Post Transplant Outcomes in Hepatitis C Positive Patients.
Montefiore Medical Center, Bronx
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A197
Keywords: Graft survival, Hepatitis C, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Kidney Complications I
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, April 29, 2017
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall D1
Hepatitis C (HCV) is associated with increased morbidity and mortality after kidney transplant (KTx). We aimed to assess outcomes of HCV positive patients at our center, including patients recently treated for HCV.
We reviewed all patients who received a KTx from January 1, 2009 until December 31, 2014. Post KTx outcomes in patients with HCV (n=51) were compared to patients without HCV (n=632).
Patient demographics were similar between the two groups, however, patients with HCV were younger (53 ± 13.6 vs 58.4 ± 8.1, p=0.01), more were African American (62.7% vs. 39.2% p=0.02) and significantly more had class II DSA at the time of transplant (class I DSA present in 11.8 vs 11.1% and class II DSA present in 19.6% vs 6.8% p<0.01). There was no difference in type of induction or type of transplant (deceased vs. living donor). There was no difference in donor age, KDPI, terminal creatinine or cold ischemia time between the two groups. After a median follow up of 3.8 years, (range 2.4-5.3), there was no difference between HCV positive versus negative patients in terms of viral infections (BK viremia, 18% vs 20.1%, BKVN 3.4% vs. 1.8%, CMV 4% vs. 10.1%), fungal infections (2% vs. 2.25%), acute or chronic rejection (acute, 10.3 vs. 10.7%, chronic 13.7% vs. 7.4%), de novo or recurrent glomerular disease (10.3% vs.6.5%) or malignancies (8% vs. 5.6%). There was no difference in most recent PRA and no difference in development of de novo DSA (21.6% vs 14.9%). Most recent creatinine was significantly higher in patients with HCV (1.79±1.02mg/dl vs. 1.55±1.02 mg/dl, p=0.03). There was no difference in patient or graft survival between the two groups (Figure 1). During the study period, a subgroup of 25 patients were successfully treated for HCV with new anti-viral agents. All treated patients cleared the virus.
Our review demonstrates excellent outcomes for HCV positive patients. Longer follow up and increased use of newly available treatments for HCV may demonstrate significantly improved outcomes in HCV patients.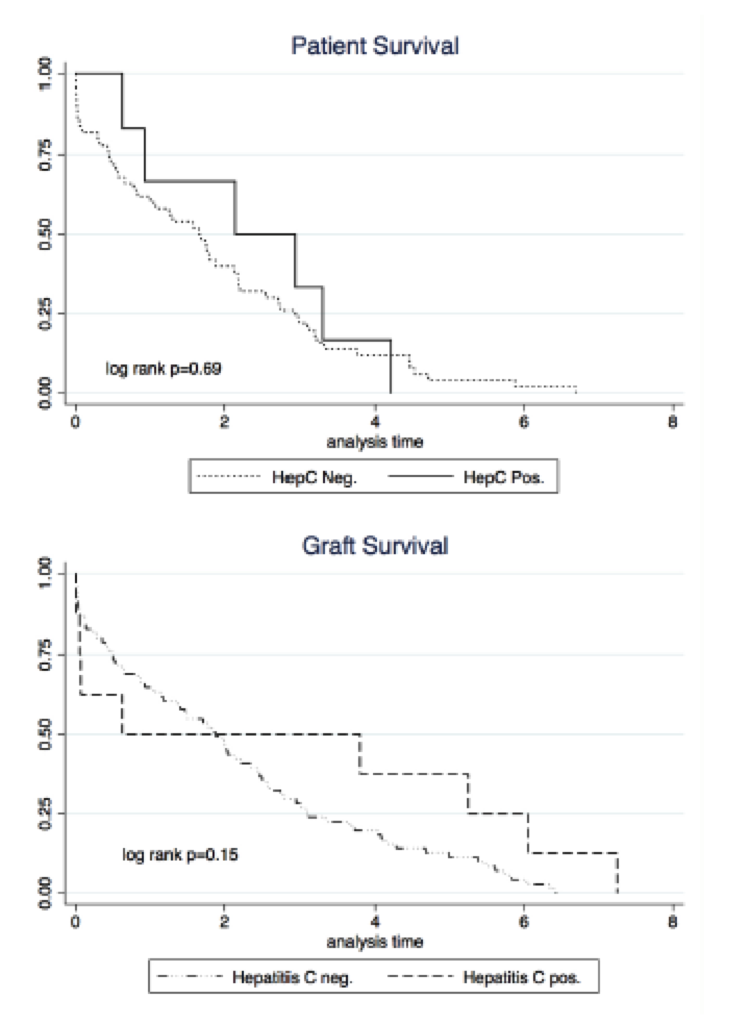
CITATION INFORMATION: Lubetzky M, Hayde N, Kamal L, Ajaimy M, Bedi P, Deboccardo G, Rocca J, Greenstein S, Graham J, Chokechanachaisakul A, Courson A, Kinkhabwala M, Akalin E. Post Transplant Outcomes in Hepatitis C Positive Patients. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lubetzky M, Hayde N, Kamal L, Ajaimy M, Bedi P, Deboccardo G, Rocca J, Greenstein S, Graham J, Chokechanachaisakul A, Courson A, Kinkhabwala M, Akalin E. Post Transplant Outcomes in Hepatitis C Positive Patients. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/post-transplant-outcomes-in-hepatitis-c-positive-patients/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
