Percentage of CD19+ B Cells as a Predictor of Acute Antibody-Mediated Rejection After Administration of Rituximab in ABO-Incompatible Kidney Transplantation.
Urology, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A49
Keywords: Antibodies, B cells
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Clinical Science: Kidney Immunosuppression: Desensitization
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, April 29, 2017
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall D1
[Introduction] Administration of rituximab to ABO-incompatible kidney transplant (ABOi-KTx) recipients is recognized as effective and safe. A single dose of 375 mg/m2 rituximab is generally sufficient for B-cell depletion. However, dosage should be adjusted according to individual response to rituximab to prevent over- and under-immunosuppression. Therefore, in this study, we aimed to determine the appropriate rituximab dosage and the target B-cell population after rituximab-based desensitization therapy .
[Materials and Methods] Forty-four consecutive ABOi-KTx recipients (28 men and 16 women) were enrolled in this retrospective study. They were administered rituximab (65–400 mg/body) 2–4 weeks before transplantation and subsequently subjected to plasmapheresis and desensitization therapy with intravenous immunoglobulin. Induction therapy with basiliximab was initiated, and the recipients were maintained on triple immunosuppressants. Their mean age at transplantation was 50.3 ± 15.4 years, and their mean pre-transplant dialysis period was 2.7 ± 3.8 years. Percentage of CD19+ B cells among the total lymphocytes (%CD19) in the peripheral blood was determined before transplantation. The recipients were divided into 2 groups according to the pre-transplant %CD19: low %CD19 group (%CD19 ≤ 1.2%; n = 35) and high %CD19 group (%CD19 > 1.2%; n = 9). The relationship between %CD19 and incidence of acute antibody-mediated rejection (AAMR) was evaluated.
[Results] AAMR was observed in 6 recipients, whose pre-transplant %CD19 was significantly higher than that of recipients who did not experience AAMR (3.1% vs. 0.6%; p = 0.004). Incidence of AAMR was significantly higher in the high %CD19 group than in the low %CD19 group (44.4% vs. 5.7%, p = 0.006). Furthermore, multivariate analysis showed that %CD19 > 1.2% was an independent factor to predict AAMR (p = 0.038).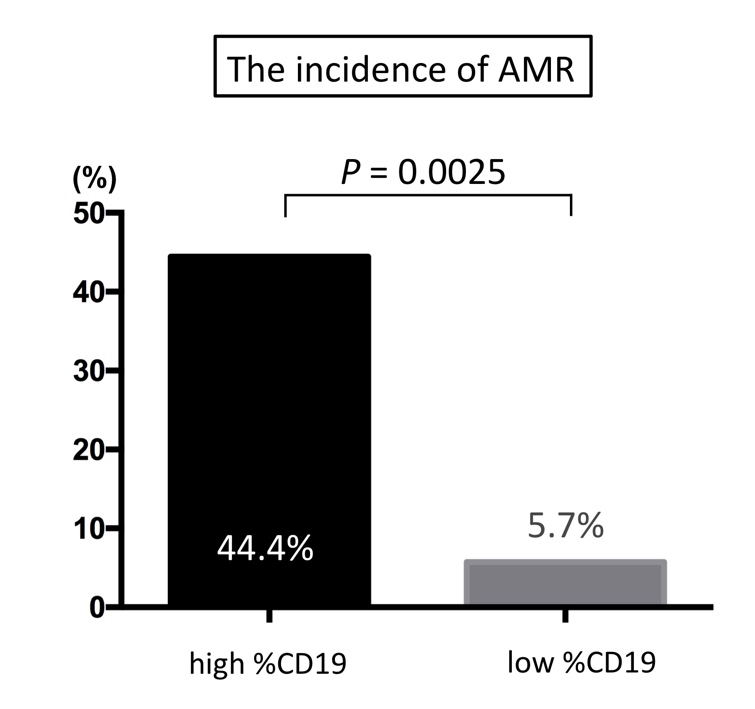 [Conclusion] High %CD19 after rituximab administration in ABOi-KTx recipients implies insufficient B-cell depletion that can lead to AAMR. Measurement of %CD19 would aid in identifying patients who need additional administration of rituximab.
[Conclusion] High %CD19 after rituximab administration in ABOi-KTx recipients implies insufficient B-cell depletion that can lead to AAMR. Measurement of %CD19 would aid in identifying patients who need additional administration of rituximab.
CITATION INFORMATION: Hirose T, Iwami D, Hotta K, Sasaki H, Higuchi H, Shinohara N. Percentage of CD19+ B Cells as a Predictor of Acute Antibody-Mediated Rejection After Administration of Rituximab in ABO-Incompatible Kidney Transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hirose T, Iwami D, Hotta K, Sasaki H, Higuchi H, Shinohara N. Percentage of CD19+ B Cells as a Predictor of Acute Antibody-Mediated Rejection After Administration of Rituximab in ABO-Incompatible Kidney Transplantation. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/percentage-of-cd19-b-cells-as-a-predictor-of-acute-antibody-mediated-rejection-after-administration-of-rituximab-in-abo-incompatible-kidney-transplantation/. Accessed February 24, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
