Parathyroidectomy Outcomes in Renal Transplant Recipients: Subtotal vs. Total
R. Rathore,1,2 A. Sharma,2 A. Halawa.2
1Renal Medicine, University Hospitals of North Midlands, Stoke-on-Trent, United Kingdom
2Faculty of Health, University of Liverpool, Liverpool, United Kingdom.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A212
Keywords: Graft survival, Hyperparathyroidism, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Kidney: Cardiovascular and Metabolic
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 2, 2018
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Introduction:
Best practice in management of persistent hyperparathyroidism in renal transplant recipients has been debated and there is no consensus on whether medical or surgical management is better.Subtotal parathyroidectomy (SP) is considered superior than total parathyroidectomy(TP) and we have conducted this study with following aims:
1. To compare outcomes of SP(after adenoma identified on MIBI imaging) with TP in terms of calcium, PTH and graft function over 12 months
2. To determine if there was sustained decline in graft function post parathyroidectomy
Methods:
In this single centre retrospective study,we identified kidney transplant recipients that had parathyroidectomy between 1/01/2007 and 1/01/2017(n=22).Graft survival and bone biochemistry were evaluated over 12 months.
Patients with failed transplants and multiple transplants were excluded.Remaining 11 patients were divided into 2 groups –total parathyroidectomy (TP) vs. subtotal parathyroidectomy (PP)
Results:
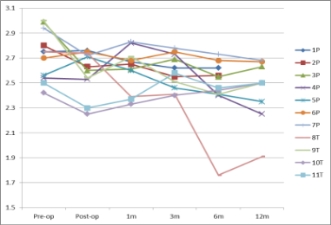
1. In TP group,100% achieved normocalcaemia and in SP group, 57%. Calcium levels were marginally elevated in remaining 43%
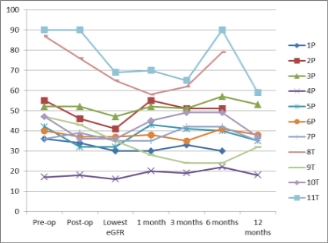
2. In 75% of TP group,there was sustained decline in eGFR at 1 year.
3. Only minor complications (cysts) occurred post-op
4. IV Calcium post-operatively was required in 1 patient in TP group and in none of SP group.
Conclusions:
1. SP can safely lower calcium and PTH levels in renal transplant recipients with persistent hyperparathyroidism.
2. No requirement for IV Calcium makes SP more favourable.
3. Graft function is largely unaffected by either procedure and for those that have decline in graft function post-op- in the majority, eGFR stabilises by 1 year.
4. Longer term study is needed to determine best practice to improve long term outcomes in terms of bone biochemistry and associated morbidity.
CITATION INFORMATION: Rathore R., Sharma A., Halawa A. Parathyroidectomy Outcomes in Renal Transplant Recipients: Subtotal vs. Total Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rathore R, Sharma A, Halawa A. Parathyroidectomy Outcomes in Renal Transplant Recipients: Subtotal vs. Total [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/parathyroidectomy-outcomes-in-renal-transplant-recipients-subtotal-vs-total/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress