Prediction Model of Post-Donation Renal Function Using Dynamic Kidney CT Volumetry in Living Donor
1Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Songpa, Korea, Republic of, 2Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Gangnam, Korea, Republic of
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1711
Keywords: Donation, Multicenter studies, Prediction models, Renal failure
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » 42 - Kidney Living Donor: Selection
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney Living Donor: Selection
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Tuesday, June 7, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: The risk of renal failure after live kidney donation can be predicted based on various clinical information. We tried introduce a model to predict the risk of renal failure after live kidney donation using pre-donation variables including residual kidney volume proportion (RKP, remnant kidney volume/total kidney volume) measured by CT volumetry
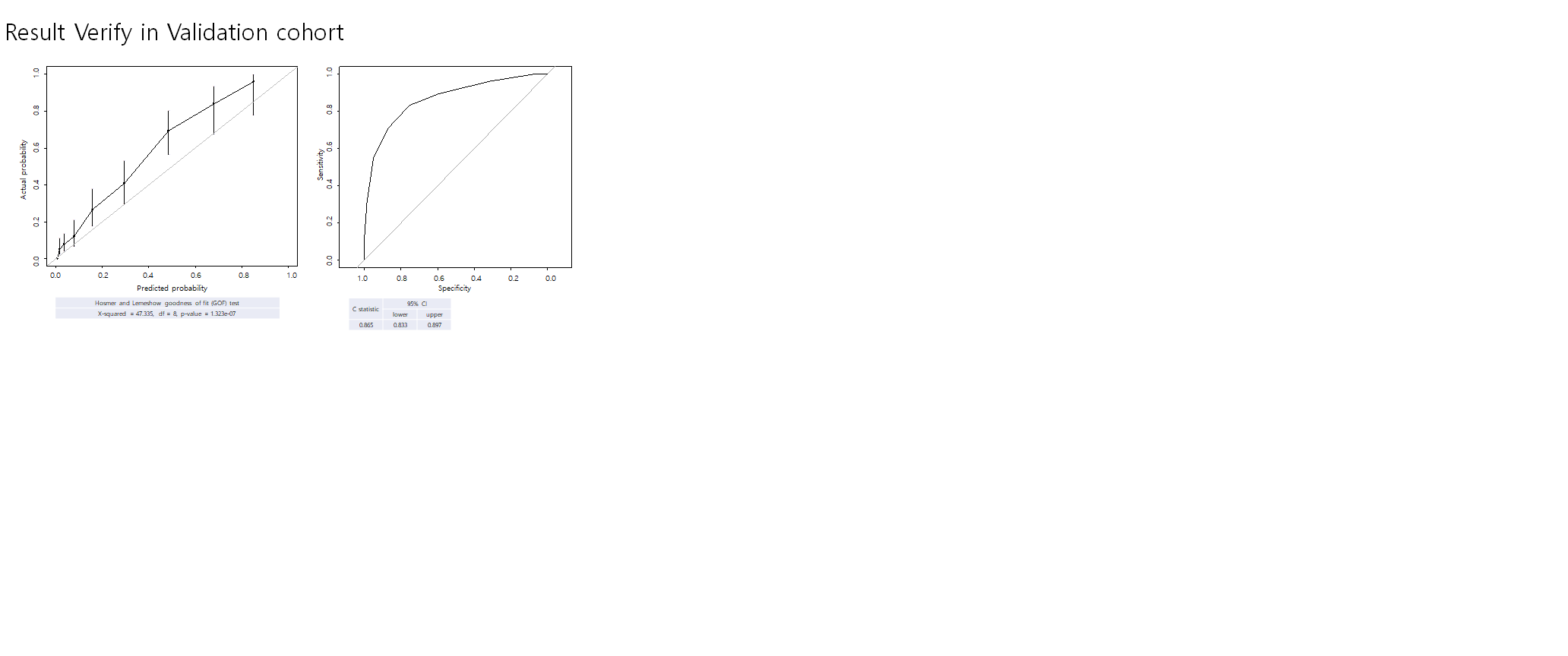
*Methods: Patients who had donor nephrectomy between May 2007 and December 2019 in two independent centers. Age, sex, body mass index (BMI), hypertension, smoking history, preoperative eGFR and RKP were investigated. Primary end point is eGFR less than 60 mL/min/m2 six months after kidney donation. Univariable and multivariable analysis was performed using the Cox hazard regression model to find significant risk factors for the primary end point. Thereafter, a prediction model for the primary end point was constructed based on the weight of each variable. The fit of the regression model was assessed by using the Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test.
