Pre-Kidney Transplant Inflammation and Post-Transplant Outcomes.
Department of Surgery, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B178
Keywords: Inflammation, Kidney transplantation, Survival
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney Living Donor: Long Term Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 3, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Background: Patients with ESRD have higher inflammation levels, which may cause adverse outcomes after they receive a kidney transplant (KT). In this study, we quantified the association between inflammation and post-KT outcomes.
Methods: 378 participants were enrolled in a prospective cohort at the time of KT (10/2009-3/2017). Inflammatory markers were measured immediately prior to KT. Elevated inflammation level was defined as more than 1 SD increase above the mean of IL-6, sTNFR1, and HSCRP (on the log scale) as well as an inflammatory index calculated using IL-6 and sTNFR1. Mortality and death-censored graft loss were assessed using Cox proportional models; DGF was evaluated by modified Poisson regression models; and length of stay was assessed using Poisson regression models adjusted for age, sex, race, donor type, time on dialysis, cause of ESRD.
Results: Among KT recipients, the median IL-6 level was 4.6 pg/ml; the median sTNFR1 level was 14.3 ng/ml; the median CRP level was 3.7 ug/ml; and the median inflammation score was 6.9. Elevated IL-6 was associated with an increased odds of DGF (OR=1.50, 95%CI: 1.07-2.09). Elevated sTNFR1 was associated with increased odds of DGF (OR=1.64, 95%CI: 1.22-2.22) and increased risk of death-censored graft loss (HR=2.81, 95%CI: 1.03-7.71). An elevated inflammatory index was associated with an increased risk of mortality (HR=2.43, 95%CI: 1.16-5.06), DGF (OR=1.71, 95%CI: 1.25-2.33) and longer length of stay (RR=1.10, 95%CI: 1.01-1.20). 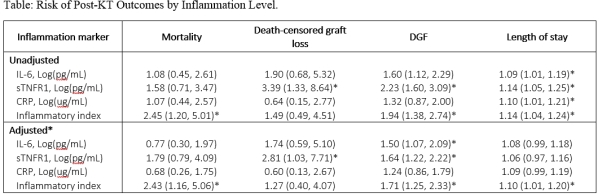
Conclusions: Elevated levels of IL-6 are associated with increased risk of DGF. Higher level of sTNFR1 was associated with death-censored graft loss and DGF. A comprehensive index that integrates these two inflammatory markers was associated with post-KT outcomes such as mortality, DGF and length of stay. Measurement of inflammatory markers prior to KT may be an objective tool for post-KT risk stratification.
CITATION INFORMATION: Ying H., McAdams DeMarco M., Segev D. Pre-Kidney Transplant Inflammation and Post-Transplant Outcomes. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ying H, DeMarco MMcAdams, Segev D. Pre-Kidney Transplant Inflammation and Post-Transplant Outcomes. [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/pre-kidney-transplant-inflammation-and-post-transplant-outcomes/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
