Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder: Risk Analysis for Pancreas Transplant Patients.
E. Minja, T. Dunn, A. Matas, T. Pruett, R. Kandaswamy, E. Finger.
Dept of Surgery, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C214
Keywords: Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), Pancreas transplantation, Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD), Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Pancreas and Islet (Auto and Allo) Transplantation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, May 1, 2017
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall D1
Objective: Determine incidence, risk factors, and impact of PTLD in pancreas transplantation (PTx).
Methods: Retrospective review of all PTx performed between 7/25/1978 and 12/17/2015 at a single center. Bivariate (BV) and multivariable (MV) methods were used to assess the association of PTLD, graft survival, and patient survival with predictive risk factors.
Results: Of 2228 PTx analyzed, 104 PTx developed PTLD (4.7% overall incidence) with 87 cases unique to primary or most recent re-txp patients (3.9%). Median time to developing PTLD was 7.2 yrs (range 0.03–23.1). The incidence of PTLD demonstrate an initial spike in the first 6 months(1% unique incidence), a plateau, then 0.53 cases/100 patient-yrs in yrs 3-15 (Fig 1).
Detailed analysis was conducted using a cohort of 1337 recent PTx (1998-2015). In BV analysis, only SPK PTx (p= 0.042), and recipient EBV- status (p < 0.001) predicted risk of developing PTLD. 5-yr risk of PTLD for EBV- recipients was 8.1% vs 1.4% in EBV+ (Fig. 1). There was a trend towards significance of acute rejection(p=0.120) as a risk factor. No other factors were associated with PTLD (notably retxp, donor EBV, or immunosuppression agents, all p>0.4)
MV regression showed recipient EBV- status had a 4-fold increased risk of PTLD (HR 4.061, CI 1.826-9.031, p=0.001). History of PTx rejection increased PTLD risk 2.6-fold (HR 2.668, CI 1.289-5.552, p=0.008). Male donor/female recipient had trend towards protection(HR 0.519, CI 0.213-1.260, p=0.147). All other factors studied (including SPK PTx, retxp, immunosuppressive agents, and age) were non-significant (all p>0.2).
Development of PTLD did not impact patient survival (p=0.797), but was unexpectedly associated with improved graft survival in both BV (p=0.007) and MV analysis (HR 0.538, CI 0.303-0.955, p=0.034). In PTx recipients, PTLD was the cause of death in 33 (3.9%) of patients.
Conclusion: Recipient EBV- status and history of rejection are risk factors for developing PTLD. PTLD did not affect patient survival and actually increased graft survival. Further study of the potential causal associations will be informative.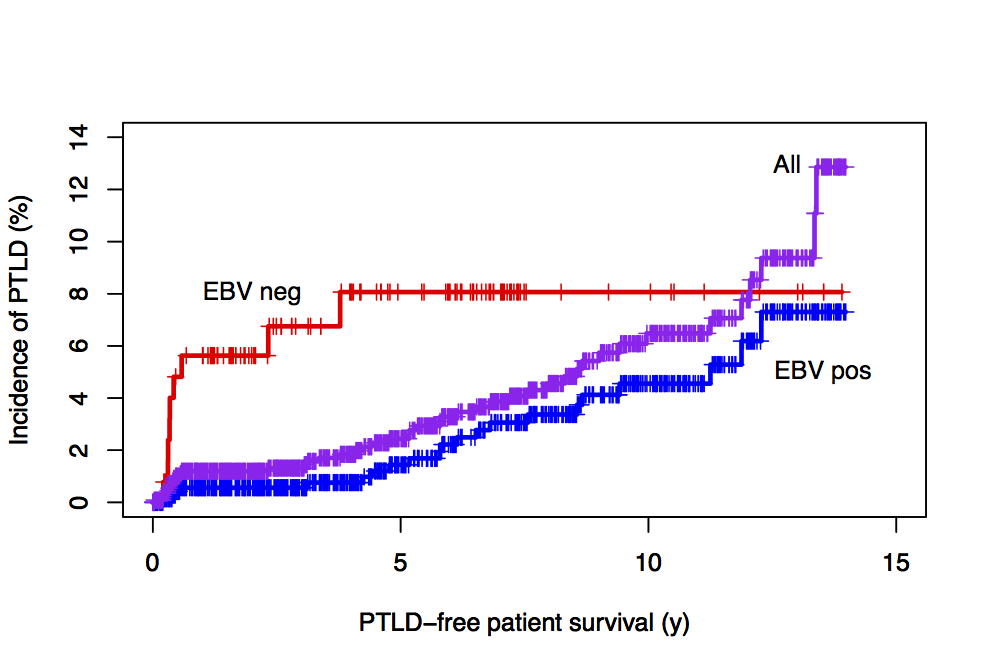
CITATION INFORMATION: Minja E, Dunn T, Matas A, Pruett T, Kandaswamy R, Finger E. Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder: Risk Analysis for Pancreas Transplant Patients. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Minja E, Dunn T, Matas A, Pruett T, Kandaswamy R, Finger E. Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder: Risk Analysis for Pancreas Transplant Patients. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/post-transplant-lymphoproliferative-disorder-risk-analysis-for-pancreas-transplant-patients/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
