver Perfusate Associate with Early Allograft Dysfunction
University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1304
Keywords: Liver grafts, Preservation solutions
Topic: Basic Science » Basic Science » 16 - Biomarkers: -omics and Systems Biology
Session Information
Session Name: Biomarkers: -omics and Systems Biology
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Monday, June 6, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: Early allograft dysfunction (EAD) in liver transplantation (LT) is associated with poor long-term graft and patient survival. Prior to LT, while organs are stored or reperfused, they release uniquely packed EVs in response to ischemic conditions. Capturing the spill of EV-derived miRNAs into perfusate will allow for a better understanding of the early stress signals that culminate in EAD.
*Methods: Perfusate was collected from 24 LT patients. EVs were quantified using TRPS and Imaging Flow Cytometry. Total RNA was isolated using the miRNeasy Micro Kit (Cat # 74004). MiRNA expression was evaluated using Human miFinder miScript miRNA PCR arrays (MIHS-116Z) which include 84 of the most abundantly expressed miRNAs and 12 control wells. To identify the differentially expressed miRNAs, ΔΔCt values were calculated by performing global normalization of each plate. In silico prediction of miRNA targets was done using the top 100 genes from miRDB and gene lists were analyzed using Metascape. EAD was defined by the presence of one or more of the following 1) total bilirubin ≥ 10 mg/dL or INR ≥ 1.6 on day 7, and/or 2) ALT or AST > 2,000 IU/L within the first 7 days.
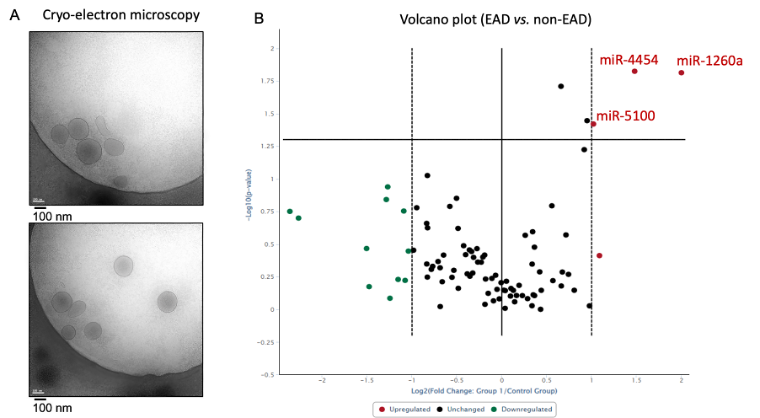
*Results: Using 600μl of perfusate, we were able to recover an average of 1.5×108 EVs (images in Fig 1A). Three miRNAs (miR-1260a, miR-4454, miR-5100) were found to be overexpressed (p<0.05, FC≥2; Fig 1B) in the perfusate of LT patients who experienced EAD (n=4) compared to those grafts which functioned normally (n=20). MiRNAs were associated with metabolic processes and DNA repair (Table 1). No donor/recipient characteristics were statistically significant between groups (including age, race, and cold ischemia time), except the MELD score, which was significantly lower in the EAD patients (p=0.006).
*Conclusions: Perfusate miRNAs can function as specific, noninvasive measures assessing risk of EAD, even in the absence of significant clinical characteristics. Such findings can elucidate the pretransplant tissue responses that influence long-term outcomes, and may ultimately guide posttransplant management.
| miRNA | Fold Change | p-value | Predicted functions |
| miR-1260a | 4 | 0.0154 | Apoptotic processes, negative regulation of cell motility, regulation of DNA repair, cell cycle |
| miR-4454 | 2.8 | 0.0150 | Metabolic processes, ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic processes |
| miR-5100 | 2.1 | 0.0380 | Metabolism of lipids, regulation of response to DNA damage stimulus, chromatin organization |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bardhi E, Williams E, McDaniels J, Rousselle T, Mas V, Maluf D. Pretransplant microRNAs in Liver Perfusate Associate with Early Allograft Dysfunction [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/pretransplant-micrornas-in-liver-perfusate-associate-with-early-allograft-dysfunction/. Accessed March 6, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress