Poor Long-Term Outcome of Liver Transplant Recipients with Preexisting Renal Insufficiency
1University Transplant Center, University Medical Center Hamburg Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany, 2Department of Medicine, University Medical Center Hamburg Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany, 3Department of Visceral Transplantation, University Medical Center Hamburg Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A283
Keywords: Lamivudine, Liver transplantation, Outcome, Renal failure
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Liver - Kidney Issues in Liver Transplantation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 1, 2019
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: Due to the MELD based allocation system the number of patients undergoing orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT) with severely impaired renal function has markedly increased. Therefore, we here investigated long term outcome of OLT recipients with advanced renal dysfunction.
*Methods: All adult patients who underwent OLT with chronic kidney disease (CKD) stage 4/5 at the University Hospital Hamburg Eppendorf between 01/2011 and 12/2015 were included in the study. Patient survival and renal outcome were retrospectively assessed. CKD 4/5 or status post kidney transplantation (KTx) at last follow-up were defined as poor renal outcome.
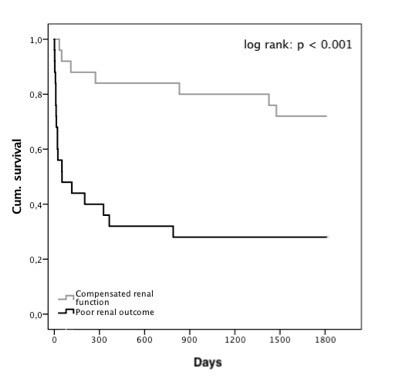
*Results: Altogether 60 patients with CKD 4 (22/60 (37%)) or CKD 5 (38/60 (63%)) pre transplant were studied. Median follow-up post transplant was 1099 days. In the immediate postoperative period, 42 (70 %) patients required dialysis for a median of 21 days. On long term follow-up 18/60 (30%) needed dialysis, only 5 of these patients (28%) subsequently underwent KTx after a median period of 274 days (IQR 201-1461). 29 patients (48%) had a poor renal outcome at the end of follow-up, while in 52% of patients renal function improved. There was no difference in terms of age, CKD stage, time on dialysis prior to OLT, length of stay on ICU, type of immunosuppression, presence of diabetes, arterial hypertension or hyperlipidemia between patients with improved renal function or those with poor renal outcome at last follow-up (p=n.s.). The only risk factor for poor renal outcome was post-operative need for dialysis. Overall 3- and 5-year patient survival was 60% and 42% respectively. 1- and 5- year mortality was significantly higher in patients with poor as compared to improved renal outcome (59% vs. 13%, p<0.001 and 72% vs. 28%, p<0.001; respectively).
*Conclusions: In this long-term follow-up study, about half of the patients with CKD 4 and 5 prior to OLT had poor long-term renal outcome, going along with a very low 5 year patient survival rate of only 28%. Therefore, further studies should investigate if outcome of these patients improves with combined OLT and KTx.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sterneck M, Touma M, Horvatits T, Pischke S, Herden U, Lohse A, Fischer L. Poor Long-Term Outcome of Liver Transplant Recipients with Preexisting Renal Insufficiency [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/poor-long-term-outcome-of-liver-transplant-recipients-with-preexisting-renal-insufficiency/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress