Patterns and Associated Risk Factors for Early Readmissions Post Total Pancreatectomy and Islet Auto-Transplantation(TP-IAT).
University of Minnesota, Minneapolis
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C217
Keywords: Employment, Islets
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Pancreas and Islet (Auto and Allo) Transplantation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, May 1, 2017
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall D1
Introduction: For four decades, TP-IAT has been performed to provide pain relief and preserve insulin function in patients(pts) with chronic/acute relapsing pancreatitis. Despite advances in surgical technique and perioperative management, TP-IAT remains a complex procedure with complicated post-operative management that is associated with high-rate of readmissions. We studied patterns and risk factors(RFs) associated with early readmissions post-TP-IAT with aim to identify modifiable causes to decrease rate of readmissions and improve the care for our patients.
Methods: 179 pts underwent TP-IAT(2014-2015).Demographics, pre- and peri-operative characteristics were compared between readmission(RG) and no readmission group(NRG) in univariable(UA) and multivariable(MVA) analyses. Timing, number, causes, temporal patterns of readmissions were examined.
Results:Of 179 pts, 79(44%) were readmitted within 3months, 99(55%) within 6 months, 125(70%) within one year of TP-IAT, with median number of readmissions 2(1-14) days and median time to first readmission 46(1-365) days. Demographics, pre- and peri-operative characteristics are shown(Table 1). In UA model initial length of stay(LOS) was significantly different between RG, 12 vs. 11 days for NRG; significance was lost in MVA. When intra- and post-operative events were studied in MVA, chyle leak associated with odds of readmission(p=0.04)(Table 2). Most common causes of readmission(CofR) were GI complications 87(70%), infection 78(63%), 36(29%)pain control(Table3). GI was common CofR throughout first year, frequency of ifx and pain management complications decreased over time. Glycemic control as CofR was an early event(Table4). 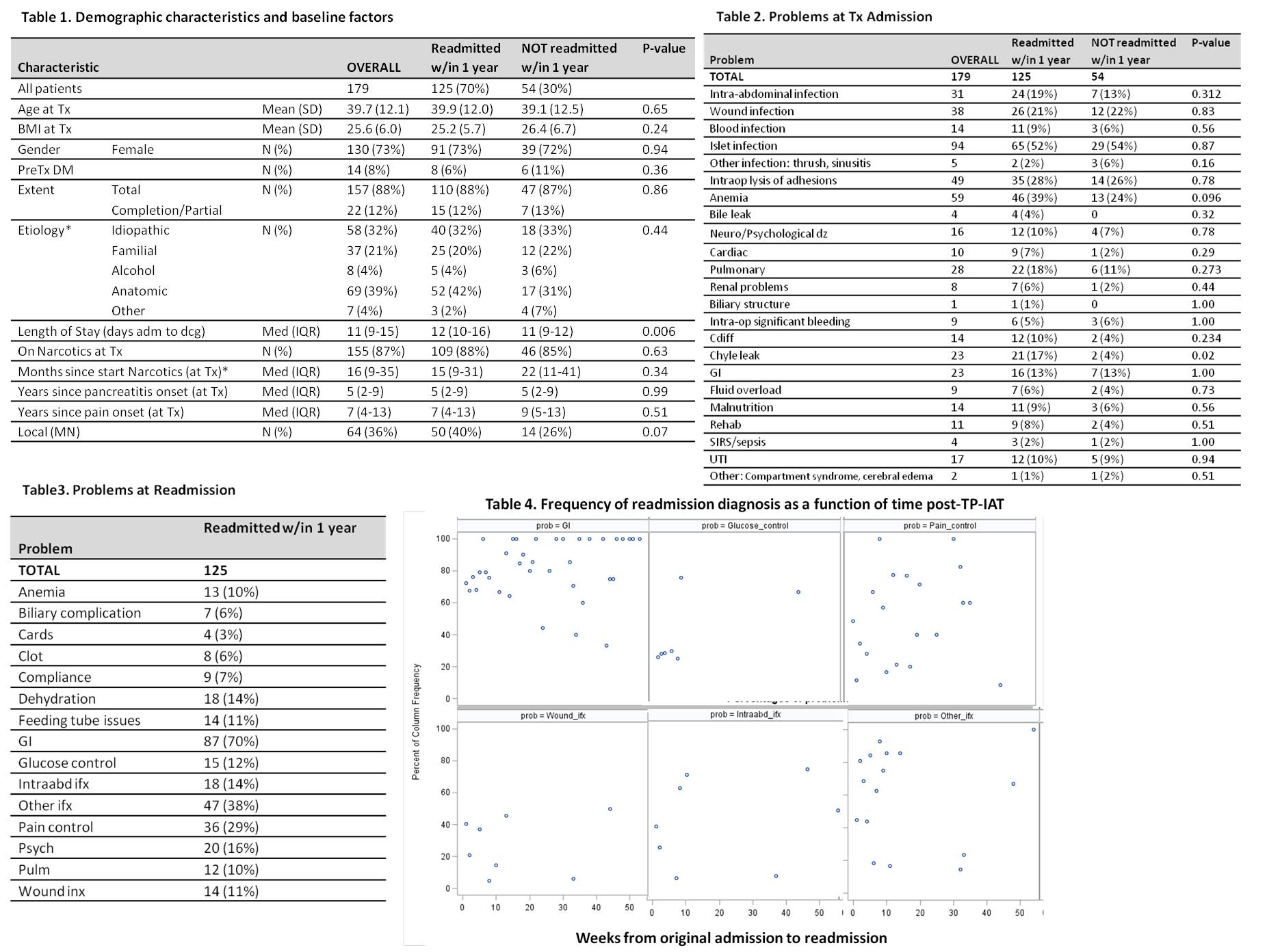
Conclusion: TP-IAT is associated with high rate of readmissions(55% at 6 months). Chyle leak is a RF for readmission, which may suggest complexity of specific original surgical cases. GI complications are most common CoR, persists throughout first year post-TP-IAT; more detailed review may provide identification of preventable GI complications in this cohort.
CITATION INFORMATION: Kirchner V, Bagdiwala A, Vock D, Bellin M, Beilman G, Berry L, Chinnakotla S, Dunn T, Freeman M, Sutherland D, Pruett T. Patterns and Associated Risk Factors for Early Readmissions Post Total Pancreatectomy and Islet Auto-Transplantation(TP-IAT). Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kirchner V, Bagdiwala A, Vock D, Bellin M, Beilman G, Berry L, Chinnakotla S, Dunn T, Freeman M, Sutherland D, Pruett T. Patterns and Associated Risk Factors for Early Readmissions Post Total Pancreatectomy and Islet Auto-Transplantation(TP-IAT). [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/patterns-and-associated-risk-factors-for-early-readmissions-post-total-pancreatectomy-and-islet-auto-transplantationtp-iat/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
