Prediction of 90 Days Readmission after Kidney Transplantation Including Natural Language Processing
1Department of Surgery, Emory University, Atlanta
2Department of Epidemiology, Emory University, Atlanta
3Emory Transplant Center, Emory Healthcare, Atlanta
4School of Medicine, Emory University, Atlanta
5Department of Pediatrics, Emory University, Atlanta
6Rollins School of Public Health, Emory University, Atlanta.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C168
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Methodology, Prediction models
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Kidney Technical
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 4, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Early identification of hospital readmission for End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) patients who obtained kidney transplantation potentially help decrease their risk of readmission after transplantation, which could also help decrease the morbidity and cost. We aims to develop statistical models to predict the probability of hospital readmission after transplantation.We used 1400 ESRD patients' electronic health record (EHR) information who obtained transplantation at Emory hospital from 2005 to 2015 including the free-text social worker notes, to identify the probabilities of patients' readmission after kidney transplantation. We incorporated natural language processing (NLP) in multivariable logistic regression models to examine whether the incorporation of free-text social worker notes improve the prediction for hospital readmission after transplantation.Among the 1,400 adult ESRD patients obtained kidney transplantation, 547(39.0%) resulted in hospital readmission after 90 days of transplantation. The area under receiver operating curves (AUC) was 0.62 (95% CI 0.61-0.63) in the model including only structured variables, and 0.61(95% CI 0.59-0.62) in the model including only free-text data.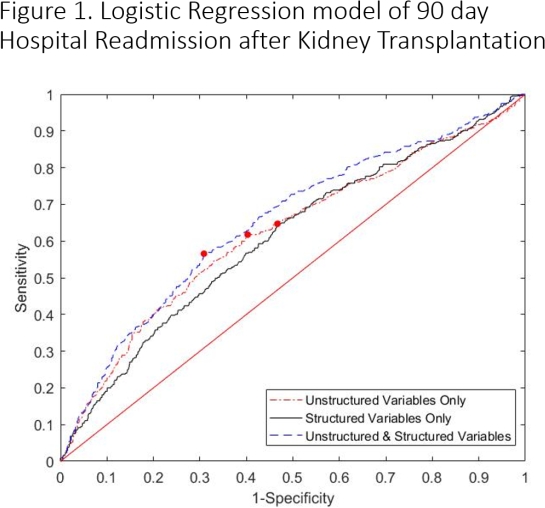 When both structured variables and free text variables were included, the AUC reached 0.65 (95% CI 0.63-0.68). Patient's EHR medical information were associated with and can be used to predict readmission after kidney transplantation. Predictive models including free-text social worker notes could improve the prediction performance in identifying the hospital readmission risk. The study is in process, as we have thus far only used 60% of the data sources and 32 variables but have illustrated a proof of concept that the AUC was improved by including NLP.
When both structured variables and free text variables were included, the AUC reached 0.65 (95% CI 0.63-0.68). Patient's EHR medical information were associated with and can be used to predict readmission after kidney transplantation. Predictive models including free-text social worker notes could improve the prediction performance in identifying the hospital readmission risk. The study is in process, as we have thus far only used 60% of the data sources and 32 variables but have illustrated a proof of concept that the AUC was improved by including NLP.
CITATION INFORMATION: Zhang X., Arenson M., Kim J., Karadkhele G., Hogan J., Zhang Y., Adams A., Patzer R. Prediction of 90 Days Readmission after Kidney Transplantation Including Natural Language Processing Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zhang X, Arenson M, Kim J, Karadkhele G, Hogan J, Zhang Y, Adams A, Patzer R. Prediction of 90 Days Readmission after Kidney Transplantation Including Natural Language Processing [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/prediction-of-90-days-readmission-after-kidney-transplantation-including-natural-language-processing/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