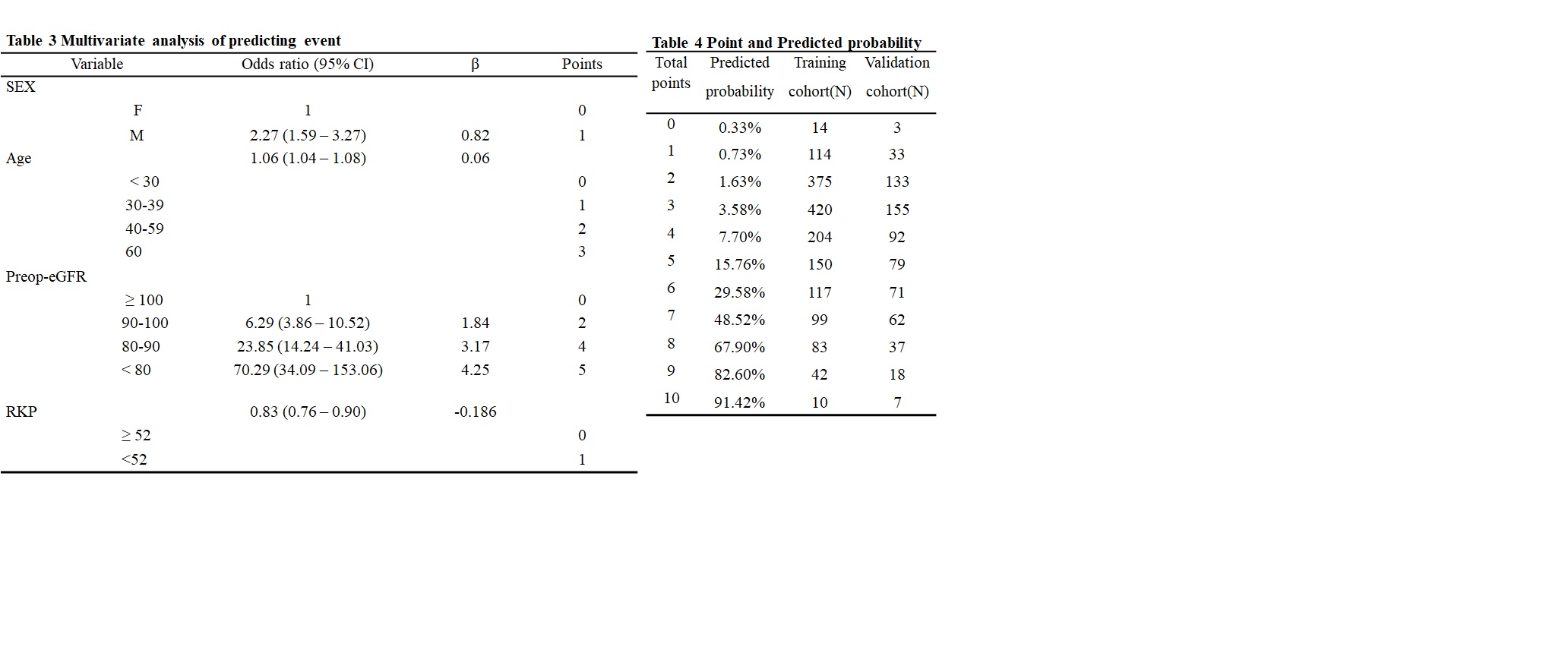
*Results: A total of 1628 and 690 live kidney donors were included in training and validation cohort, respectively. The eGFR was less than 60 mL/min/m2 six months after kidney donation in 235 donors (14.4%) of the training cohort and 178 donors (25.8%) of the validation cohort. In univariable analysis, gender, age, BMI, hypertension, preoperative eGFR, and remnant kidney proportion were significantly associated with the primary end point. After multivariable analysis, the variables used in the score system of the prediction model were gender, age, eGFR, and remnant kidney proportion. The sum of score ranges from 0 to 10 [Sex (Male:1, Female:0)], [Age at operation (<30:0, 30-39:1, 40-59:2, ≥60:3)], [Pre-op eGFR (≥100:0, 90-99:2, 80-89:4, <80:5)], [RKP (≥52:0, <52:1)]. This prediction model for the primary end point showed good discrimination.
*Conclusions: Our prediction model based on dynamic CT volumetry and clinical data may be useful to estimate the risk of significant renal dysfunction after kidney donation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lim S, Kwon J, Ko Y, Kwon H, Jung J, Kwon H, Kim Y, Park J, Lee K, Shin S. Prediction Model of Post-Donation Renal Function Using Dynamic Kidney CT Volumetry in Living Donor [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/prediction-model-of-post-donation-renal-function-using-dynamic-kidney-ct-volumetry-in-living-donor/. Accessed February 22, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress