Pre-Liver Transplant Renal Dysfunction is an Independent Predictor of Post-Liver Transplant Return to the Operating Room
Department of Transplant, Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A290
Keywords: Liver transplantation, Renal dysfunction, Surgical complications
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Liver - Kidney Issues in Liver Transplantation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 1, 2019
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: Pre-liver transplant (LT) renal dysfunction predicts worse outcomes post-LT but the reasons for this are unclear. We aimed at identifying the effect of pre-LT kidney function on return to the operating room (RTO) within 90 days after LT.
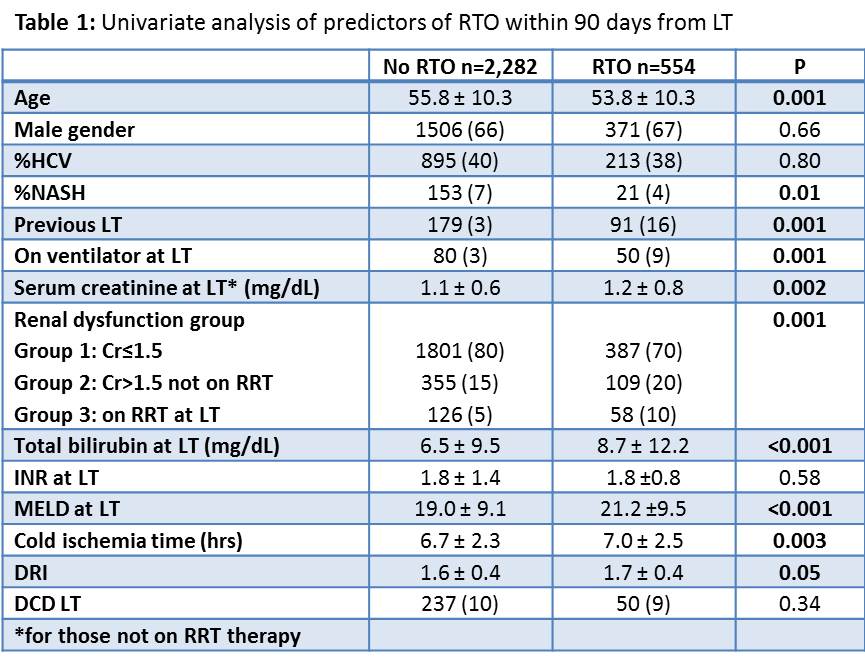
*Methods: Data on 2,836 LT alone performed between 2/98 and 5/16 were retrospectively reviewed. Simultaneous liver-kidney transplant recipients were excluded. The cohort was divided into 3 groups according to serum creatinine and renal replacement therapy (RRT) at LT. Group 1 (n=2,188): creatinine ≤1.5 mg/dl, group 2 (n=464): creatinine >1.5 mg/dl and no RRT; group 3 (n=184): on dialysis at LT. A univariate analysis was performed to identify predictors of RTO within 90 days from LT. A Cox logistic hazards ratios were constructed to identify independent predictors of RTO after LT.
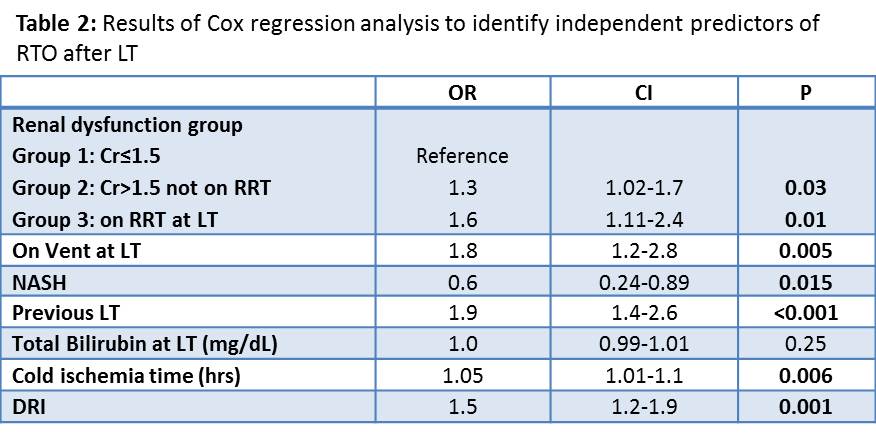
*Results: Of the 2,836 LT recipients, 554 (19%) required RTO within 90 days from LT. Post-LT bleeding was the most common reason for RTO occurring in 210 (38%) of cases. RTO was 18% in group 1, 24% in group 2 and 32% in group 3 (P<0.001). Bleeding accounted for 35%, 43% and 48% of RTO cases in group 1, 2 and 3, respectively (P=0.07).Predictors of RTO on univariate analysis are presented in Table 1. Cox logistic regression demonstrated that pre-LT renal dysfunction is an independent predictor of RTO after LT with the highest risk being in patients on RRT at LT (Table 2). 1-year survival for patients on RRT at LT (group 3) was 81% for those who had no RTO and 63% for the RTO patients, Log Rank P<0.05.
*Conclusions: 1) Pre-LT renal dysfunction is an independent predictor of post-LT RTO. 2) The incidence of RTO for bleeding increases in parallel to the decline in kidney function. 3) LT recipients on RRT at LT who RTO have lower 1-year survival compared to those who had no RTO after LT. 4) RTO could partially account for the lower survival for recipients on RRT at LT.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wadei HM, Mai ML, Taner C, Keaveny AP, Mao S, Abader P, Kroner P, Croome K. Pre-Liver Transplant Renal Dysfunction is an Independent Predictor of Post-Liver Transplant Return to the Operating Room [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/pre-liver-transplant-renal-dysfunction-is-an-independent-predictor-of-post-liver-transplant-return-to-the-operating-room/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress