Panel Reactive Antibody Stratification as a Guide to Induction Selection in Deceased-Donor Kidney Transplantation: Impact of Clinical Practice on Outcomes
1Medicine, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, 2Ubon Ratchathani University, Ubonratchathani, Thailand
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B210
Keywords: Induction therapy, Kidney transplantation, Outcome, Panel reactive antibodies
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney Immunosuppression: Induction Therapy
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: We aimed to determine the outcomes associated with anti-thymocyte globulin (ATG), alemtuzumab (ALM) or interleukin-2 receptor antagonist (IL2-RA) induction in adult deceased-donor (DD) kidney transplant (KT) recipients (KTRs) stratified into cohorts based on pre-transplant calculated panel reactive antibody (cPRA) .
*Methods: Using 12/5/2007-7/16/2015 OPTN data, we analyzed outcomes associated with induction in the (0-9%, 10-79% and >/=80%) cPRA cohorts using logistic or Cox regression adjusted for covariates which included: KDRI; recipient race/ethnicity; primary diagnosis: dialysis duration; no. of HLA mismatches; re-transplantation status; maintenance immunosuppressants and ; cold ischemic time.
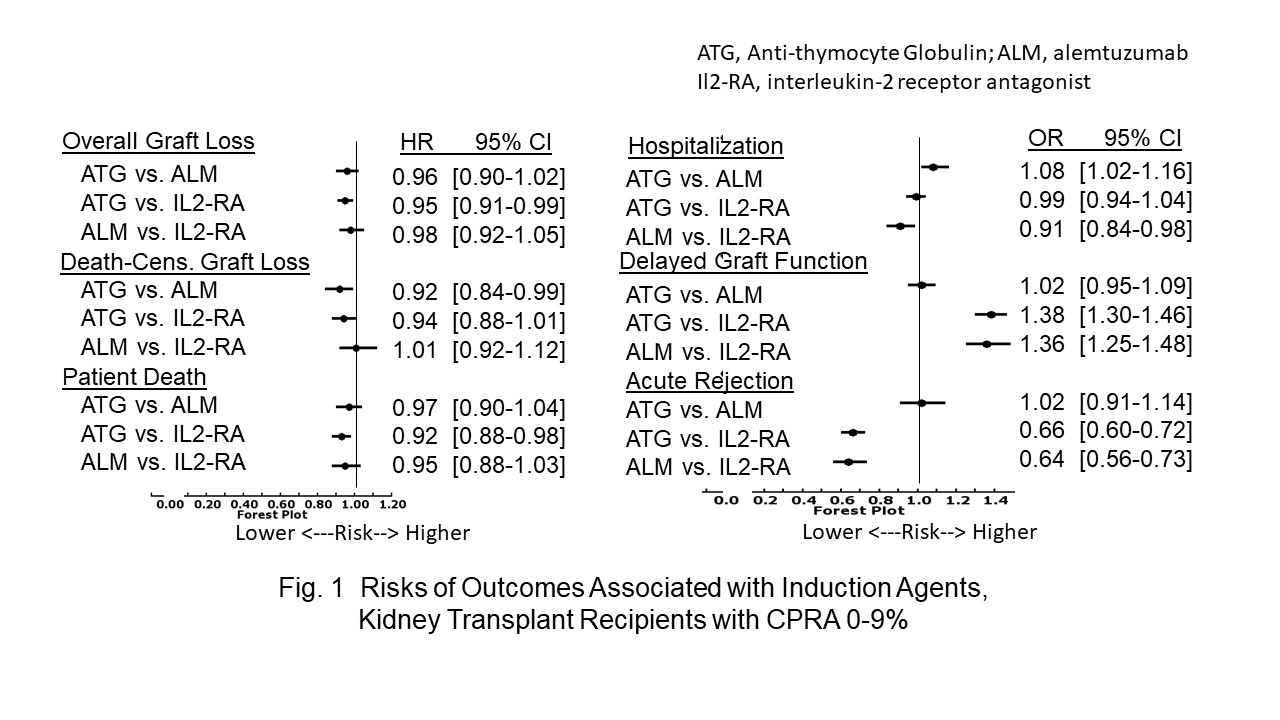
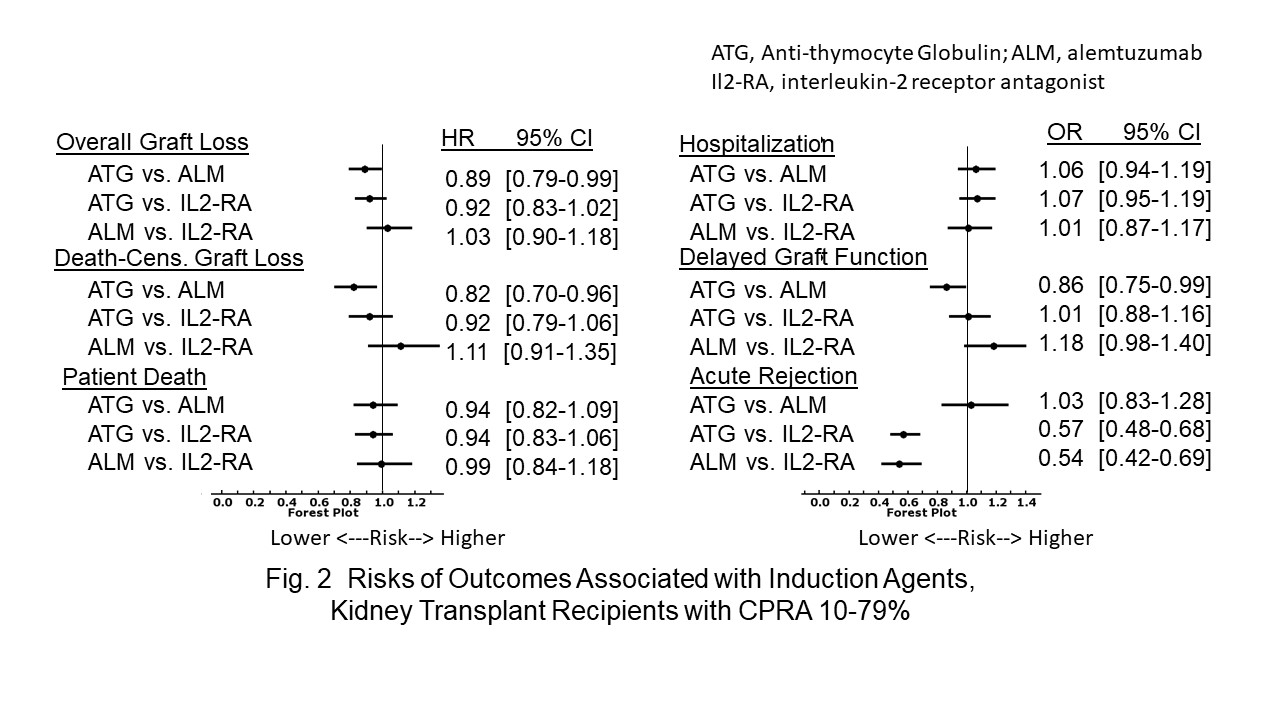
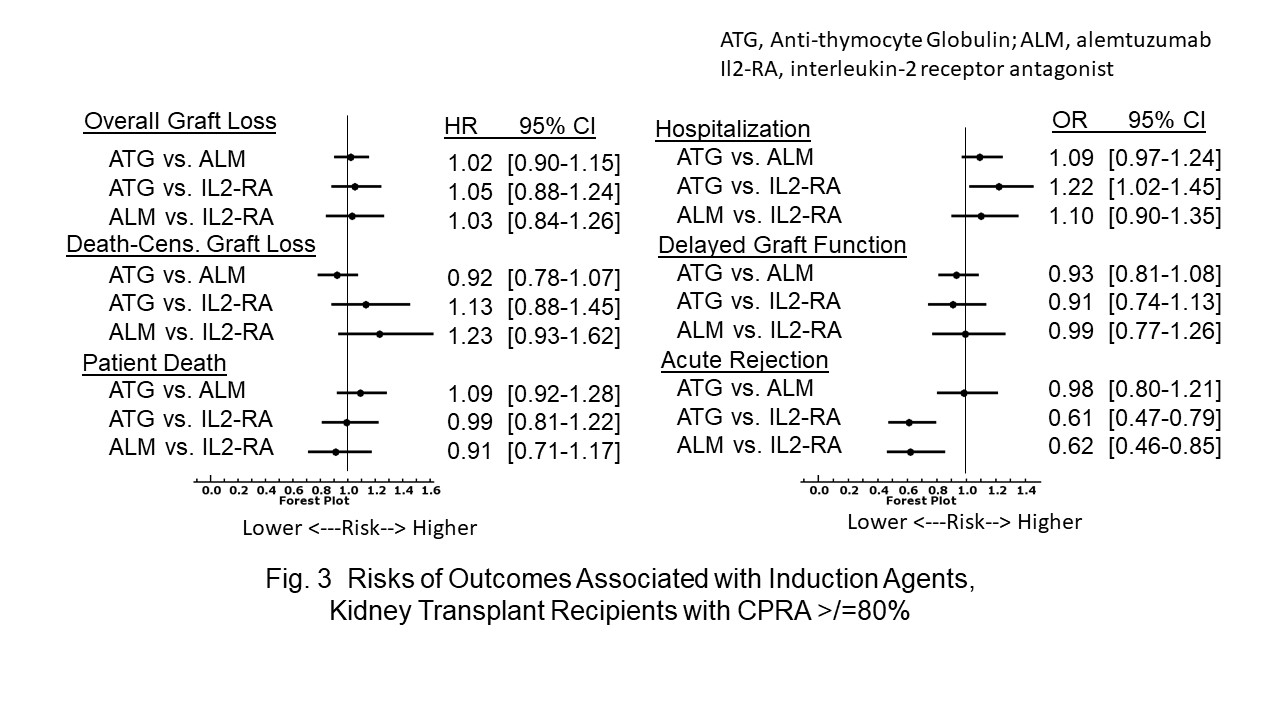
*Results: In all cPRA cohorts, ATG or ALM was associated with a lower risk of 1-year acute rejection than IL2-RA [Fig 1-3]. The risk of first transplant-year re-hospitalization was higher with ATG than ALM or IL2-RA in the <10% [Fig. 1] or >/= 80% [Fig. 3] cPRA cohort, respectively.
In the <10% cPRA cohort, ATG was associated with lower risk(s) of 5-year: (i) overall graft loss (OAGL) and mortality than IL2-RA and (ii) death-censored graft loss (DCGL) than ALM [Fig. 1]. In the same <10% cPRA cohort, ATG and ALM were associated with higher risk of delayed graft function (DGF) than IL2-RA.
In the 10-79% cPRA cohort, ATG was associated with lower risks of DGF and 5-year OAGL and DCGL than ALM [Fig. 2].
*Conclusions: Among induction agents in adult DD-KTRs, T lymphocyte-depleting antibodies (ATG and ALM) provide better protection against acute rejection than IL2-RA in all cPRA strata; however, only ATG is associated with lower 5-year mortality and/or allograft loss risk/s, albeit limited to KTRs in the <80% cPRA strata.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ibrahim H, Gregg J, Alquadan K, Akanit U, Womer KL, Santos AH. Panel Reactive Antibody Stratification as a Guide to Induction Selection in Deceased-Donor Kidney Transplantation: Impact of Clinical Practice on Outcomes [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/panel-reactive-antibody-stratification-as-a-guide-to-induction-selection-in-deceased-donor-kidney-transplantation-impact-of-clinical-practice-on-outcomes/. Accessed March 7, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress