Pharmacokinetics of Mycophenolic Acid Following Enteric-Coated Mycophenolate Sodium Administration in Chinese Renal Transplant Recipients
MyERA Study Group, Hangzhou, China.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C114
Keywords: Area-under-curve (AUC), Immunosuppression, Kidney transplantation, Pharmacokinetics
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Kidney Immunosuppression: Novel Regimens and Drug Minimization
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 4, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Background: Mycophenolic acid (MPA), active component of mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) or enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium (EC-MPS), is the most commonly used immunosuppressant in renal transplant recipients (RTR) in China. However, it exhibits large intra-individual variability in pharmacokinetics (PK). Here, we assess the PK of MPA after EC-MPS administration in Chinese RTR receiving organs from cardiac death donors.
Method: This non-interventional, open-label, multicenter, prospective Phase IV observational study enrolled 250 RTR, receiving standard (s; 1440 mg/d) or high (h; >1440 mg/d) dose EC-MPS with calcineurin inhibitors (CNI: cyclosporine, CsA or tacrolimus, TAC) from 19 centers in China. The key secondary endpoint of this study was to evaluate the PK profiles of MPA in patients within 7 days of RT. The PK analysis set included 124 RTR with at least 8 evaluable serum MPA concentrations on Day (D) 3 or D7 post RT.
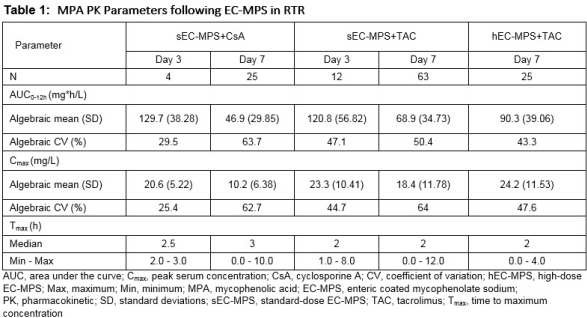
Results: The mean AUC0-12h of MPA on D7 in sEC-MPS+CsA, sEC-MPS+TAC, and hEC-MPS+TAC arms were 46.9, 68.9, and 90.3 mg.h/mL, respectively. The mean Cmax were 10.2, 18.4, and 24.2 mg/L, respectively. The mean AUC0-12h and Cmax of MPA on D3 were ~2-3 folder higher than on D7 in sEC-MPS+CsA and sEC-MPS+TAC arms. The median Tmax of MPA was 2-3 h on both days, independent of initial dose and CNI type. MPA exposures on D7 showed moderate inter-individual variability, with coefficient of variation (CV) for AUC0-12h and Cmax ranging from 43.3%-63.7% on D7 (Table 1).
Conclusions: This study provided preliminary PK characterization of MPA in RTR in sEC-MPS+CsA, sEC-MPS+TAC, and hEC-MPS+TAC arms. The preliminary analysis suggests that in the clinical D7 might be suitable to monitor drug concentration for dose confirmation if needed. In addition, the PK data and analysis in this study also assisted to the development of optimal simplified equations for MPA exposure estimation in Chinese population.
CITATION INFORMATION: Peng W., Tian C., Chen Z., Xue W., Wang G., Ye Q., Zhang X., Gu M., Zhao M., Wang C., Huang C., Yan J., Zhang W., Ding C., Fu Y., Ye S., Hu X., Tan R., Li M., Deng R., Ke Y., Wu W., Fan M., Chen J. Pharmacokinetics of Mycophenolic Acid Following Enteric-Coated Mycophenolate Sodium Administration in Chinese Renal Transplant Recipients Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Peng W, Tian C, Chen Z, Xue W, Wang G, Ye Q, Zhang X, Gu M, Zhao M, Wang C, Huang C, Yan J, Zhang W, Ding C, Fu Y, Ye S, Hu X, Tan R, Li M, Deng R, Ke Y, Wu W, Fan M, Chen J. Pharmacokinetics of Mycophenolic Acid Following Enteric-Coated Mycophenolate Sodium Administration in Chinese Renal Transplant Recipients [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/pharmacokinetics-of-mycophenolic-acid-following-enteric-coated-mycophenolate-sodium-administration-in-chinese-renal-transplant-recipients/. Accessed February 19, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress