Predicting Liver Allograft Discard: The Discard Risk Index
Abdominal Transplantation, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A277
Keywords: Donation, Donors, Liver transplantation, marginal
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Liver: MELD, Allocation and Donor Issues (DCD/ECD)
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 2, 2018
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall 4EF
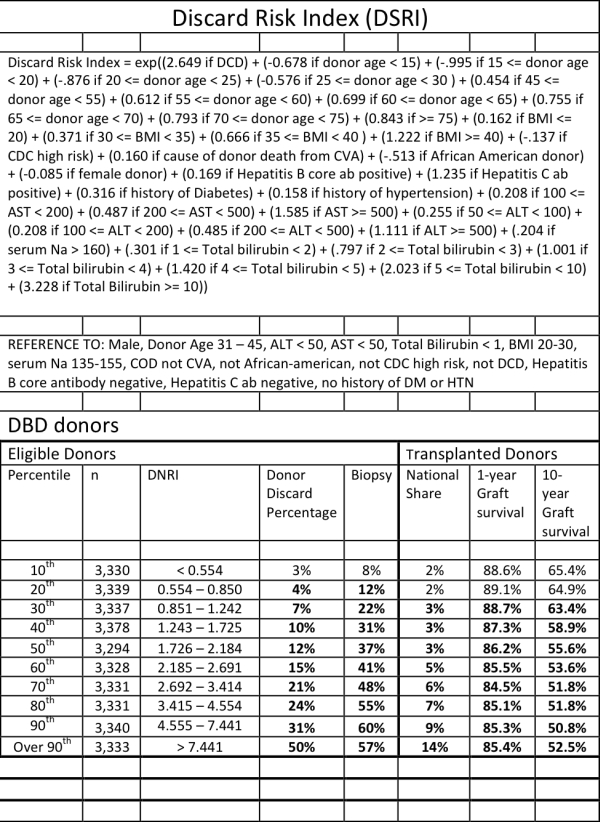
Background: An index that predicts liver allograft discard can effectively grade allografts and can be used to preferentially allocate marginal allografts to aggressive centers. Aim: to devise an index to predict liver allograft discard using only risk factors available at the time of initial DonorNet offer.
Methods: Using univariate and multivariate analyses on a training set of 72,297 deceased donors, we identified independent risk factors for liver allograft discard. Multiple imputation was used to account for missing variables.
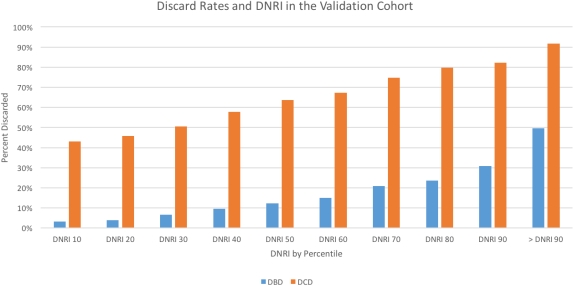
Results: We identified 15 factors as significant predictors of liver allograft discard; the most significant risk factors were: total bilirubin > 10 mg/dl (OR 25.23, CI 17.32-36.77), donation after cardiac death (OR 14.13, CI 13.30-15.01), and total bilirubin 5 – 10 mg/dl (OR 7.57, CI 6.32-9.05). The resulting Discard Risk Index (DSRI) accurately predicted the risk of liver discard with a C-statistic of 0.80. We internally validated the model with a validation set of 37,243 deceased donors and also achieved a 0.80 C-statistic. At a DSRI at the 90th percentile, the discard rate was 50% (OR 32.34 CI 28.63-36.53), while at a DSRI at the 10th percentile only 3% of livers were discarded.
Conclusions: The use of the DSRI can help predict liver allograft discard. The DSRI can be used to effectively grade allografts and preferentially allocate marginal allografts to aggressive centers in order to maximize the donor yield and expedite allocation.
CITATION INFORMATION: Rana A., Kueht M., Galvan N., Cotton R., Miloh T., O'Mahony C., Goss J. Predicting Liver Allograft Discard: The Discard Risk Index Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rana A, Kueht M, Galvan N, Cotton R, Miloh T, O'Mahony C, Goss J. Predicting Liver Allograft Discard: The Discard Risk Index [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/predicting-liver-allograft-discard-the-discard-risk-index/. Accessed March 7, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress