Pattern of Renal Allograft Injury in Recipients with Normal Donor-Derived Cell-Free DNA
University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C-343
Keywords: Graft function, Infection, Rejection, Screening
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Biomarkers, Immune Assessment and Clinical Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
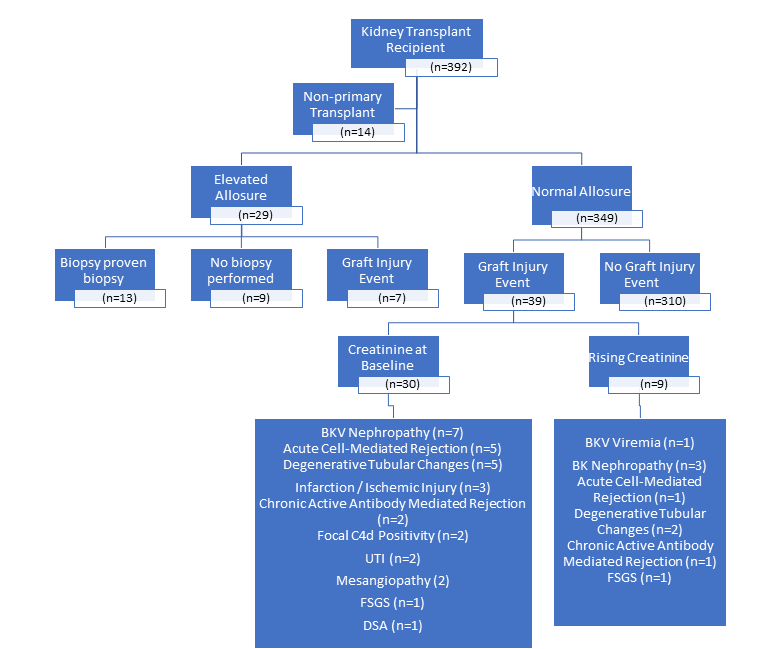
*Purpose: Donor-derived cell-free DNA (dd-cfDNA) is a novel non-invasive test currently used as a biomarker for identification of transplant rejection or injury. Here, we sought to examine the pattern of graft injury in the setting of normal dd-cfDNA in relation to normal and abnormal serum creatinine.
*Methods: Retrospective review of primary kidney transplant recipients who underwent dd-cfDNA testing and had a graft biopsy within 2 months of testing at a single institution between November 2017 to August 2019 was performed. Concomitant serum creatinine levels were reviewed. Variables that could indicate graft injury including urine cultures, serum BKV viral load, and donor specific antibodies (DSA) were evaluated.
*Results: 392 recipients underwent a total of 746 dd-cfDNA tests. 39 recipients had a normal dd-cfDNA (<1%). Of the recipients with normal dd-cfDNA, nine recipients had rising creatinine at time of their dd-cfDNA assessment. Concurrent events that could indicate graft injury include BKV viremia (n=1), BKV nephropathy (n=3), focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (n=1), acute cell-mediated rejection (n=1), degenerative tubular changes (n=2), chronic active antibody mediated rejection (n=1). Of the 30 with normal creatinine and normal dd-cfDNA levels, the most common graft injuring event detected was BKV nephropathy (n=7). However, acute T-cell mediated rejection (n=5) was also found on graft biopsy in this group despite normal dd-cfDNA and normal creatinine.
*Conclusions: Subclinical graft injuring events, including acute T-cell mediated rejection, can occur even in the setting of normal creatinine and dd-cfDNA. Further characterization of the sensitivity and specificity of dd-cfDNA for rejection as well as other graft injuring events will allow for better clinical interpretation of dd-cfDNA results.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Xie W, Goussous N, Haririan A, Weir M, Bromberg J. Pattern of Renal Allograft Injury in Recipients with Normal Donor-Derived Cell-Free DNA [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/pattern-of-renal-allograft-injury-in-recipients-with-normal-donor-derived-cell-free-dna/. Accessed March 1, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress