Polyfunctional T-cell Impairment to Sars-cov-2 Coronavirus in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients with Acute Covid-19 Infection
A. Favà1, L. Donadeu2, V. Pernin3, M. Meneghini1, E. Crespo2, N. Sabé4, L. Lladó5, J. Gonzalez-Costello6, O. Thaunat7, O. Bestard1
1Kidney Transplantation Unit, Bellvitge University Hospital- IDIBELL, L'Hospitalet de Llobregat. Barcelona, Spain, 2Experimental Nephrology Laboratory, IDIBELL, Bellvitge University Hospital, L'Hospitalet de Llobregat. Barcelona, Spain, 3Kidney Transplant Unit, Hospital de Montpellier, Montpellier, France, 4Infectious Disease Department, Bellvitge University Hospital, L'Hospitalet de Llobregat. Barcelona, Spain, 5Liver Transplant Unit, Bellvitge University Hospital, L'Hospitalet de Llobregat. Barcelona, Spain, 6Heart Transplantation Unit, Bellvitge University Hospital, L'Hospitalet de Llobregat. Barcelona, Spain, 7Department of Transplantation, Edouard Herriot Hospital Lyon, Lyon, France
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 23
Keywords: Immunosuppression, Monitoring, Pneumonia, T cell activation
Topic: Clinical Science » Infectious Disease » All Infections (Excluding Kidney & Viral Hepatitis)
Session Information
Session Name: COVID-19 Session 1
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Saturday, June 5, 2021
Session Time: 4:30pm-5:30pm
 Presentation Time: 4:50pm-4:55pm
Presentation Time: 4:50pm-4:55pm
Location: Virtual
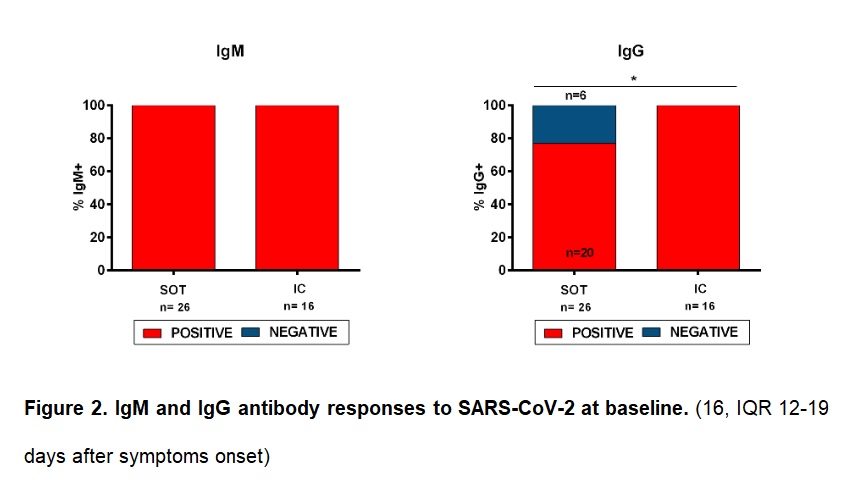
*Purpose: The emerged COVID-19 pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2 has paralyzed the world, due to its high infectivity and fatal outcomes, especially among more vulnerable individuals. While description of protective humoral and T-cell immune responses has been reported among immunocompetent (IC) individuals, its characterization and determinants of poorer outcomes among the at-risk Solid Organ Transplant (SOT) patient population has not been thoroughly investigated.
*Methods: SARS-CoV-2-specific serological and functional T-cell immune responses against main immunogenic antigens were tracked in 28 SOT recipients during acute infection and over the following 40 days of convalescence and were compared to 16 IC patients admitted with similar moderate/severe COVID-19.
*Results: We show a more severe polyfunctional T-cell and serological impairment in SOT at the infection onset as compared to IC individuals, especially against membrane antigen.
Worse clinical outcomes (need of mechanical ventilation or death) more frequently occurred within SOT and were associated with a significantly impaired Th1 polarized immune response to antigens spike and membrane. Nonetheless, SOT achieved robust serological and functional Th1 and Th2 immune responses at convalescence, similarly to those of IC patients.
*Conclusions: Our data show a delay of serological and functional T-cell immune activation to SARS-CoV-2 in SOT, which may entail poorer clinical outcomes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Favà A, Donadeu L, Pernin V, Meneghini M, Crespo E, Sabé N, Lladó L, Gonzalez-Costello J, Thaunat O, Bestard O. Polyfunctional T-cell Impairment to Sars-cov-2 Coronavirus in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients with Acute Covid-19 Infection [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/polyfunctional-t-cell-impairment-to-sars-cov-2-coronavirus-in-solid-organ-transplant-recipients-with-acute-covid-19-infection/. Accessed February 23, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress