Predictors of Estimated GFR and Recurrent Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) after Simultaneous Liver and Kidney Transplantation (SLKT): Results from the US Multicenter SKLT Consortium
1Michigan Medicine, Ann Arbor, MI, 2UCSD, San Diego, CA, 3Duke, Durham, NC, 4UCLA, LA, CA, 5University of Washington, Seattle, WA, 6Westchester Medical Center, Weschester, NY, 7Columbia, New York, NY, 8UCSF, San Francisco, CA, 9Northwestern, Chicago, IL
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 259
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Liver transplantation, Outcome
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney Issues in Liver Transplantation
Session Type: Oral Abstract Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:45pm
 Presentation Time: 3:39pm-3:51pm
Presentation Time: 3:39pm-3:51pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: SLKT is a life-saving intervention for patients with decompensated cirrhosis and concomitant end stage renal disease, irreversible acute kidney injury and select inherited metabolic disorders. However, recurrent CKD is common, and factors that impact long-term eGFR after SLKT are not well studied.
*Methods: The US Multicenter SLKT consortium consists of candidate, donor and recipient data on all adult (≥18yrs) recipients of SLKT performed at six large US centers in 6 different UNOS regions between 2/29/2002-6/30/17. eGFR was calculated at 1-, 3- 5-yrs post-transplant and at the end of follow-up using MDRD-4 equation. Multivariable linear regression was used to identify the predictors of eGFR at the last follow up. Kaplan-Meier analysis was used to determine the cumulative incidence of stage 4-5 CKD.
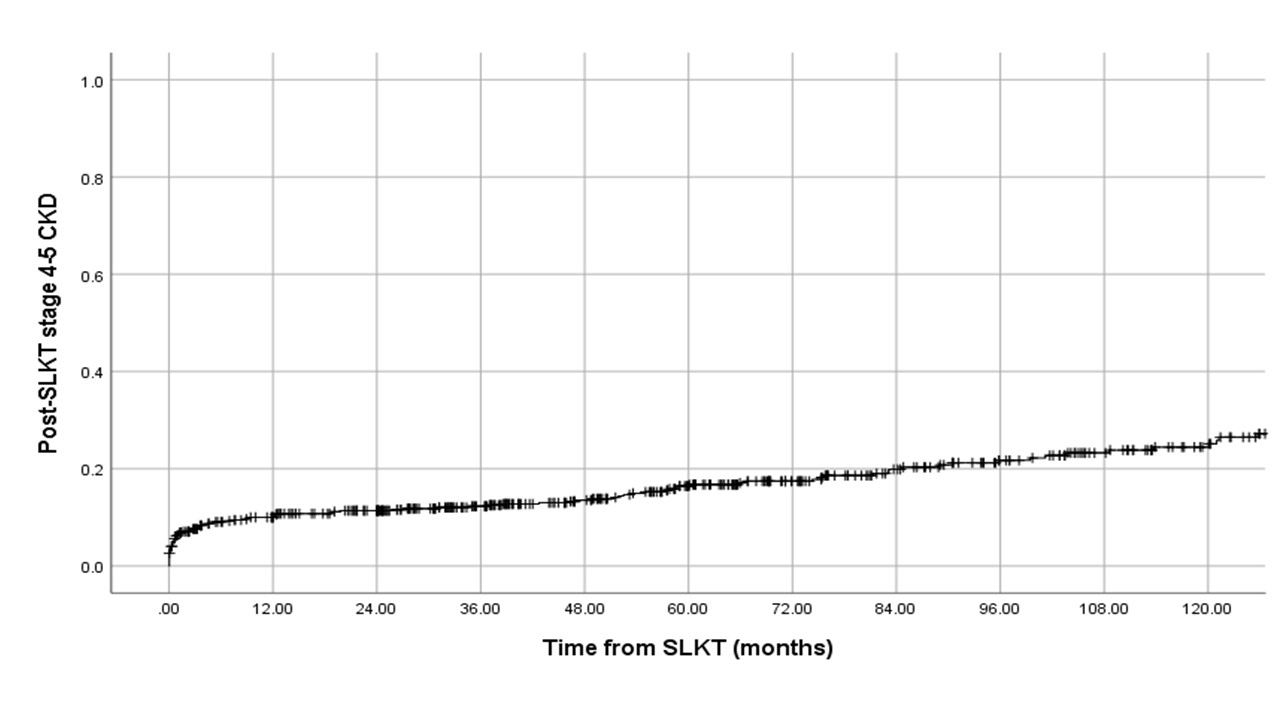
*Results: Median age of the cohort (N=570) was 58yrs, 63% male, 76% Caucasian, 33% hepatitis C, 20% NASH cirrhosis, 23% alcoholic liver disease. Median MELD-Na at SLKT was 28 (IQR:23-34). Only 39% were on renal replacement therapy(RRT) at SLKT. Median eGFR after the median follow-up of 63 months (IQR:28.2-11.7) was 54ml/min (IQR:33-65) with 68% eGFR≤60ml/min at last follow-up. One hundred and twenty (21%) developed stage 4-5 CKD at the last follow-up, with a crude rate of 3.8 per 100 patient-years. Female sex (β=-6.22ml/min,P=0.004), NASH (β=-7.26;p=0.026), delayed graft function (β=-7.25;P=0.007) and donor age (β=-0.35/year;P<0.0001) were significantly associated with low eGFR at last follow-up. Cumulative incidence of post-SLKT stage 4-5 CKD at 1-,3-,5- and 10-year was 10%, 12%, 16% and 25% (Figure 1). Post-transplant patient mortality was significantly higher in those with post-SLKT stage 4-5 CKD compared to those without (55%vs.25%;P<0.001).
*Conclusions: Recurrent CKD following SLKT impacts most patients, with two-thirds developing stage 3 or higher. Female sex, NASH, delayed graft function and advanced donor age were associated with significant reduction in eGFR. Further studies are needed to identify the role of personalized renal sparing strategies based upon sex and liver disease in preserving renal function among SLKT recipients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sharma P, Sui Z, Zhang M, Magee J, Barman P, Patel Y, Walters K, Biggins S, Schluger A, Cullaro G, Wong R, Lai J, Jo J, Sinha J, VanWagner L, Verna E. Predictors of Estimated GFR and Recurrent Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) after Simultaneous Liver and Kidney Transplantation (SLKT): Results from the US Multicenter SKLT Consortium [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/predictors-of-estimated-gfr-and-recurrent-chronic-kidney-disease-ckd-after-simultaneous-liver-and-kidney-transplantation-slkt-results-from-the-us-multicenter-sklt-consortium/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress