Predicting HCC Recurrence Following Liver Transplant – A Machine Learning Approach
1Department of Surgery, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2The Center for Computational Medicine, The Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, ON, Canada
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 149
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma, Liver transplantation, Prediction models, Recurrence
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Liver Transplant Oncology
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:18pm-5:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:18pm-5:30pm
Location: Room 311
*Purpose: The liver transplant listing criteria for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is controversial. Policies aim to prevent tumor recurrence but it has been difficult to encompass the numerous contributive factors. This study takes advantage of machine learning algorithms to incorporate all available features in a post-transplant recurrence prediction calculator.
*Methods: The calculator was developed using the University of Toronto HCC database, which is a comprehensive dataset including all patients with HCC listed for liver transplantation between 2000-2016. The dataset includes comprehensive features including serial imaging morphology, AFP, details of bridging therapy, treatment response, and post-transplant outcome. A Cox proportional hazards model was used to model time to recurrence following transplant. The model was estimated through a least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) penalized maximum likelihood procedure in order to encourage sparsity of the coefficients, thereby discouraging overfitting. The coefficients were learned on 90% of the data (the training set). The regularization hyperparameter was learned on the same set of training data. Performance was evaluated over 1000 iterations by assessing the area under the receiver operating curve (AUC) and concordance on the held-out data (the testing set). Variables selected by LASSO in over 50% of iterations were selected to run the analysis of the 5-year recurrence risk in the model. The same dataset was then used to train alternative recurrence risk algorithms (AFP score and MORAL) to compare its predictive power.
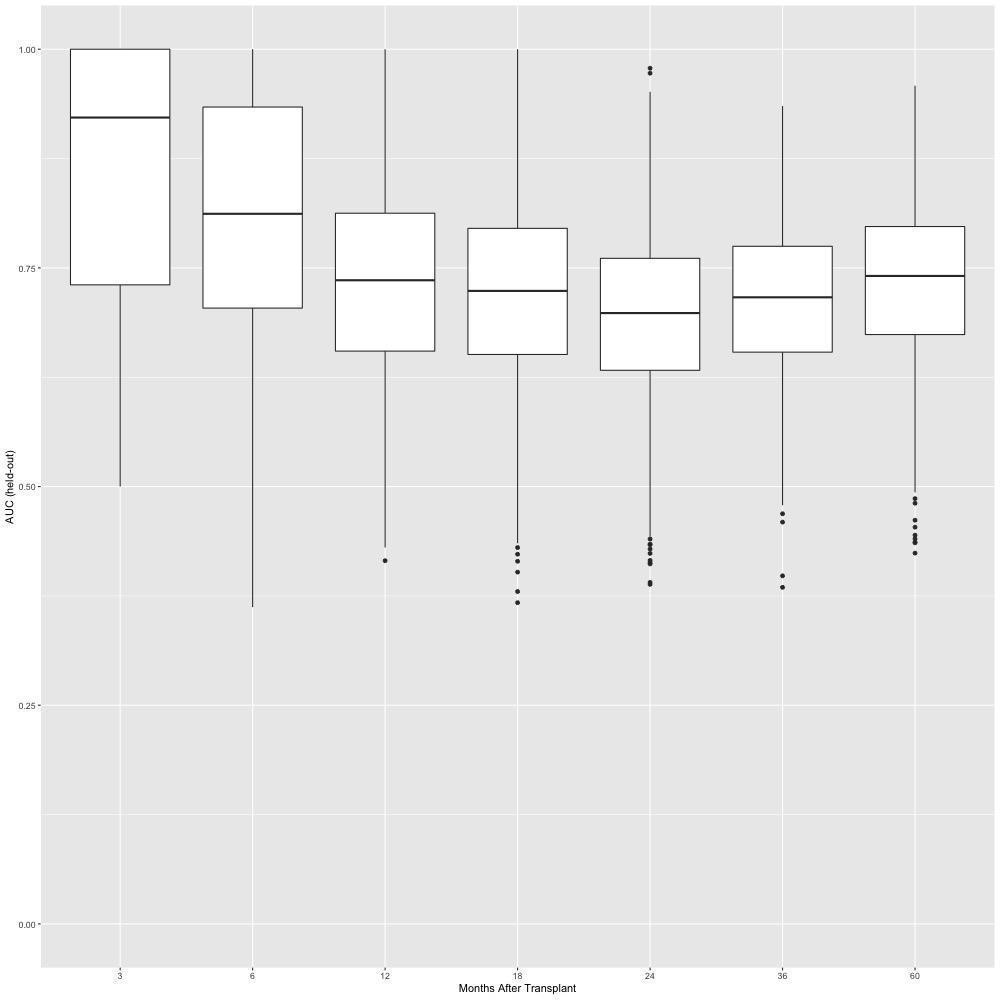
*Results: The dataset included 694 patients who underwent liver transplant for HCC. The overall concordance of score with disease-free survival was satisfactory (concordance 0.706, sd: 0.075). The AUC for prediction of recurrence show the predictive power of the model (Figure 1). Including all variables meeting the selection criteria, the AUC at 5 years post transplantation was 0.756 (95% CI 0.708-0.804). By comparison, the AUC for AFP score at 5 years post transplantation was 0.616 (95% CI 0.558-0.675) and that of MORAL was 0.595 (95% CI 0.536-0.655).
*Conclusions: A comprehensive HCC recurrence risk calculator using machine learning is possible with higher accuracy than other available scores.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lau LF, Nelson W, Gorgen A, Erdman L, Abreu P, Goldenberg A, Sapisochin G. Predicting HCC Recurrence Following Liver Transplant – A Machine Learning Approach [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/predicting-hcc-recurrence-following-liver-transplant-a-machine-learning-approach/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress